Chapter 4 4-1: Factors and Monomials Objectives: Determine
advertisement

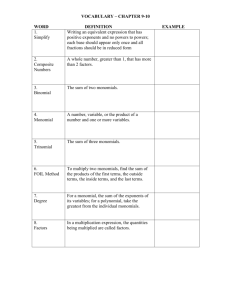
Chapter 4 4-1: Factors and Monomials OBJECTIVES: Determine whether one number is a factor of another. Determine whether an expression is a monomial. VOCABULARY: Factors: Two or more numbers that are multiplied to form a product. Divisible: When you divide and you get a remainder of 0. Monomial: A number, a variable, or a PRODUCT of numbers and/or variables. Notes: Divisibility Rules: A number is divisible by 2 if the ones digit is divisible by 2. A number is divisible by 3 if the sum of its digits is divisible by 3. A number is divisible by 5 if the ones digit is 0 or 5. A number is divisible by 6 if the number is divisible by 2 and 3. A number is divisible by 10 if the ones digit is 0. Note on identifying Monomials: A monomial is a product of variables and rational numbers and may have a number as a denominator, but not a variable. 4-2: Powers and Exponents Objectives: Write expressions using exponents. Evaluate expressions containing exponents. VOCABULARY: Base: The number that is multiplied. Exponent: How many times the base is used as a factor. Power: The number that can be expressed using an exponent. Notes: Very important to know how to “say” powers. Remember: Any number raised to the zero power is equal to 1 4-3: Prime Factorization Objectives: Write the prime factorizations of composite numbers. Factor Monomials. VOCABULARY: Prime Number: A whole number that has exactly two factors, one and itself. Composite Number : A whole number that has more than two factors. Prime Factorization: When a composite number is expressed as the product of prime factors. Factor Tree: A method for finding a prime factorization of a number. Factor: To write a number as a product of its factors. Notes: When “factoring” monomials, if the monomial is negative, you must include -1 as one of the factors. When “factoring” a non-negative monomial, you should not include a 1 as a factor. 4-4: Greatest Common Factor (GCF) Objectives: Find the greatest common factor of two or more numbers or monomials. Use the distributive property to factor algebraic expressions. VOCABULARY: Greatest Common Factor: The greatest number that is a factor of two or more numbers. Notes: Factor Algebraic Expressions: You can find the GCF of two or more monomials by finding the product of their common prime factors. 4-5: Simplifying Algebraic Fractions Objectives: Simplify fractions using the GCF. Simplify algebraic fractions. VOCABULARY Simplest Form: When the GCF of the numerator and denominator is 1. Algebraic Fraction: A fraction with variables in the numerator or denominator. Remember: When simplifying fractions, if a common factor is used that is NOT the GCF, the resulting fraction will not be in simplest form, which means you will have to simplify again. 4-6: Multiplying and Dividing Monomials Objectives: Multiply Monomials. Divide Monomials. Notes: 1. 2. Product of Powers: When you multiply powers with the same base, you add their exponents. Quotient of Powers: When you divide powers with the same base, you subtract their exponents. 4-7: Negative Exponents Objectives: Write expressions using negative exponents. Evaluate numerical expressions containing negative exponents. Notes: Negative exponents must be rewritten with a positive exponent using the following rule: Algebraic expressions containing negative exponents can be written using positive exponents and evaluated. 4-8: Scientific Notation Objectives: Express numbers in standard form and in scientific notation. Compare and order numbers written in scientific notation. VOCABULARY Scientific Notation: method for writing very large numbers or very small numbers. Notes: A number is expressed in scientific notation when it is written as the product of a factor and a power of 10. The factor must be greater than or equal to 1 and less than 10. Positive and Negative Exponents in Scientific Notation: When the number is 1 or greater, the exponent is positive. When the number is between 0 and 1, the exponent is negative.