Socialization

Socialization
1.
Adoptive parents are least likely to influence the ________ of their adopted children. a.
personality traits b.
religious beliefs c.
political attitudes d.
moral values e.
genetic disposition
2.
Intense and reactive infants become unusually anxious and aroused when facing new or strange situations.
This best illustrates the importance of: a.
the X chromosome. b.
temperament. c.
personal space. d.
individualism. e.
parenting.
3.
When twins are separated, the adoptive parent influence this the LEAST. a.
Values b.
Intelligence c.
Beliefs d.
Politics e.
Attitude
4.
In Pavlov’s experiment, the dog’s salivation to the bell is the: a.
unconditioned stimulus. b.
unconditioned response. c.
conditioned stimulus. d.
neutral stimulus e.
conditioned response.
5.
Which of the following would be an example of Classical Conditioning being applied to practical problems? a.
Teaching a dog to wag its tail? b.
Using methadone (kind of a lesser form of heroin) for heroin addicts. c.
Applying electric shock to depressed patients. d.
Giving alcoholics a drug to make them sick if they drink.
6.
In ____, a response (behavior) is increased in order to avoid something unpleasant. a.
positive punishment. b.
negative reinforcement. c.
partial reinforcement. d.
positive reinforcement. e.
negative punishment
Socialization
7.
Even when punishment changes behavior, it has several drawbacks, including: a.
punishment doesn’t teach the correct response. b.
punishment may result in fear of the one punishing. c.
effects may be only temporary. d.
all of the above.
8.
Albert Bandura contends that most human behavior: a.
is shaped through repeated trial-and error. b.
is reinforced through classical conditioning. c.
is planned out and not accidental. d.
is acquired through insight. e.
is acquired through observational learning.
9.
Last year, Dr. Kno cleaned Bill’s skin with rubbing alcohol prior to administering each of a series of painful rabies shots. Which of the following processes accounts for Bill currently becomes fearful every time he smells rubbing alcohol? a.
Negative reinforcement b.
Classical conditioning c.
Latent learning d.
Operant conditioning e.
Observational learning
10.
One Christmas, I ate Del Taco and got really sick. The thought of Del Taco makes me nauseous. Now Del
Taco would be: a.
Unconditioned Response b.
Neutral Stimulus c.
Unconditioned Stimulus d.
Conditioned Response e.
Conditioned Stimulus
11.
This researcher locked cats in a cage. He stated behavior changes because of its consequences and rewards strengthen behavior. What was the researcher’s name and what was his theory called. a.
Skinner, operant conditioning b.
Thorndike, Law of Effect c.
Skinner, Law of Effect d.
Pavlov, Law of Effect e.
Thorndike, classical conditioning
12.
The addition of something pleasant. a.
Positive Reinforcement: b.
Negative Reinforcement: c.
Positive punishment d.
Negative punishment e.
Token economy
Socialization
13.
A cat is banished from the house after shredding the sofa. The cat has fewer incidents of couch destruction after that. a.
Positive Reinforcement b.
Negative Reinforcement c.
Positive Punishment d.
Negative Punishment e.
Primary Reinforcement
14.
A volleyball player rolls her eyes at a teammate who delivered a bad pass; the teammate makes fewer errors after that. a.
Negative Reinforcement b.
Positive Punishment c.
Negative Punishment d.
Primary Reinforcement e.
Positive Reinforcement
15.
A professor allows those students with A averages in the class to skip the final exam. Students work harder for As. a.
Positive Reinforcement b.
Negative Reinforcement c.
Positive Punishment d.
Negative Punishment e.
Primary Reinforcement
16.
After Jodi flirted with someone else at the party (tsk, tsk), her boyfriend yelled at her. Jodi didn't flirt at the next party. a.
Positive Reinforcement b.
Negative Reinforcement c.
Positive Punishment d.
Negative Punishment e.
Primary Reinforcement
17.
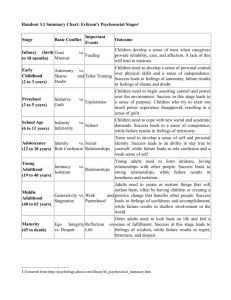
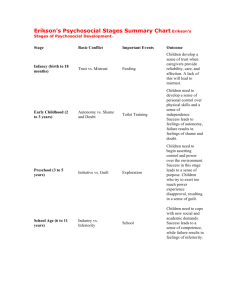
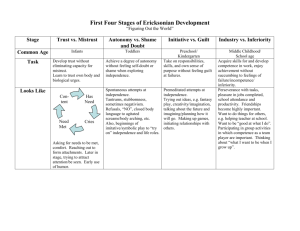
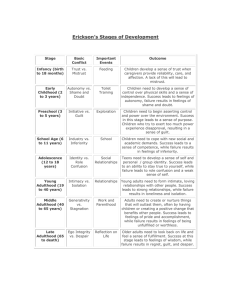
According to Erik Erikson’s Psychosocial Stages of Development, adolescence must deal with the psychosocial conflict of: a.
intimacy vs. isolation b.
identity vs. role confusion. c.
industry vs. inferiority. d.
initiative vs. guilt. e.
autonomy vs. shame and doubt
18.
The second stage of Erikson’s psychosocial stages is called: a.
Identity vs Role confusion b.
Trust vs Mistrust c.
Generativity vs Stagnation d.
Autonomy vs Shame and Doubt e.
Initiative vs Guilt
Socialization
19.
According to Erik Erikson’s Psychosocial Stages of Development, infants must deal with the psychosocial conflict of: a.
trust vs. mistrust. b.
identity vs. role confusion. c.
industry vs. inferiority. d.
initiative vs. guilt. e.
autonomy vs. shame and doubt
20.
Coach Knowles is experiencing another mid life crisis. He purchases a Harley and hits the highways. BORN
TO BE WILD!!!!! What stage of psychosocial development is Knowles having difficulties with? a.
Identity vs Role confusion b.
Trust vs Mistrust c.
Generativity vs Stagnation d.
Autonomy vs Shame and Doubt e.
Initiative vs Guilt
21.
When she was 8 years old, Inge was abused by her uncle. At 14, Inge felt uncomfortable whenever she saw this uncle but was unable to understand why she felt this way. A psychoanalyst would be most likely to suggest that Inge is using the defense mechanism of: a.
repression. b.
reaction formation. c.
rationalization. d.
regression. e.
displacement.
22.
Re-channel their unacceptable impulses towards more acceptable or socially approved activities. a.
Reaction formation b.
Regression c.
Sublimation d.
Denial e.
Displacement
23.
In what psychosocial stage do toddlers begin to control their bodies (toilet training) and control temper tantrums. The Big word is “NO”. a.
trust vs. mistrust. b.
identity vs. role confusion. c.
industry vs. inferiority. d.
initiative vs. guilt. e.
autonomy vs. shame and doubt
24.
In what psychosocial stage do people look back on life and wonder whether their life was meaningful or regretful? a.
Identity vs Role confusion b.
Trust vs Mistrust c.
Integrity v. Despair d.
Autonomy vs Shame and Doubt e.
Initiative vs Guilt
Socialization
25.
In what psychosocial stage are people evaluated by a formal system and our peers? This can lead to us feeling bad and giving us a complex about ourselves for the rest of our lives. a.
A) trust vs. mistrust. b.
B) identity vs. role confusion. c.
C) industry vs. inferiority. d.
D) initiative vs. guilt. e.
E) autonomy vs. shame and doubt
26.
The second stage of Erikson’s psychosocial stages is called: a.
Identity vs Role confusion b.
Trust vs Mistrust c.
Generativity vs Stagnation d.
Autonomy vs Shame and Doubt e.
Initiative vs Guilt
27.
According to Erik Erikson’s Psychosocial Stages of Development, infants must deal with the psychosocial conflict of: a.
A) trust vs. mistrust. b.
B) identity vs. role confusion. c.
C) industry vs. inferiority. d.
D) initiative vs. guilt. e.
E) autonomy vs. shame and doubt
28.
In what psychosocial stage do children want to understand the world and ask questions. The big word changes from “NO” to “WHY?” a.
Identity vs Role confusion b.
Trust vs Mistrust c.
Generativity vs Stagnation d.
Autonomy vs Shame and Doubt e.
Initiative vs Guilt
29.
This researcher said we learn through modeling behavior from others. a.
Sigmund Freud b.
George Mead c.
Sigmund Freud d.
B.F. Skinner e.
Albert Bandura f.
Charles Cooley
30.
This person created the theory that personality is made up of three structures: Id, Ego and Superego a.
Sigmund Freud b.
George Mead c.
Sigmund Freud d.
B.F. Skinner e.
Albert Bandura f.
Charles Cooley
Socialization
31.
This theorist stated people develop an image of themselves by imagining how we appear to others. a.
Sigmund Freud b.
George Mead c.
Sigmund Freud d.
B.F. Skinner e.
Albert Bandura f.
Charles Cooley
32.
This theorist stated we not only see ourselves as others see us but we also take on the role of the “others” to anticipate what others expect of us. a.
Sigmund Freud b.
George Mead c.
Sigmund Freud d.
B.F. Skinner e.
Albert Bandura f.
Charles Cooley
33.
Which sociologist below used the phrase looking-glass self to emphasize that the self is the product of our social interactions with other people? a.
Sigmund Freud b.
George Mead c.
Sigmund Freud d.
B.F. Skinner e.
Albert Bandura f.
Charles Cooley
34.
In this Mead theory, children take on the role of significant other at this stage a.
the play stage b.the game stage c.
initiative vs guilt stage d.the imitation stage e.
autonomy vs. shame & doubt
35.
In this Mead theory, children internalize an abstract understanding of how society sees them. a.
the play stage b.
the game stage c.
initiative vs guilt stage d.
the imitation stage e.
autonomy vs. shame & doubt
After the exam, please go to my sociology website and go to create a game.
You will be looking at Game 2
This game will need to ready by Thursday (11/20)
You should be researching and planning today.