File
advertisement

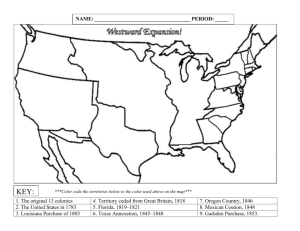
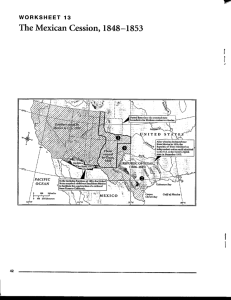
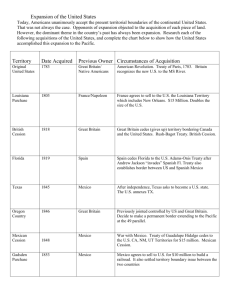
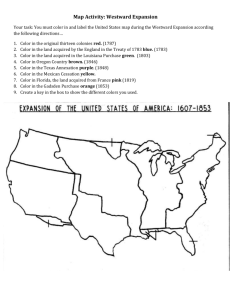
Name: ____________________________________ Date: ______________________ Period: __________ AIM: How was the United States able to fulfill Manifest Destiny between 1800 and 1853? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ DO NOW: Complete the steps below. Step 1 – Go sit down at a computer on your own and log on Step 2 – Go to Mr. Amador’s Teacher Website Step 3 – Click the Button Link on the Homepage that says Westward Expansion Interactive Map Name: ________________________________________ Date: ___________________________ Period: ________ Territorial Expansion of the United States: (1783–1853) Directions: 1. Go to http://pages.uoregon.edu/maphist/english/US/US09-01.html 2. On the map below, color in each territory that was acquired by the United States during Westward Expansion. Color in the map key with the color used for each territory. Label each territory with its name and date obtained. Use a different color for each territory. Map Key US Territories 1783 Florida Acquisitions 1810-1812 Oregon Country 1846 Gadsden Purchase 1853 Louisiana Purchase 1803 Texas Annexation 1845 Mexican Cession 1848 Name: ______________________________________ Date: _____________________________ Period: ________ Territorial Expansion of the United States: 1783–1853 Directions: As you color in the map, fill in the blanks below from the information underneath the map on the website. 1. United States and territories in 1783: In the _________________________________, which formally ended the Revolutionary War in 1783, England recognized American territorial claims that included most of the land _________________________________________ and east of the ____________________________________. The precise borders of modern Maine and the lines between Lake Superior and the headwaters of the Mississippi remained vague, but no European settlements had yet been established along those borders. Spain retained its claims to land bordering the Gulf of Mexico. 2. Louisiana Purchase in 1803: In 1803, following secret negotiations, President __________________________ engineered the purchase of French claims to the so-called Louisiana Territory, claims that France had recently obtained from Spain. Congress approved the ___________________________ appropriation only after bitter wrangling. Though no one knew for sure exactly what the president had bought, the Louisiana Territory was generally understood to include the entire western half of the ________________________________ watershed. This purchase nearly doubled the total size of the United States (at the price of about three cents an acre), gave the United States control over the interior of North America, secured access to the Gulf of Mexico, and opened one of the richest agricultural regions in the world to development by the United States. 3. Florida Acquisitions 1810-1812: In 1810, to ensure control over the mouth of the _________________________________, the United States seized the westernmost section of Spanish Florida. Embroiled in war at home, Spain was in no position to contest the seizure. During the __________________________ (1812-1814), the United States extended its control of West Florida to include Mobile Bay. Continuing friction along the Florida border reached crisis level in 1818, when General ______________________________________ crossed into Spanish territory in pursuit of Native American and African American guerilla raiders. Facing revolts throughout Latin America and weakened by defeat in Europe, Spain signed a treaty in 1819 that ceded what remained of its Florida holdings to the United States in return for recognition of a fixed border between American Louisiana and Spanish Texas. 4. Texas Annexation in 1845: Americans living in the Mexican state of Texas had rebelled from the central government at Mexico City in 1835, and in 1836 they established an ______________________________. The United States recognized the so-called ______________________________ but rebuffed initial overtures of annexation. The Mexicans did not recognize either the independence of the rebellious Texans or the generous borders they were claiming. During the presidential election campaign of 1844, the Democratic party endorsed national expansion, in the form of "________________________________," and Congress annexed Texas by joint resolution in 1845, following the Democratic victory. 5. Oregon Country in 1846: The so-called Oregon Country, encompassing modern Oregon, Washington, and British Columbia, had been jointly claimed and jointly occupied by the _____________________________ and _________________________since 1818. In 1846 the two powers agreed to divide the area roughly in halves along the ____________________________ (the present border between the United States and Canada in that area), which had also been recognized as the northern border of the Louisiana Territory in the original treaty of joint occupation back in 1818. 6. Mexican Cession 1848: Following American annexation of Texas in 1845, President _____________________ used the long-simmering border disputes between _______________________ and ______________________ to provoke war with the Mexican government. Polk favored extending American control over large portions of North America owned by Mexico, and at one point appears to have considered seizing all of Mexico. Following its defeat, Mexico was forced in the 1848 Treaty of Guadalupe-Hidalgo to cede to the United States its Pacific coastal state of upper ____________________________ (which had revolted from the Mexican central government during the war to create the so-called Bear Flag Republic under American protection) along with all of the land north of the Rio Grande and Gila Rivers. 7. Gadsden Purchase in 1853: The contiguous borders of the United States as they still exist in the twenty-first century were solidified by the Gadsden Purchase of 1853. Bought from _________________________ for $10 million, the area was regarded as essential for a ___________________________ between the Gulf of Mexico and the Pacific coast.