International Economics
advertisement

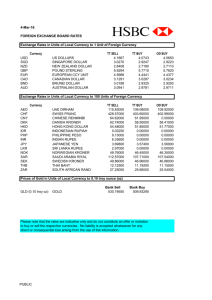
Unit IV: International Economics Chapters 17 Unit II: Supply, Demand, Equilibrium and Market Structures 17: International Trade Grade Vocabulary FIB Notes Daily 10 Current Events Chapter Activity Written Response Study Guide Participation Total / / / / / / / / / Test Name Grade /100 /100 /100 Final Unit II Test /100 International Economics SSEIN1 The student will explain why individuals, businesses, and governments trade goods and services. a. Define and distinguish between absolute advantage and comparative advantage. b. Explain that most trade takes place because of comparative advantage in the production of a good or service. c. Explain the difference between balance of trade and balance of payments. SSEIN2 The student will explain why countries sometimes erect trade barriers and sometimes advocate free trade. a. Define trade barriers as tariffs, quotas, embargoes, standards, and subsidies. b. Identify costs and benefits of trade barriers over time. c. List specific examples of trade barriers. d. List specific examples of trading blocks such as the EU, NAFTA, and ASEAN. e. Evaluate arguments for and against free trade. SSEIN3 The student will explain how changes in exchange rates can have an impact on the purchasing power of individuals in the United States and in other countries. a. Define exchange rate as the price of one nation’s currency in terms of another nation’s currency. b. Locate information on exchange rates. c. Interpret exchange rate tables. d. Explain why, when exchange rates change, some groups benefit and others lose. Unit IV: International Economics Chapter Standards Chapter 17 EF1c, EIN1a,b,c, EIN3a,b,c,d Standards Update Sheet Name:________________________________Class:_______________Instructor:___________________ + mastery Standard EIN1a EIN1b EIN1c EIN2a EIN2b EIN2c EIN2d EIN2e EIN3a EIN3b EIN3c EIN3d - needs improvement Activity Activity Activity Activity Activity Activity Activity Activity Activity Name: ____________________________________________________________________________________________ CHAPTER 17.1: – Interdependence and the Gains from Trade Definition Describe Definition Describe Definition Describe I think Draw I think Draw I think Draw Definition Describe Definition Describe I think Draw I think Draw W.R.:http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Vvfzaq72wd0 Activator Two men live alone on an isolated island. To survive they must undertake a few basic economic activities like water carrying, fishing, cooking and shelter construction and maintenance. The first man is young, strong, and educated. He is also, faster, better, more productive at everything. The second man is old, weak, and uneducated. He produces less than the younger man. In some activities the difference between the two is great; in others it is small. For instance, the younger man can gather 50 coconuts every hour, or catch 150 fish. While the older man can only gather 5 coconuts or catch 25 fish every hour. 1. 2. 3. 4. Who is better at all activities in the scenario above? ______________________ What is the opportunity cost for the younger man if he dedicates his hour to gathering coconuts? ____________ What is the opportunity cost for the older man if he dedicates his hour gathering coconuts________________ Should they work separately or together on the island? Explain. _______________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ Absolute Advantage – person or nation can produce _________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ Comparative Advantage – the ability to produce ____________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ Law of comparative advantage – a nation or person is better off when it produces goods ans services for which it has a ____________________________________________ Globalization - the process by which regional economies, societies, and cultures have become ________________________________ through ________________________________, transportation, and ________________________________. Coconuts or Fish? Comparative Advantage Absolute Advantage Coconuts Coconuts Fish Young Young Old Old Fish Young Man has ______________________________ advantage because he can __________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ OGO – “Other goes over” method shows the _______________________________________________________ Young Man has ______________________________ advantage because he _____________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________than the old man. His opportunity cost for collecting coconuts is ____________________________ relative to the old man. The old man has the ________________________ advantage in catching fish because he gives ______________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ His opportunity cost for catching fish is ________________________________ relative to the young man. Important Note: the only time two people/nations/firms will not trade is if there is no _________________________________________________, opportunity cost is the ______________________. Steps for Determining Comparative Advantage o Scenario: Canada and Mexico are considering the trade of two goods. Canada can produce 100 Furs or 100 trees. Mexico can produce 50 furs or 200 trees. Step 1 – Input the Data Productive Output Fur Trees Canada Mexico Step 2 – Find the Opportunity Cost of Production Opportunity Cost Fur Trees Canada _____ ÷_____ = _____ _____ ÷_____ = _____ Mexico _____ ÷_____ = _____ _____ ÷_____ = _____ Step 3 – Analyze the data to determine comparative advantage • • • • • It costs Canada ______ fur for every tree it produces. It costs Mexico ______ fur for every tree it produces. It costs Canada ______ tree for every fur it produces. It costs Mexico ______ tree for every fur it produces. Therefore, ____________________________ should specialize in the production of Fur, while _____________________________ should specialize in the production of trees Kate and Carl Productivity Per Hour T-Shirts per hour Birdhouses per hour Kate 6 _____ ÷_____ = _____ 2_____ ÷_____ = _____ Carl 1 _____ ÷_____ = _____ 1 _____ ÷_____ = _____ Who has absolute advantage in this situation? It costs Kate ________ birdhouses to produce 1 t-shirt. It costs Kate ________ shirts to produce 1 birdhouse. It costs Carl ________ to produce 1 t-shirt. It costs Carl ________to produce 1 birdhouse. ________ has a comparative advantage when producing t-shirts. ________ has a comparative advantage when producing birdhouses. Therefore, ___________ should produce t-shirts and __________ should produce birdhouses. 17.2: Trade Barriers and Agreements Definition Describe Definition Describe Definition Describe I think Draw I think Draw I think Draw Definition Describe Definition Describe Definition Describe I think Draw I think Draw I think Draw Definition Describe Definition Describe Definition Describe I think Draw I think Draw I think Draw Definition Describe Definition Describe Definition Describe I think Draw I think Draw I think Draw Definition Describe Definition Describe I think Draw I think Draw W.R: Cuba trade embargo http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tzo4qs4LvC0 Closed and Open Economies Closed economy - does ________________________________ with other economies in the world Open economy - interacts ________________________ with other economies around the world Exports – __________________________ produced goods and services that are __________________________ Imports - goods and services produced ___________________________________________________________ Trade Barriers and Agreements Trade Barrier – a trade ________________________________, used to prevent a foreign product from_______________________________________________________________________________ Tariffs – a tax on ________________________________ Customs Duty – a tax on items _______________________________________________ Import Quotas – a limit on the amount of a good that ________________________________________________ Voluntary Export Restraint – a ___________________________________________ on the number of products shipped to a particular country (exports) Balance of Trade Trade surplus - excess of ___________________________________________ o Exports____ Imports Trade deficit - excess of ___________________________________________ o Exports_____ Imports Balanced trade - exports ___________________________________________ o Exports ______ Imports W.R.: Protectionism http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Y2X3KPilAt0 Arguments for Protectionism Protectionism – the use of _________________________________________ to protect industries from __________________________________ Infant industry – a_________________________ founded industry in the ________________________________ International Cooperation and Agreements International Free Trade Agreement – results from ________________________________ between countries to reduce trade ________________________________and ________________________________ to promote ________________________________ 1. North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) – agreement between________________________________, ________________________________ and the __________________ to eliminate tariffs and other trade barriers 2. European Union (EU) – a regional trade organization of ________________________________ 3. World Trade Organization (WTO) – a worldwide organization whose goal is to promote ____________________ ________________________________, supervises ___________________________________________ Award ________________________________________________________________ 17.3: Measuring Trade Definition Describe Definition Describe Definition Describe I think Draw I think Draw I think Draw Definition Describe Definition Describe Definition Describe I think Draw I think Draw I think Draw Definition Describe Definition Describe Definition Describe I think Draw I think Draw I think Draw Measuring Trade Exchange Rate – the value of one ________________________________________________________in relation to another nation’s ______________________________ Fixed exchange rate system – a currency system in which governments try to keep the value of their currencies ________________________________________________________ Flexible exchange rate system – a currency system that allows the exchange rate to be determined by ________________________________________________________ (most major currencies have this) Determining the Rate of Exchange 1 Dollar = 12 Mexican Pesos ________/________ = _________ ________x ________ = ________ Hotel room costs ________ Pesos per night ________/________ = ________ Currency Conversion Practice Conversion for the value of the American Dollar in that foreign country. 2001 2002 2003 U.S. 1.00 1.00 1.00 Canada 1.55 1.60 1.35 Mexico 9 pesos 10 pesos 11 pesos Great Britain 0.70 pound 0.65 pound 0.60 pound Answer the following questions: 1. How much is the American dollar worth in Canada? 2001______________________ 2002 _______________________ 2003 ________________ Is the American Dollar stronger or weaker? _______________________________________ 2. How much is the American Dollar worth in Mexico? 2001______________________ 2002 _______________________ 2003 ________________ Is the American Dollar stronger or weaker? _______________________________________ 3. How much is the American Dollar worth in Great Britain? 2001______________________ 2002 _______________________ 2003 ________________ Is the American Dollar stronger or weaker? _______________________________________ Convert the above currency information to the value of the foreign currency in America Formula : 2001 2002 2003 USD/current rate = U.S. Canada Mexico Great Britain 1.00 1.00/1.55 = .63 1.00/9 = .11 1.00/.70 = 1.43 1.00 1.00 Convert the currency between countries according to the question. Hint: when wanting to know the value of currency from one country to another divide. Examples are provided for the year 2001. 4. Canadian Dollar value in Mexico 1 Canadian dollar is worth how much in Mexico? 2001____.63/.11= 5.72___ Written explanation: The Canadian dollar is worth 5.72 to every 1 Mexican peso 2002 __________/_________=____ Written explanation: 2003 _______/_____=____ Written explanation: 5. Mexican Peso value in Canada 1 Mexican Peso is worth how much in Canada? 2001____.11/.63=.17 Written explanation: The Mexican Peso is worth only .17 to every 1 Canadian Dollar 2002 __________/_________=____ Written explanation: 2003 _______/_____=____ Written explanation: 6. Mexican Peso value in Great Britain 1 Mexican Peso is worth how much in Great Britain? 2001____.11/1.43=.077 Written explanation: The Mexican Peso is worth .077 to every 1 British Pound 2002 _________/_________=_____ Written explanation: 2003 ______/_____=_____ Written explanation: 7. British Pound value in Mexico 1 British Pound is worth how much in Mexico? 2001___1.43/.11=14.3 Written explanation: The British Pound is worth 14.3 to every 1 Mexican Peso 2002 __________/________=_____ Written explanation: 2003 _______/____=_____ Written explanation: Answer the following questions: Hint: Multiply Mexico: 20 Mexican pesos would convert to how much money in the U.S.? 2000:__.11(20)= 2.20 American Dollars 2002 _______________________ 2003 ________________ Can you buy more or less in the United States? 2001______________________ 2002 _______________________ 2003 ________________ Canada: 50 Canadian Dollars would convert to how much money in the U.S.? 2001:__.63(50)= 77.50 American Dollars 2002 _______________________ 2003 ________________ Can you buy more or less in the United States? 2001______________________ 2002 _______________________ 2003 ________________ Great Britain: 15 British Pounds would convert to how much money in the US? 2001:__1.42(15)= 21.30 American Dollars 2002 _______________________ 2003 ________________ Can you buy more or less in the United States? 2001______________________ 2002 _______________________ 2003 ________________ Values: 1.3 = $1.30 One Dollar and Thirty cents .30 = $.30 30 cents .03 = $.03 3 cents Exchange rate work sheet: People, firms and nations exchange products for money and use the money to buy other products or to pay for the use of resources. Within an economy, prices are stated in the domestic currency, such as US dollars or European euros. Buyers use their currency to purchase goods. International markets are different. Producers in other countries who export goods want to be paid in their own currencies so they can carry out transactions. As a result, a foreign exchange market develops where national currencies can be exchanged. Such markets serve the need of all international buyers and sellers. The equilibrium prices in these markets are called exchange rates. An exchange rate is the rate at which the currency of one nation is exchanged for the currency of another. The following shows the exchange rates for selected countries for 2 separate months of the same year. British pound Canadian Dollar European euro Japanese Yen Mexican Peso Swedish Krona Cost of foreign currency in US dollars (US dollars / foreign currency) May Aug 1.4 1.8 .64 .63 Cost of US dollar in foreign currency (Foreign currency/ US Dollars May Aug .71 .56 1.56 1.58 .87 .0083 .11 .094 1.14 120.48 9.08 10.63 .91 .0090 .15 .093 1.09 111.111 6.65 10.75 Using the data from above, calculate the cost of the following products in US dollars. To solve, divide the cost of the product in the foreign currency by the cost of the US dollar in the foreign currency. May Aug A dinner for 2 that cost 500 pesos A hotel room that cost 30,000 yen A BMW that cost 85,000 euros A Pound of Swedish meatballs that cost 30 Krona A pair of pants that cost 72 pounds in London A leather jacket that cost 1,800 Canadian Dollars Determine whether or not the dollar is appreciating or depreciating in value for each foreign currency. Graph the resulting change in the market for currency for each situation. You must write a rationale. 1. Prices of US goods rise relative to the prices of German goods: Euro price of dollars US price of euros Quantity of US dollars Quantity of Euro Rationale: 2. Interest Rates in the US rise faster than interest rates in Canada: Canadian / US dollar exchange rate (price of US dollars in Canadian in dollars) Canadian/ US dollar exchange rate (price of Canadian in US dollars) Quantity of US dollars Quantity of Canadian Dollars Rational: 3. French Tourist flock to Mexico’s beaches Euro/ Peso exchange rate (Euro price of Pesos) Peso /Euro exchange rate (Peso price of euros) Quantity of Peso Rational: Quantity of Euro 4. Japanese video games become popular with US children: Yen/ US dollar exchange rate (yen price of dollars) Yen/ US dollar exchange rate (dollar price of Yen) Quantity of US dollars Quantity of Yen Rational: Worksheet Currency Exchange Use the exchange rates from the following table. Note that exchange rates change every day. These rates are just examples. C$1 In C$ (value of C$ in respective country below) (value of respective country’s currency in Canada) .991051 .616697 .727323 82.413 83.6623 1.00903 1.62154 1.37490 .012134 .011953 US dollar $ British Pound £ Euro € Japanese Yen ¥ Jamaican Dollar J$ 1. Convert C$435 to the following currencies. a) U.S. dollars b) Euros I.E.: C$435(1.00903)= $438.92 c) British pounds d) Japanese yen 2. Convert each of the following amounts to Canadian dollars. a) US$255 b) J$95 I.E.: 255/1.00903= $252.72 c) ¥25 000 d) £4300 3. Which amount has the greatest value in Canadian dollars? US$15 €11 £10 15(1.00903)=15.14 4. Which amount has the least value in Canadian dollars? J$54 631 ¥54 133 54,631(.011953)=653 US$649 5. While on a holiday in Montego Bay, Jamaica, Marilyn shops for souvenirs for friends. She has budgeted C$120 for souvenirs. a) How much does she have in Jamaican dollars to spend on souvenirs? b) In one shop, she finds a T-shirt for J$668. At a shop a few streets away, she finds the same T-shirt for J$680. How much does each T-shirt cost in Canadian dollars? c) Should she go back to the first shop to buy the T-shirt? Explain. Check Your Understanding 6. Su Mei is looking at online classified ads. She finds a used cell phone for US$99 plus US$30 for shipping. The same cell phone costs C$199 new at a local store. a) What is the total cost of the used cell phone in Canadian dollars? b) Do you think Su Mei should buy the cell phone online? Why? 7. While in Manchester, England, Chelsea bought a sweater for £28. When she returned, she saw the same sweater for C$38. Which sweater cost more? By how much in Canadian dollars? 8. Sonya found a dress online for US$139. She found a similar dress in a store where she lives for C$230. Give Sonya advice on which dress to buy. Include pros and cons of shopping online versus shopping in her local store. Daily Assignment Questions, pgs. 441 - 447 1. Describe how there is an unequal resource distribution in the world ____________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Describe why there is a need for trade ___________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 3. Describe the difference between absolute and comparative advantage__________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 4. What is the position of the United States relative to other countries regarding International trade? ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 5. Where does the United States stand as an exporter? ________________________________________________ 6. What countries are numbers 2 and 3 respectively? __________________________________________________ 7. What are the two reasons that the U.S. is successful as an exporter? ____________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 8. What services does the U.S. export? ______________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 9. Where does the United States stand as an importer? ________________________________________________ 10. How much does the U.S. import every year? _______________________________________________________ DAQ’s pgs. 449 -456 11. Explain how import quotas affect the United States import of cotton ___________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 12. What are some other barriers to trade? __________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 13. How do increased prices for foreign goods affect the consumer? _______________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 14. What is a trade war? __________________________________________________________________________ 15. How do trade wars affect both countries? _________________________________________________________ NAFTA: Is Free Trade a Good Idea? Pg 465 1. What was the debate in the 1980’s and early 1990’s over regarding NAFTA? _____________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. What were the Pro-NAFTA arguments? ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 3. What were the Anti-NAFTA arguments? ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 4. When did NAFTA go into effect? _________________________________________________________________ 5. List the consequences of NAFTA? ________________________________________________________________ 6. Based on the table on page 465, which of the provisions have benefited the United States? _________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ Name ____________________________________________________________ Date_____________ Period _________ Chapter 17 Study Guide – International Trade Section 1 – Why Nations Trade 1. A person or nation has an ________________________________ advantage when it can produce more of a given product using a given amount of resources. 2. A person or nation has an ________________________________ advantage when it can produce a given product more efficiently given all the other products that could be produced 3. Comparative advantage measures the _____________________________________________ cost of producing one product over another. 4. According to the law of comparative advantage ____________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ Section 2 – Trade Barriers and Agreements 5. A ____________________________________________________is a means of preventing a foreign product from freely entering a nation’s territory. 6. Describe the three types of trade barriers: a. Import Quota____________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ b. Voluntary Export Restraint__________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ c. Tariff ___________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 7. What are the effects of trade barriers on supply? ___________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 8. What are the effects of trade barriers on prices for foreign goods? _____________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 9. How do trade wars affect trade between two countries? _____________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 10. Protectionism is ______________________________________________________________________________ 11. Describe the three arguments for protectionism: a. Protecting jobs___________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ b. Protecting Infant Industries_________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ c. Safeguarding National Security______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 12. An agreement that results from cooperation between at least two countries to reduce trade barriers and tariffs and to trade with each other is an _______________________________________________________________ 13. Describe each of the following: a. World Trade Organization__________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ b. European Union__________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ c. NAFTA__________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ Section 3 – Measuring Trade 14. The exchange rate is __________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 15. Describe the difference between appreciation and depreciation of currency ______________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 16. Describe the difference between a trade deficit and trade surplus ______________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 17. The relationship between a nation’s imports and its exports is its ______________________________________ 18. Suppose your family is planning a trip to Mexico this summer and wants to determine the cost of staying in a hotel. If a hotel room in Mexico costs 1000 pesos per night and the exchange rate is 10.0 pesos per dollar, how much will a hotel room cost? ___________________________________________________________________ *Hint, divide the number of pesos by the exchange rate ratio of pesos per dollar* 19. Suppose your family is planning a trip to France this summer and wants to determine the cost of staying in a hotel. If a hotel room in France costs 1000 Euro per night and the exchange rate is 0.69 Euros per dollar, how much will a hotel room cost? ___________________________________________________________________ Absolute and Comparative Advantage Practice: 16. Mexico and Colombia are considering trade of two products, Corn and Oil. Colombia can produce 30 bushels of corn or 15 barrels of oil. In Mexico, they can produce 20 bushels of corn and 10 barrels of oil. Fill in the tables based on the scenario: Productive Output Corn Oil Mexico Colombia Which country enjoys an absolute advantage in both oil and corn? _____________________________________ Opportunity Costs for Mexico and Colombia Opportunity Cost of Producing Corn Opportunity Cost of Producing Oil Mexico _______ ÷ ________ = __________ _______ ÷ ________ = __________ _______ ÷ ________ = __________ _______ ÷ ________ = __________ Colombia 17. Based on the scenario, why should Mexico and Colombia not trade goods? ______________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. Word Bank: Absolute, Comparative, Opportunity, Law of Comparative Advantage, Trade Barrier, Import Quota, Voluntary Export Restraint, Tariff, Customs Duty, Trade War, Protectionism, International Free Trade, World Trade Organization, European Union, NAFTA, Exchange Rate, Appreciation, Depreciation, Trade Deficit, Trade Surplus, Balance of Trade. ACROSS 3 An increase in the value of currency 6 A person or nation has this type of advantage when it can produce given product more efficiently given all the other products that could be produced 11 A self-imposed limitation on the number of products shipped to a particular country 16 An agreement that will eliminate all tariffs and trade barriers between Canada, Mexico, and the United States 18 A person or nation has this type of advantage when it can produce more of a given product using a given amount of resources 19 Is a means of preventing a foreign product from freely entering a nation’s territory 20 When a nation imports more than it exports 21 A decrease in the value of currency DOWN 1 This law states that two countries should trade products when it produces products for which it has a comparative advantage 2 A worldwide organization whose goal is to increase free global trade and lower tariffs 4 Comparative advantage measures this type of cost, which is the next best use of time, money, resources, etc. 5 Agreement that results from cooperation between at least two countries to reduce trade barriers and tariffs to trade with each other 7 A regional trade organization made up of European nations 8 A cycle of increasing trade restrictions between two countries 9 The use of trade barriers to protect a nation’s industries from foreign competition 10 The relationship between a nation’s imports and its exports 12 When a nation exports more than it imports 13 The value of a foreign nation’s currency in terms of the home nation’s currency 14 A limit on the amount of a good that can be imported 15 A tax on certain items purchased abroad 17 A tax on imported goods