File - Principles of Biology 103
advertisement

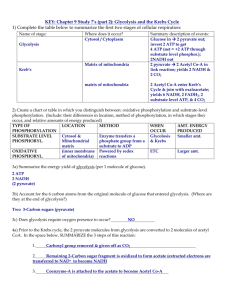
Chapter 7: How Cells Release Chemical Energy Study Guide 1. How do cells harness the energy stored in sugars: A. Oxygen released from sugars directly drive life-sustaining reactions B. Sugar molecules are joined with ATP molecules C. The oxygen backbones of sugars are broken down to make ATP D. The carbon backbones of sugars are broken down to make ATP E. Carbon released from sugars directly drives life-sustaining reactions 2. Four of the five answers listed below are compounds associated with anaerobic pathways. Select the exception: A. PGAL B. Pyruvate C. Ethanol D. Oxaloacetate E. Lactic acid 3. Which of the following metabolic pathways require(s) molecular oxygen: A. Aerobic respiration B. Lactate fermentation C. Alcoholic fermentation D. All of the above 4. What occurs when molecules are broken apart in respiration: A. ADP is released as a waste product B. The oxygen in the compounds that are broken apart is used as an energy source C. The heat produced is used to drive biological reactions D. The energy released is used in ATP synthesis E. ATP is converted into ADP 5. What is the correct operational sequence of the three processes listed below: I. Glycolysis II. Electron transfer phosphorylation III. Kreb’s cycle A. I – II – III B. II – I – III C. III – I – II D. II – III – I E. I – III – II 6. What is a requirement for glycolysis to proceed: A. Heat must be supplied B. Carbon dioxide must be available C. Glucose must enter the mitochondria D. Oxygen must be available E. There must be an input of energy from ATP 7. Glycolysis starts and ends in the: A. Nucleus B. Mitochondrion C. Plasma membrane D. Cytoplasm 8. Yeast fermentation produces: A. Lactate B. CO2 C. Ethanol D. Ethanol and lactate E. Ethanol and CO2 9. In the breakdown of glucose, the compound formed after two phosphorylation reactions is split into two three-carbon compounds. The three-carbon compound is named: A. PGAL B. Acetyl CoA C. Lactate D. Acetaldehyde E. Pyruvate 10. Pyruvate can be regarded as the end product of: A. Electron transport chain B. Glycolysis C. Fermentation D. Kreb’s cycle E. Acetyl CoA formation 11. Glycolysis ends with the formation of ATP by: A. Cyclical driven phosphorylation B. Phosphatase-dependent phosphorylation C. Proton transfer phosphorylation D. Electron transfer phosphorylation E. Substrate level phosphorylation 12. For each glucose molecule, glycolysis yields a net production of A. Four NADH, two ATP, and four pyruvate B. Two NADH, four ATP, and two pyruvate C. Four NADH, four ATP, and four pyruvate D. Two NADH, four ATP, and four pyruvate E. Two NADH, two ATP, and two pyruvate 13. Which molecule does not form during glycolysis: A. NADH B. Pyruvate C. Oxygen D. ATP 14. Which of the following reaction pathways is not part of the second stage of aerobic respiration: A. Electron transfer phosphorylation B. Acetyl-CoA formation C. Krebs cycle D. Glycolysis E. A and D 15. Aerobic respiration's second stage begins when A. Oxaloacetate enters a mitochondrion and acetyl-CoA is formed B. Acetyl-CoA leaves a mitochondrion and oxaloacetate is formed C. Pyruvate enters a mitochondrion and acetyl-CoA is formed D. Pyruvate leaves a mitochondrion and acetyl-CoA is formed E. Acetyl-CoA enters a mitochondrion and oxaloacetate is formed 16. During electron transfer phosphorylation, which ions accumulate in the intermembrane space of the mitochondria? A. Calcium B. Oxygen C. Sodium D. Hydrogen E. Phosphorus 17. When oxygen accepts electrons in aerobic respiration, it is converted to: A. CO2 B. O2 C. OH D. H2O E. CO 18. Under anaerobic conditions, muscle cells produce: A. Acetaldehyde B. Ethyl alcohol C. Citrate D. Pyruvate E. Lactate 19. NADH transfers electrons to oxygen through which process: A. Glycolysis B. Kreb’s cycle C. Substrate-level phosphorylation D. Electron transfer phosphorylation E. Acety CoA formation 20. During which phase(s) of aerobic respiration is ATP produced directly by substartelevel phosphorylation: A. Glycolysis only B. Kreb’s cycle only C. Kreb’s cycle and glycolysis D. Acetyl CoA formation only E. Glycolysis, acetyl CoA formation, and Kreb’s cycle 22. The Kreb’s cycle starts as one carbon atom is transferred from: A. Oxaloacetate to acetyl CoA B. Acetyl CoA to pyruvate C. Acetyl CoA to oxaloacetate D. Pyruvate to oxaloacetate E. Acetyl CoA to oxaloacetate 23. Which two molecules produced during glycolysis and the Kreb’s cycle provide electrons and hydrogen ions to the electron transport chain: A. O2 and CO2 B. NADH and CO2 C. NADH and FADH2 D. O2 and NADH E. O2 and FADH2 24. How do hydrogen ions facilitate the formation of ATP during electron transfer phosphorylation: A. Hydrogen ions break ADP bonds to form ATP B. Hydrogen ions drive substrate level phosphorylation C. Hydrogen ions accept electrons at the end of electron transfer chains D. Hydrogen ions flow through ATP synthases E. Hydrogen ions donate electron to the electron transfer chain 25. In the third stage of aerobic respiration, _____ is the final acceptor of electrons. A. Water B. Hydrogen C. Oxygen D. NADH 26. Hydrogen ion flow drives ATP synthesis during _____. A. Glycolysis B. The Krebs cycle C. Aerobic respiration D. Fermentation E. A and C 27. The net total ATP produced by 1 glucose molecule is: A. 32 B. 34 C. 36 D. 28 28. Which pathway generates the most ATP: A. Fermentation B. Photosynthesis C. Glycolysis D. Electron transport phosphorylation E. Kreb’s cycle 29. Substrate level phosphorylation: A. Is not part of fermentation pathways B. Involves the direct transfer of a phosphate group from a substrate C. Produces most of the ATPs during aerobic respiration D. Requires the presence of NADH 30. What similarities do aerobic respiration and fermentation share: A. They both utilize electron transfer chains B. They both begin with glycolysis C. They both yield the same amount of ATP D. They both rely on oxygen E. The both utilize the Kreb’s cycle 31. In alcoholic fermentation, the electrons and hydrogen are transferred from NADH to acetaldehyde forming: A. Carbon dioxide B. Lactate C. NAD+ and ethanol D. Ethanol 32. Pyruvate is broken down into this in alcoholic fermentation. A. Oxygen B. Pyruvate C. Acetaldehyde D. Ethanol 33. Which of the following is not produced by an animal muscle cell operating under anaerobic conditions: A. Lactase B. ATP C. NAD+ D. All are produced 34. Which of the following is NOT produced by an animal muscle cell in a anaerobic condition: A. Heat B. Lactic acid C. ATP D. NAD+ E. All are produced 35. You just ate a snickers bar. Glucose is running amok in your bloodstream. Your mitochondria have just broken down the glucose into two pyruvate molecules. What stage of cellular respiration are we talking about? A. Glycolysis B. Krebs cycle C. Electron transport chain (ETC) D. Calvin cycle