The Integumentary System
advertisement

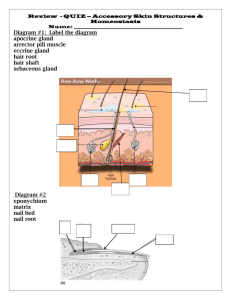
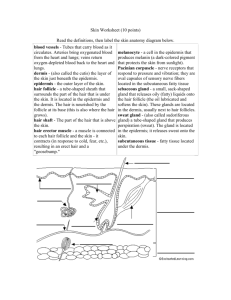
The Integumentary System SKIN HAIR NAILS Medical Terminology cutane/o : skin cyan/o : blue epi- : over, upper erythro- : red lip/o : fat melan/o : black sub- : under, below Terminology Practice liposuction dermatitis dermatoplasty melanoma cyanotic subcutaneous epigastric erythrocyte Skin Diagram Draw and color a cross-section diagram of the skin. Label and briefly describe each of the following structures: Epidermis Artery Dermis Vein Subcutaneous fascia Hair follicle Sebaceous gland Hair shaft Sudoriferous gland Arrector pili muscle Nerve Pores Sebaceous (oil) gland Pore Hair Epidermis Sudoriferous (sweat) gland Dermis Nerve Subcutaneous fascia Artery Hair follicle Vein Arrector pilli muscle Functions of the Skin 1. Protection - From ultraviolet rays and pathogens - Holds moisture in 2. Sensory Perception - Pain, pressure, temperature, and touch 3. Body Temperature Regulation - Blood vessels dilate to release heat and constrict to conserve heat - Cool body through evaporation of sweat 4. Storage - Fat, glucose, water, vitamins, and salts 5. Absorption - Some medications 6. Excretion - Salt, excess water, and some wastes eliminated through the sweat 7. Production - Produces Vitamin D Pigmentation • Melanin: a brownish-black pigment • Carotene: a yellowish-red pigment * The amounts of these two pigments determine a person’s skin color Abnormal Colors of the Skin • Albino : the absence of pigmentation • Erythema : reddish color of skin • Jaundice : yellow discoloration of skin Cyanosis : a bluish discoloration of the skin due to a lack of oxygen Skin Eruptions • Macules : flat spots on the skin • Papules : firm raised areas • Vesicles : fluid-filled sacs or blisters • Pustules : pus-filled sacs • Crusts : areas of dried pus and blood (scabs) • Wheals : itchy, elevated areas with an irregular shape • Ulcer : a deep loss of skin surface Decubitus Ulcers (Bedsores) • Open sores in the skin and underlying tissues due to pressure over a bony area • Cuts off the blood supply and the tissue dies Diseases Acne : an inflammation of the sebaceous glands - Caused by a blockage of the hair follicles with dirt, cosmetics, excess oil, and/or bacteria Alopecia : baldness; a permanent loss of hair on the scalp Verrucae : rough, hard, elevated, rounded surface forms on the skin - warts - Caused by a viral infection of the skin Skin Cancers : - Forms that are usually localized – don’t spread to other areas of body Basal cell carcinoma Squamous cell carcinoma Skin Cancers - Form that CAN spread to other parts of the body and be fatal Malignant Melanoma Signs of Malignant Melanoma Asymmetrical in shape Borders of lesion are scalloped or irregular Colors are varied – black, brown, white, red Diameter is larger than a pencil eraser