Air Pollution Reading Guide Pages 67
advertisement

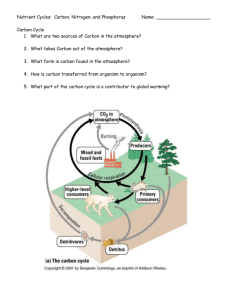
Air Pollution Reading Guide Pages 67-71 Biogeochemical Cycles Carbon Cycle 1. List the 4 biomolecules in which carbon can be found. 2. What two processes does the carbon cycle depend on? 3. Explain the effects of too much or not enough carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. 4. Identify the role of each in the carbon cycle: terrestrial/aquatic producers, consumers, decomposers. 5. How do we interfere with the carbon cycle? 6. Draw a diagram of the carbon cycle below. Nitrogen Cycle 1. Where does the majority of nitrogen come from? 2. Nitrogen is a component of ________________________. 3. What 2 natural processes “fix” nitrogen? 4. List the 4 major steps of the nitrogen cycle. 5. How do we interfere with the nitrogen cycle? 6. Draw a diagram of the nitrogen cycle below. Phosphorus Cycle 1. This cycle is different from the other cycles because it does not include the __________. 2. What is the major reservoir for phosphorus? 3. What is phosphorus used for? 4. Where it phosphorus trapped/lost for long periods of time? 5. Who do we interfere with the phosphorus cycle? 6. Draw a diagram of the phosphorus cycle below. Sulfur Cycle 1. Where is most of the sulfur stored? 2. How does sulfur enter the atmosphere? 3. What happens once it is in the atmosphere? 4. Where is sulfate converted to sulfides? 5. How do we interfere with the sulfur cycle? 6. Draw a diagram of the sulfur cycle below. Pages 474-478 1. What are the effects of lead on humans? 2. What are the sources of this lead? 3. What is being done to prevent further illnesses from occurring? 4. Write a short equation to represent the process of industrial smog formation. 5. Where is industrial smog an issue? 6. Define: photochemical reaction and photochemical smog. 7. What are the “ingredients” of photochemical smog? 8. What produces brown smog? 9. Define photochemical oxidants and give some examples. 10. What leads to higher levels of ozone? 11.