Immune and Integumentary Systems
advertisement

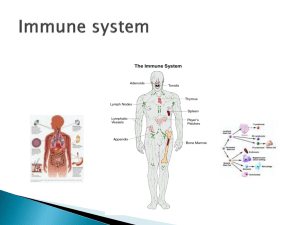
Immune and Integumentary Systems Immune System Functions • The immune system defends against disease. • It recognizes, attacks, and destroys foreign invaders such as bacteria and viruses. Organs • Tonsils – lymph nodes in the throat • Thymus – T-Cells made in the bone are matured here. • Lymph Nodes – small bean-shaped masses • Spleen – filters blood for foreign particles carried by the white blood cells. • Bone Marrow – makes white blood cells. Immune System Tonsils Thymus Lymph node Spleen Lymphatic vessel Bone marrow Tissues • White Blood Cells – blood cells whose main function is to defend the body against disease. • Lymphocytes – white blood cells. o T-Cells – lymphocytes made in the bone marrow and mature in the Thymus gland whose function is to attack cells that have been invaded by viruses. o B-Cells – lymphocytes made in the bone marrow that make antibodies to attack viruses in the blood. How It Works 1. Recognition – White Blood Cells identify the antigens that do not belong in the body. (viruses & bacteria) 2. Activation – White Blood Cells attach to the foreign cells or viruses and destroy them. 3. Disposal – foreign cells and viruses are filtered out of the blood in the spleen. Integumentary System (Skin) Functions • • • • • • • Regulates body temperature Keeps germs out of the body Senses temperature, texture, pressure, and pain. Releases oil, waste and salt in sweat. Shields body from UV rays Produces vitamin D from UV rays. Provides waterproof covering that prevents dehydration. Specialized Cells • Epidermis – outer layer of skin mostly made up of dead cells. • Dermis – functional layer of skin below the epidermis. How It Works Epidermis • Keratin – strong flexible protein that make skin tough and waterproof. • Melanin – pigment that gives skin its color and shields the body from UV rays. Dermis • Contains – blood vessels, nerves, sweat glands, oil glands, and hair follicles. • Collagen – protein fibers that make skin flexible.