Deriving Energy From Food
advertisement

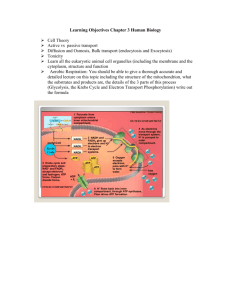
To remain alive, living things must acquire energy and then put that energy into a form they can use Oxygen Heat Metabolism • Life is a combustion process • You are using oxygen to burn fuel (food) to create energy (and waste heat) Hydrocarbon Fuel + O 2 CO 2 + H 2 O Heat Combustion in a Pop Bottle Demonstration Lipids (fats) = 9.3 kcal/gram Protein = 4.1 kcal/gram Carbohydrates = 4.1 kcal/gram Add 2 ATP to a 6 Carbon glucose molecule creating 2 3 carbon pyruvic acid molecules and 4 ATP This creates a Net Yield of 2 ATP Occurs in the cytoplasm of all tissue cells, but is also important in: Tissues with no mitochondria: mature RBCs, cornea and lens. Tissues with few mitochondria: Testis, leucocytes, medulla of the kidney, retina, skin and gastrointestinal tract. Tissues undergo frequent oxygen lack: skeletal muscles especially during exercise. Alcohol Fermentation Uses NADH to convert pyruvic acid into alcohol This produces a steady stream of ATP and CO2 Lactic Acid Fermentation: Uses NADH to convert pyruvic acid to lactic acid This produces a steady stream of ATP One carbon is broken off of each pyruvic acid moelcule This carbon combine with oxygen and is released as carbon dioxide waste. The remaining 2 2 carbon acetic acid molecules combine with an enzyme (coenzyme A) forming acetyl CoA. Acetyl CoA gives its 2 carbons to a 4 carbon citric acid molecule forming a 6 carbon molecule. One carbon is broken off at each step releasing CO2 and forming NADH and FADH2 (another electon carrier). 2 cycles are necessary to metabolize 1 glucose molecule GLUCOSE is oxidized by a molecule which is in turn oxidized by another on down the hill. Molecules that shuttle electrons down the hill ELECTRON CARRIERS Many of these electrons are bound as Hydrogen (1p+ and 1e-) NAD+ is positive when it is empty (not carrying electrons) It picks up a Hydrogen atom and an electron. This makes it NADH (neutral) Because it took an electron from another substance it is reduced and the substance that it took electrons from is oxidized NADH moves downhill and drops off its electron passengers with substances that have a greater attraction for them. Electrons fall down the energy hill to drive the uphill production of ATP Electron carriers NADh and FADH2 bring electrons and Hydrogens to ETC (in inner membrane of the mitochondria) The electron carriers are reduced when they give their electrons over to the ETC. Energy is released as the electrons move downhill The hydrogen bind with the final acceptor O2 forming water that is released as water vapor in the breath ATP Yield= 36 You got your mitochondria from your mother in the egg cell from which you came. Mitochondria have their own DNA which can be used to trace your mother's mother's mother's mother's mother back through thousands of years. Thanks, Mom. Function cellular respiration generate ATP from breakdown of sugars, fats & other fuels in the presence of oxygen break down larger molecules into smaller to generate energy = catabolism generate energy in presence of O2 = aerobic respiration 2 Membranes to increase surface area Smooth outer membrane Highly folder inner membrane The Cristae