Two Sides to Energy Resources Chart.doc
advertisement

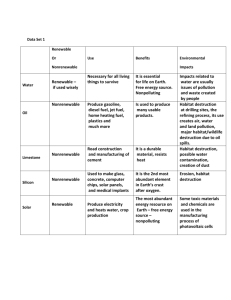
Name ______________________________________ Period _______ The Two Sides of Energy Resources Energy Resources Fossil Fuels Definition: Formed from the buried remains of plants & animals millions of years ago Coal, Oil/ Petroleum, & Natural Gas (Propane) Advantages ● ● ● Provide a large amount of thermal energy per unit of mass Easy to get and easy to transport Can be used to generate electrical energy and make products, such as plastic Easy to find Easy to get out of the ground Abundant supply of coal Efficient Safe to use Cost Effective ● ● ● Very concentrated form of energy Power plants do not produce smog No greenhouse gases Produces a lot of energy with a small amount of fuel No ground level pollution Small amount of waste ● ● NONRENEWABLE Nuclear Definition: Formed from changes in the nucleus of an atom (nuclear fission - split nuclei to harness power) Uranium NONRENEWABLE ● ● Disadvantages ● Example in the World Nonrenewable Burning produces smog Burning coal releases substances that can cause acid precipitation Risk of oil spills Need a huge amount of reserves Coal Mining is dangerous Gas leaks can have dangerous side effects Global Warming (greenhouse gases) Destroys habitats Prices raise over time Can contaminate well water Oil reserves: Middle East countries, Texas, Alaska, Gulf of Mexico, Canada, Venezuela Natural Gas: Pennsylvania, Texas, Florida, Ohio, Middle East countries Coal: Pennsylvania, West Virginia, China, England, Russia Produces radioactive waste Radioactive elements are nonrenewable Waste is hard to dispose of Waste lasts for many years as radioactive material Could be made into weapons or become a target for terrorists Unstable/reactor malfunctions All over Europe Korea Japan East Coast of U.S. Geographic Features That Allow This Resource to Thrive Oil & Natural Gas : Areas that used to be underwater or are currently underwater – places with lots of fossils Coal: Mountains Densely populated areas Water source readily available Energy Resources Solar Definition: Energy from the sun Radiant Energy Converts energy from sun to electrical energy in photovoltaic cells Advantages ● Disadvantages Almost limitless source of energy Does not produce pollution No noise Cells last 30-40 years Source (Sun) is free Easy to install Environmentally friendly ● ● ● Renewable Does not produce air pollution ● Reliable Sustainable Dams last a long time (gates can also be shut if they have enough electricity – to conserve energy) Large amount of energy ● ● Expensive to use for largescale energy production Only practical in sunny areas Pollution hinders the panels Need a lot of space Must be located (angled) correctly Materials cost a lot Example in the World Geographic Features That Allow This Resource to Thrive California, Arizona, New Mexico, Dubai (desert), near the equator, satellites that orbit the Earth Lots of sunshine Open areas for solar panels Niagara Falls Hoover Dam Near Penn State University China Brazil Netherlands Running water Large bodies of water RENEWABLE Water Definition: Potential energy is converted to Kinetic energy as water falls Kinetic energy converted into electrical energy: Hydroelectricity RENEWABLE Dams disrupt a river’s ecosystem ● Available only in areas that have rivers Expensive to build Extensive regulations Effects water quality & quantity downstream Could cause flooding (dam malfunctions etc.) Energy Resources Wind Definition: Wind causes turbines to spin Mechanical energy converted to electrical energy Advantages ● ● ● Disadvantages Example in the World Geographic Features That Allow This Resource to Thrive Renewable Relatively inexpensive to generate Does not produce air pollution Turbines take up small spaces Not affected by power outages ● Only practical in windy areas Expensive to build Wind speeds vary Noisy (noise pollution) Bird Hazard Appearance Obstruct Views Jersey Shore, Midwest farming regions, Texas, Los Angeles, Amsterdam, Belgium Windy areas Open areas Along coastlines Almost limitless source of energy Power plants require little land No Pollution Renewable ● Only practical in locations near hot spots Waste water can damage soil Expensive to build Efficiency depends on location Instability ex: Earthquakes cause them to be unstable Iceland, New Zealand, Nevada, California, Alaska, Hawaii (volcanoes), Wyoming (Old Faithful geyser) Geysers Volcanoes Hot Springs Renewable ● ● Requires large areas of farmland Produces smoke Produces some waste materials Fuel energy vs. food CO2 emissions Greenhouse gases Inexpensive Reducing waste in landfills Less pollution Readily available Africa, Ohio, Iowa, Indiana, India Almost anywhere Forests Cornfields Animals for waste production RENEWABLE Geothermal Definition: Results from the heating of the Earth’s crust Energy from underground ● ● ● RENEWABLE Biomass Definition: Organic matter such as plants, wood, & waste that contains stored energy RENEWABLE ●