Corporate Finance
advertisement

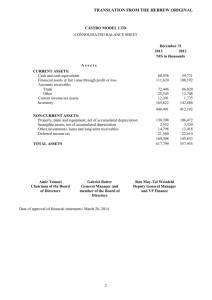
INDEX 1. Finance Overview. 2. Defining Finance. 3. Corporate Finance. 4. Investment: Assets. 5. Resources: Equity and Liabilities. 6. Relationships between Investment and Financing 7. Functions of the Financial Manager. Pg. 1 Introduction to Finance Department of Finance and Operations Management Instructor :Martha Edith Bellini Reasons to study Finance: • To manage your personal resources. •To set up a new business. •To pursue interesting and rewarding career opportunities in Finance. Pg. 2 Introduction to Finance Department of Finance and Operations Management Instructor :Martha Edith Bellini Defining Finance The field of Finance deals with the concepts of time, money, and risk and how they are interrelated. It also deals with how money is spent and budgeted. Finance…. • is analytical. • is based on economic principles. • uses accounting information as an input for decision-making. • is global in perspective. • is constantly changing. • is the study of how to invest and raise money productively. Pg. 3 Introduction to Finance Department of Finance and Operations Management Instructor :Martha Edith Bellini Defining Finance Concept of Finance: Finance Theory is the study of the behaviour of individuals in the intertemporal allocation (over time) of their resources in an uncertain environment, and the study of the function of economic institutions and markets in making these allocations possible. EconomíaFinanciera Marín, José M. / Rubio, Gonzalo Antoni Bosch, Editor, Barcelona, 2001 Pg. 4 Introduction to Finance Department of Finance and Operations Management Instructor :Martha Edith Bellini Defining Finance Finance can be divided into three main related areas: Corporate finance: Refers to the acquisition, financing and investment management. Require the use of knowledge of economics, accounting, law, financial mathematics and statistics, among others. Financial Markets and Institutions: Includes the study of the banking system and markets. Assets evaluation: Estimating the value of assets through models. Very useful for making financial decisions. Pag 5 Introduction to Finance Department of Finance and Operations Management Instructor :Martha Edith Bellini Corporate Finance Is about financial decisions made by corporations. Corporations face two broad financial questions: •What investments should the firm make? •How should it pay for those investments? •Financial managers are concerned with: - Investment Decisions (use of funds): The buying, holding or selling of types of assets. - Financing Decisions (acquisitions of funds). Pag 6 Introduction to Finance Department of Finance and Operations Management Instructor :Martha Edith Bellini Corporate Finance The discipline can be divided into long-term and shortterm decisions and techniques (according the time horizon) •Long-term decisions: Which projects receive investment. Whether to finance that investment with equity or debt when or whether to pay dividends to shareholders. •Short-term decisions: Deals with the short-term balance of current assets and current liabilities. The focus here is on managing cash, inventories, and short-term borrowing and lending. Pag 7 Introduction to Finance Department of Finance and Operations Management Instructor :Martha Edith Bellini Corporate Finance: Real Assets and Financial Assets The financial manager needs real assets and financial assets: Real assets: These are used to produce the firm's products and services. They include tangible assets such as Machinery, Factories, Vehicles, and Offices. Furthermore, real assets include intangible assets such as Technical knowledge (intellectual property IP), Trademarks, and Patents. Financial assets: The firm finances its investments in real assets by issuing financial assets (bonds, shares, etc) in the financial market for investors. A share or stock is a financial asset which has a value as a claim on the firm's real assets and on the income those assets may produce. Pg. 8 Introduction to Finance Department of Finance and Operations Management Instructor :Martha Edith Bellini Corporate Finance Financial manager The financial manager stands between the firm’s operations and the financial (or capital) markets, where investors hold the financial assets issued by the firm. Pg. 9 Introduction to Finance Department of Finance and Operations Management Instructor :Martha Edith Bellini Corporate Finance ASSETS FINANCING € Shares Loans Working Capital Bonds MANAGER FINANCIAL ASSETS Pg. 10 FINANCIAL ASSETS ENABLE FINANCING TO BE DIVIDED INTO AFFORDABLE PRODUCTS FOR INVESTORS Introduction to Finance Department of Finance and Operations Management Instructor :Martha Edith Bellini Quiz Fit each of the following terms into the most appropriate space: financing, real, shares, airplanes, financial, investment, brand names. Companies usually buy ________ assets. These include both tangible assets such as ____________ and intangible assets such as __________________. In order to pay for these assets, they sell ______________ assets such as _________. The decision regarding which assets to buy is usually termed the __________ decision . The decision regarding how to raise the money is usually termed the _____________ decision. Introduction to Finance Department of Finance and Operations Management Instructor :Martha Edith Bellini Investment or Assets. ASSETS INVESTMENTS Fixed Assets ASSETS Tangible Intangible Financial Current Assets Inventories Accounts Receivable Cash Pg 12 Introduction to Finance Department of Finance and Operations Management Instructor :Martha Edith Bellini Investment or Assets. ASSETS INVESTMENTS Assets are resources (money, properties or rights) of the business enterprise. Assets fall into one of two categories: • Current assets • Fixed or non-current assets Current assets are assets that can be turned into cash in one operating cycle. Non-current assets are all other assets; that is, assets that cannot be liquidated quickly. Pag 13 Introduction to Finance Department of Finance and Operations Management Instructor :Martha Edith Bellini Investment or Assets. Current assets are likely to be used or turned into cash in the near future. Fixed assets have a gross and a net value. The Gross Value is what the assets originally cost, but they are unlikely to maintain their value. Accountants must estimate the depreciation in the value of these assets. The company also has valuable intangible assets, such as its brand name or skilled management and is called goodwill. Pag 14 Introduction to Finance Department of Finance and Operations Management Instructor :Martha Edith Bellini Investment and Assets. Example: ASSETS Non-Current Assets: Property and equipment Minus accumulated depreciation Net-Non Current Asset (fixed assets) Net intangible assets Other fixed assets Current Assets Inventories Accounts receivable Other current assets Cash and equivalent Total Assets Pag 15 Introduction to Finance Department of Finance and Operations Management Instructor :Martha Edith Bellini Resources: Equity and liabilities FINANCIAL STATEMENT RESOURCES Common Stock Retained Earnings Long Term Debt Bank Loans Other long term liabilities Short Term Liabilities Long Term Liabilities RESOURCES Short Term Loans Accounts Payable Other Current Liabilities Pág. 16 Introduction to Finance Department of Finance and Operations Management Instructor :Martha Edith Bellini Resources: Equity and liabilities Equity = ownership of the business enterprise. The difference between assets and liabilities represents the amount of the shareholders´equity. Every corporation has common equity. Equity also includes retained earnings or capital in excess . Pag 17 Introduction to Finance Department of Finance and Operations Management Instructor :Martha Edith Bellini Resources: Equity and liabilities Liabilities are obligations of the business enterprise. They are either current liabilities or long-term liabilities. Current liabilities are obligations due within one year. 1. Accounts payable are amounts due to suppliers for purchases on credit. 2. Wages and salaries payable are amounts due to employees. 3. Short-term bank loans or current portion of long-term debt. Pag 18 Introduction to Finance Department of Finance and Operations Management Instructor :Martha Edith Bellini Resources: Equity and liabilities Long-term liabilities are debts that last more than one year. There are different types of long-term liabilities, including: 1. Payable notes and bonds, which are loans in the form of securities. 2. Bank loans. Pag 19 Introduction to Finance Department of Finance and Operations Management Instructor :Martha Edith Bellini Resources: Equity and liabilities Example: EQUITY & LIABILITIES Equity Common stock (shareholder equity) Retained earnings Non-Current Liabilities Long-term debt Bank loans Other long-term liabilities Current Liabilities Short-term loans Accounts payable Accrued income taxes Other current liabilities Total Equity & Liabilities Pag 20 Introduction to Finance Department of Finance and Operations Management Instructor :Martha Edith Bellini Balance Sheet •The balance sheet is a report of the assets, liabilities, and equities of a firm at a point in time (generally at the end of a fiscal quarter or fiscal year). • The balance sheet is made up of assets, equity, and liabilities. ASSETS EQUITY & LIABILITIES Non-Current Assets: Equity Property and equipment Common stock (shareholder equity) Minus accumulated depreciation Retained earnings Net-Non Current Asset (fixed assets) Non-Current Liabilities Net intangible assets Long-term debt Other fixed assets Bank loans Other long-term liabilities Pag 21 Current Assets Current Liabilities Inventories Short-term loans Accounts receivable Accounts payable Other current assets Accrued income taxes Cash and equivalent Other current liabilities Total Assets Total Equity & Liabilities Introduction to Finance Department of Finance and Operations Management Instructor :Martha Edith Bellini Profitability and Costs of Capital BALANCE SHEET EQUITY Profitability Rate of Return: R(%) ASSETS LIABILITIES Cost of Capital (dividends + interest) K (%) R (%) - K(%) = Net Return: r (%) If R(%) > K(%) or r(%) = or >0 Pag 22 Introduction to Finance then the project is feasible Department of Finance and Operations Management Instructor :Martha Edith Bellini Two different points of view in Finance Point of view of Shareholders EQUITY ASSETS LIABILITIES Point of view of the manager Both want to maximize Net Profit = dividends + retained earnings. Their opinions differ about the allocation of Net Profit. Pg. 23 Introduction to Finance Department of Finance and Operations Management Instructor :Martha Edith Bellini Functions of the Financial Manager The financial manager faces three decision areas, which define the content of Corporate Finance. - First, how much money should the company invest? What kind of assets must be acquired? What cash flows are expected? These are the investment decisions. - Second, which financing structure is the best? Which is the length of time that funds will be needed? These are the financing decisions. - Third, the financial manager stands between the firm’s operations and the financial (or capital) markets, where investors hold the financial assets issued by the firm. The function of the financial manager is the management of cash flows to make a profit for the firm´s owners. Pg. 24 Introduction to Finance Department of Finance and Operations Management Instructor :Martha Edith Bellini Functions of the Financial Manager Financial management requires the coordination of all areas of a business to effectively benefit the owners. Within a company, financial decision-making is usually managed by the Chief Financial Officer The Controller and the Treasurer. CHIEF FINANCIAL OFFICER (CFO) Responsible for: • Financial policy • Corporate Planning TREASURER Responsible for: • Cash Management • Raising capital • Banking Relationships CONTROLLER Responsible for: • Financial Statements • Accounting • Taxes Pg. 25 Introduction to Finance Department of Finance and Operations Management Instructor :Martha Edith Bellini Functions of the Financial Manager REAL ASSETS CASH CASH INVESTORS FINANCIAL MANAGER ACTIVITY OF THE COMPANY CASH CASH FINANCIAL ASSETS Remuneration and repayment of funds Pg. 26 Introduction to Finance Department of Finance and Operations Management Instructor :Martha Edith Bellini