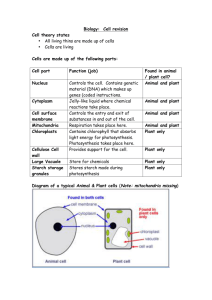
Q1. Sally investigated how the human body digests and absorbs

Q1.
Sally investigated how the human body digests and absorbs starch.
She used saliva to digest the starch.
To model digestion she used special bags made from a semi-permeable membrane. These bags have lots of very small holes.
Sally sets up the equipment as shown below. There is one special bag in each beaker.
She keeps the water in the beakers at 37ºC.
After 20 minutes, Sally tested the contents of each beaker and bag for starch and sugar.
The table below shows S ally’s results. beaker A beaker B beaker C
Was starch found in the bag?
Was sugar found in the bag?
Was starch found in the water?
Was sugar found in the water?
(a) Suggest why Sally kept the water at 37ºC.
......................................................................................................................
1 mark
(b) (i) Explain why sugar was found in the bag in beaker A.
.............................................................................................................
1 mark
Page 1
(ii) Starch was not found in the water outside the bag in any beaker.
Suggest why.
.............................................................................................................
1 mark
(c) Why did Sally set up beaker C? Tick the correct box. for a fair test for accuracy for reliability for a control
1 mark
(d) Sally used diagrams to show what happened in her investigation.
Use the diagrams above to answer the following questions.
(i) Which diagram shows the results of beaker B ? Write the letter.
......................
1 mark
(ii) Which diagram shows the results of beaker A ? Write the letter.
Page 2
......................
1 mark
(e) What does saliva contain that causes starch to change in beaker A?
......................................................................................................................
1 mark
(f) Sally chewed a piece of bread for 5 minutes without swallowing.
What would she notice about the taste of the bread after chewing for 5 minutes?
Use Sally’s results to help you.
......................................................................................................................
1 mark maximum 8 marks
Q2.
Table 1 gives information about 100 g of five different foods. food energy per
100 g of food
(kJ) (g) nutrients per 100 g of each food protein fat
(g) carbohydrate
(g) calcium
(mg)
403 1.2 0.3 23.2 6 banana wholemeal bread
914 9.2 2.5 41.6 54 butter 3031 0.5 81.7 0 15 cheese 1708 22.5 34.4 0.1 720 milk 275 3.2 3.9 4.8 115 table 1
(a) Look at table 1 .
(i) Which of the four nutrients , protein, fat, carbohydrate or calcium, provides
Page 3
most of the energy in the cheese?
................................................................................................................
(ii) Which of the four nutrients provides most of the energy in the wholemeal bread?
................................................................................................................
(iii) Which of the four nutrients is needed for growth and repair?
................................................................................................................
3 marks
(b) The recommended daily amount of protein for a woman is 45 g.
Look at table 1 .
How many grams of cheese would provide 45 g of protein?
Tick the correct box.
50 g 100 g 150 g 200 g
1 mark
(c) Not all the types of nutrients needed for a balanced diet are shown in table 1 .
Give the name of one of the missing types of nutrient.
.............................................................
1 mark
(d) Table 2 shows the recommended daily amount of calcium for a person in four stages of the human life cycle.
We need calcium for healthy teeth and bones . person a baby aged 6 months a woman before she is pregnant a pregnant woman a breast-feeding woman recommended daily amount of calcium (mg)
600
500
1200 table 2
Page 4
(i) Use information in table 2 to estimate how much calcium a breast-feeding woman should have each day.
............. mg
(ii) Explain why she would need this amount of calcium.
................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................
2 marks maximum 7 marks
Q3.
The diagram below shows the digestive system.
Page 5
(a) (i) Give the letter which labels the stomach.
............
1 mark
(ii) Give the letter which labels the small intestine.
............
1 mark
(iii) Glucose is absorbed in the small intestine.
What carries glucose from the intestine to other parts of the body?
.............................................................................................................
1 mark
(b) Some athletes take glucose tablets before a race.
Why do they take glucose?
Tick the correct box.
for growth for healthy bones and teeth
to prevent disease to provide energy
1 mark
(c) The table below shows what four people ate for lunch. name
Jon
Nadia
Clare
Zak lunch chicken and salad cheeseburger and chips lemonade and a jam doughnut mushroom soup and an orange
(i) Whose lunch had the most sugar in it?
Page 6
...........................................................
1 mark
(ii) Whose lunch had the most fat in it?
...........................................................
1 mark
(iii) Eating too much fat is bad for you.
Give one reason for this.
.............................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................
1 mark maximum 7 marks
Q4.
Andy investigated the digestion of a protein called gelatin.
He used an enzyme called pepsin from the human stomach, and three cubes of gelatin each 1 cm
3
.
He set up the experiment shown below and put the test-tubes in a waterbath at 37°C.
He measured the time for the digestion of the gelatin.
Page 7
(a) Why did Andy choose a temperature of 37°C for the water-bath?
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
1 mark
(b) In test-tube C, the cube of gelatin that had been cut into pieces was digested more quickly than the whole cube in test-tube A.
Give the reason for this.
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
1 mark
(c) The boiled pepsin in test-tube B did not digest the gelatin.
Why did boiling this enzyme stop it working?
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
1 mark
(d) Protein is needed for growth and repair.
The digestion of protein begins in the stomach and is completed in the small intestine.
(i) What are the products of the digestion of protein?
Tick the correct box.
amino acids
sugars
energy
vitamins
1 mark
(ii) Why is it necessary to digest protein before it can be used for growth and repair?
Page 8
.............................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................
1 mark maximum 5 marks
Q5.
The table shows the mass of water, fat, fibre and vitamin C in 100 g of potato cooked in three different ways. water, in g fat, in g fibre, in g vitamin C, in mg
100 g of chips 57 7 2 9
100 g of boiled, peeled potato
80 hardly any 1 6
100 g of potato baked in its skin
63 hardly any 3 14
(a) Use information from the table to help you fill the gaps in the following sentences.
(i) Chips are crisper than boiled potatoes because chips contain less
...................................................................
1 mark
(ii) Most of the fibre in a baked potato is in the ............................................... of the potato.
1 mark
(b) Use the information in the table to work out how much vitamin C there is in:
200 g of chips .............. mg;
200 g of potato baked in its skin .............. mg.
1 mark
Page 9
(c) People do not always eat a balanced diet.
Draw one line from each fact about a person's diet to the organ it harms.
Draw only three lines.
3 marks
Maximum 6 marks
Q6.
Sailors used to suffer from an illness called scurvy caused by a poor diet on long journeys. James Lind was a doctor who tested treatments for scurvy. He predicted that all acids cure scurvy .
Page 10
He gave 6 pairs of sailors with scurvy exactly the same meals but he also gave each pair a different addition to their diet. pair of sailors addition to their diet effect after one week
1
2
3 some apple cider
25 drops of very dilute sulphuric acid to gargle with*
2 teaspoons of vinegar beginning to recover still had scurvy still had scurvy
4
5
6 half a pint of sea water*
2 oranges and 1 lemon herbs and spices and acidified barley water still had scurvy recovered still had scurvy
(a) Does the evidence in the table support the prediction that all acids cure scurvy?
Tick the correct box.
yes no
Use the table to explain your answer.
.....................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................
(*) DANGER! DO NOT TRY THIS.
(b) (i) Give the one factor James Lind changed in this experiment.
(This is called the independent variable.)
.............................................................................................................
1 mark
1 mark
Page 11
(ii) Give the factor James Lind examined in this experiment.
(This is called the dependent variable.)
.............................................................................................................
1 mark
(c) James Lind’s evidence suggested that oranges and lemons cured scurvy.
At a later time, other scientists did the following:
• They separated citric acid from the fruit.
• They predicted that citric acid would cure scurvy.
• They tested their prediction by giving pure citric acid as an
addition to the diet of sailors with scurvy.
• They found it did not cure scurvy.
The scientists had to make a different prediction.
Suggest a new prediction about a cure for scurvy that is consistent with the evidence collected.
.....................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................
(d) Explain why it is necessary to investigate the effects of changes in diet over a period of more than one week.
1 mark
.....................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................
1 mark
Maximum 5 marks
Q7.
The diagram below shows a villus. There are several thousand villi in every square centimetre of the lining of the small intestine. The cells in the lining of each villus have
Page 12
folds called microvilli on their outer surfaces. One of these cells is shown magnified in the diagram.
(a) Explain two ways in which the structure of the villus enables the products of digestion to be absorbed efficiently.
1. .............................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................
2. .............................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................
2 marks
(b) Mucus is produced by some cells in the lining of the small intestine.
One function of mucus is to protect the lining of the small intestine against the action of certain chemicals.
(i) Give the name of one type of chemical present in the small intestine which would otherwise damage the lining.
............................................................
1 mark
Page 13
(ii) Suggest one other function of mucus produced in the small intestine.
.............................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................
1 mark
(c) Bile, produced by the liver, enters the small intestine through the bile duct.
Describe the effect which bile has on fats in the small intestine.
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
1 mark
Maximum 5 marks
Q8.
A medical researcher used a tube to remove some of the liquid from a person's stomach. The researcher put the liquid into a flask which had a piece of boiled beef in it. The beef was digested in six hours. The diagrams show the flask at different stages of the experiment.
(a) (i) What type of substance in the liquid from the stomach caused the beef to be digested in six hours?
.............................................................................................................
1 mark
(ii) The researcher kept the flask at 37°C. Explain why.
.............................................................................................................
Page 14
.............................................................................................................
1 mark
(b) In the human body, the digestion of protein in meat begins in the stomach and is completed in the small intestine.
(i) What is digested protein used for in the body?
.............................................................................................................
1 mark
(ii) Describe how the products of digestion get from inside the small intestine to the cells in the rest of the body.
.............................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................
2 marks
Maximum 5 marks
Page 15
Q9.
(a) Complete the equation for photosynthesis. Draw a ring around each correct answer.
hydrogen alcohol
Carbon dioxide + nitrogen
water light energy glucose + oxygen methane
Some students investigated the effect of light intensity on the rate of photosynthesis in pondweed.
The diagram shows the apparatus the students used.
(2)
The closer the lamp is to the pondweed, the more light the pondweed receives.
The students placed the lamp at different distances, d , from the pondweed.
They counted the number of bubbles of gas released from the pondweed in 1 minute for each distance.
(b) A thermometer was placed in the glass beaker.
Why was it important to use a thermometer in this investigation?
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
Page 16
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
(3)
(c) The students counted the bubbles four times at each distance and calculated the correct mean value of their results.
The table shows the students’ results.
Distance d in cm
10
20
30
40
Number of bubbles per minute
1
52
49
32
30
2
52
51
30
10
3
54
48
27
9
4
54
52
31
11
Mean
53
50
30
(i) Calculate the mean number of bubbles released per minute when the lamp was
40 cm from the pondweed.
...............................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................
Mean number of bubbles at 40 cm = ............................................
(2)
(ii) On the graph paper below, draw a graph to show the students’ results:
• add a label to the vertical axis
• plot the mean values of the number of bubbles
• draw a line of best fit.
Page 17
Distance d in cm
(iii) One student concluded that the rate of photosynthesis was inversely proportional to the distance of the lamp from the plant.
Does the data support this conclusion?
Explain your answer.
...............................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................
(d) Light intensity, temperature and concentration of carbon dioxide are factors that affect the rate of photosynthesis.
Scientists investigated the effects of these three factors on the rate of photosynthesis
Page 18
(2)
(4)
in tomato plants growing in a greenhouse.
The graph below shows the scientists’ results.
Light intensity in lux
A farmer in the UK wants to grow tomatoes commercially in a greenhouse.
The farmer read about the scientists’ investigation.
During the growing season for tomatoes in the UK, natural daylight has an intensity higher than 30 000 lux.
The farmer therefore decided to use the following conditions in his greenhouse during the day:
• 20°C
• 0.1% CO
2
• no extra lighting.
Suggest why the farmer decided to use these conditions for growing the tomatoes.
You should use information from the scientists’ graph in your answer.
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
Page 19
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
(4)
(Total 17 marks)
Q10.
Duckweed is a plant. Duckweed grows in ponds. The leaves of duckweed float on the surface of the water and its roots hang down in the water.
The drawing shows a duckweed plant.
(a) Duckweed roots absorb nitrate ions from the water.
The nitrate ions help the duckweed to grow.
Draw a ring around the correct answer to complete the sentence.
Duckweed needs nitrate ions to make carbohydrate
. fat. protein.
(b) Some students grew duckweed plants in three different solutions of mineral ions, A , B and C , and in distilled water ( D ).
Table 1 shows the concentrations of mineral ions in each of A , B , C and D at the start of the investigation.
Table 1
Page 20
(1)
Mineral ion
Concentration of mineral ions in mg per dm
3
at the start of the investigation
A B C D
1000 4 4 0 Nitrate
Phosphate 300 0 0 0
Magnesium 200 84 24 0
The students counted the number of duckweed leaves in A , B , C and D at the start of the investigation and after 28 days.
Table 2 shows their results.
Table 2
A B C D
Number of leaves at start 4 4 4 4
Number of leaves after 28 days 50 27 14 6
(i) Using Table 1 and Table 2 , describe the effect of magnesium ions on the growth of duckweed.
...............................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................
(1)
(ii) Solution A contained the highest concentration of nitrate ions.
One student said, ‘The results show that nitrate ions are needed for the growth of duckweed.’
What evidence in Table 2 supports what the student said?
...............................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................
(1)
(c) The students measured the growth of the duckweed by counting the number of leaves.
Page 21
(i) Suggest a better method of measuring the growth of the duckweed.
...............................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................
(1)
(ii) Suggest why your method is better than the students’ method.
...............................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................
(1)
(Total 5 marks)
Q11.
A student measured the concentration of carbon dioxide in the air around a potted plant on two different days.
The diagram shows the student’s apparatus.
There was a plastic bag round the plant pot to stop microorganisms in the soil affecting the concentration of gases in the air inside the jar.
The apparatus was put near a window.
The graph shows the results.
Page 22
(a) Day 1 was cloudier than Day 2.
What evidence from the graph shows that Day 1 was cloudier?
Explain your answer.
.................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................
(2)
(b) A potted plant sometimes develops yellow leaves.
The development of yellow leaves could be due to the lack of a mineral ion.
Suggest the mineral ion that could be lacking.
.................................................................................................................................
(1)
(Total 3 marks)
Page 23
Q12.
The graph shows the uptake of carbon dioxide and the release of carbon dioxide by a bean plant on a hot summer’s day.
(a) At which two times in the day did the rate of photosynthesis exactly match the rate of respiration in the bean plant?
1 ......................................................... 2 .........................................................
(1)
(b) The bean plant respires at the same rate all through the 24 hour period.
(i) How much carbon dioxide is released each hour during respiration?
......................................................... arbitrary units
(1)
(ii) How much carbon dioxide is used by photosynthesis in the hour beginning at 3 pm?
...............................................................................................................
Page 24
...............................................................................................................
Answer = ......................................................... arbitrary units
(1)
(c) Over the 24 hour period, the total amount of carbon dioxide taken in by the bean plant was greater than the total amount of carbon dioxide given out by the bean plant.
Explain, in detail, why this was important for the bean plant.
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
(2)
(Total 5 marks)
Q13.
Students investigated the effect of changing the carbon dioxide concentration on the rate of photosynthesis in pieces of leaf.
Diagram 1 shows the type of leaf used by the students.
The students:
• cut pieces of leaf from the green region
• put the pieces into tubes
• added different concentrations of carbon dioxide to each tube
• shone lights on the tubes with either high or low light intensity
Page 25
• recorded the concentration of oxygen in the tubes after 5 hours.
Diagram 2 shows how each experiment was set up.
The graph shows the results of the investigation.
(a) (i) Describe the effect of increasing carbon dioxide concentration on the rate of photosynthesis at low light intensity.
...............................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................
(1)
(ii) Explain the effect that you have described.
In your answer you should refer to limiting factors.
...............................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................
Page 26
...............................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................
(2)
(b) What would have been the effect on oxygen concentration over the five-hour period if a white region of the leaf had been used, instead of a green region?
Effect .............................................................................................................
Explain your answer.
Explanation ....................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
(2)
(c) Some people keep indoor plants which have variegated leaves (leaves with green and white regions).
If plants with variegated leaves are kept in dim light conditions the white areas of the leaves start to turn green.
This is an advantage to the plant.
Suggest why.
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
(2)
(Total 7 marks)
Q14.
A gardener grows tomatoes.
He wants to find out how to get the biggest mass of tomatoes.
He plants different varieties of tomato against different walls in his garden.
Page 27
Use these results to answer the questions.
(a) The gardener wants his test to be fair.
Name one condition which he should keep the same for all his tomato plants.
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
(1)
(b) The table shows the gardener’s results.
Variety of tomato plant
Sungold Sungold Sungold Sungold Nugget Champion
Wall they were planted against
North West South East East East
Mean mass of tomatoes produced in kilograms per plant
3.5 3.0 1.2 2.5 3.2 2.7
(i) To obtain the biggest mass of tomatoes, against which wall is it best to grow the tomato plants?
Page 28
North wall
Tick ( ) one box.
South wall
East wall
West wall
(1)
(ii) To obtain the biggest mass of tomatoes, which variety of tomato plant would it be best to grow?
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
(c) From the information in the table, the gardener’s test was not fair.
Give one way in which the test was not fair.
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
(1)
(Total 4 marks)
Q15.
The diagram shows a section through a plant leaf.
Page 29
(a) Use words from the box to name two tissues in the leaf that transport substances around the plant. epidermis mesophyll phloem xylem
.................................................................. and
..................................................................
(1)
(b) Gases diffuse between the leaf and the surrounding air.
(i) What is diffusion ?
...............................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................
(2)
(ii) Name one gas that will diffuse from point A to point B on the diagram on a sunny day.
...............................................................................................................
(1)
(Total 4 marks)
Page 30
Q16.
The graph shows how the rate of photosynthesis is affected by different conditions.
(a) What patterns can you find from this graph?
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
(5)
(b) How useful could this information be to a grower using glasshouses? Give reasons for your answer.
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
(2)
(Total 7 marks)
Page 31
M1.
(a) • (37 °C is) body temperature accept ‘so the saliva or enzymes would work’ accept ‘it is a good or optimum temperature for digestion’
‘to make it a fair test’ is insufficient
‘so they are all the same’ is insufficient
(b) (i)
• the starch is broken down or digested
‘there is a reaction between starch and saliva’ is insufficient
1
1
(ii) any one from
• starch could not pass through the bag accept ‘starch could not get through the holes’
‘the bag is semi-permeable’ is insufficient
• starch is too big
‘the bag holds it in’ is insufficient
1
(c) • for a control if more than one box is ticked, award no mark
1
(d) (i) • P if more than one letter is given, award no mark
1
(ii) • R if more than one letter is given, award no mark
1
(e) • enzymes accept ‘amylase’ or ‘carbohydrase’
1
Page 32
(f) any one from
• sweeter or sugary accept ‘sugar’ or ‘sweet’
• it tastes of sugar (L6)
M2.
(a) (i)
• fat
(ii) • carbohydrate
(iii) • protein
(b) any one from
• 200 g if more than one box is ticked, award no mark
(c) any one from
• vitamins accept a named vitamin
• water
• fibre accept ‘roughage’ accept ‘minerals’ or a named mineral do not accept ‘calcium’
(d) (i) • 1100 accept a number from 1000 to 1300
Page 33
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
[8]
(ii) any one from
• to make milk
• milk contains calcium
• a breast-fed baby needs calcium for growth or for bones or teeth accept ‘the baby needs calcium’
• she has to have enough calcium for herself and the baby accept ‘to feed herself and the baby’ accept ‘the baby needs 600 and she needs 500’ accept ‘this is recommended for mother and baby’
‘to feed the baby’ is insufficient
1
M3.
(a) (i) D
(ii) E
(iii) any one from
• blood accept ‘plasma’
• blood vessels accept a named blood vessel accept ‘arteries’; ‘veins’ a mark should be awarded for ‘red or white blood cells’ as knowledge of the function of blood cells is not expected at this level the mark is awarded for the reference to blood
1
1
1
(b) to provide energy if more than one box is ticked, award no mark
1
Page 34
[7]
(c) (i) Clare accept ‘lemonade and jam or doughnut’
(ii) Nadia accept ‘cheeseburger and chips’ or ‘burger and chips’
1
(iii) any one from
• it causes heart disease accept ‘it is bad for your heart’
• it could give you a heart attack accept ‘it might give you a stroke’
• it clogs your arteries or blood vessels accept ‘it makes you fat’ accept ‘it is bad for the liver’
1
M4.
(a) any one from
• it is the temperature of the human body or the stomach
• the enzyme or pepsin works best at that temperature
(b) there was a larger surface for the enzyme to act on accept ‘the enzyme came into contact with more of the gelatin’ accept ‘the surface or area was bigger’
‘because the gelatin had been chopped up’ is insufficient
1
(c) it or the enzyme was destroyed or denatured do not accept ‘the enzyme was killed’
1
Page 35
1
1
[7]
(d) (i) amino acids if more than one box is ticked, award no mark
(ii) any one from
• proteins cannot be absorbed
• proteins are too big to pass through the lining of the intestine or blood vessels accept ‘so proteins or they can be absorbed’
• amino acids can be absorbed
• amino acids can pass through the wall of the intestine or blood vessels
• amino acids are small enough to be absorbed
• to make them soluble
‘they need to be digested or broken down’ is insufficient
1
1
M5.
(a) (i) water
(ii) skin or peel
1
1
(b) 18
28 answers must be in the correct order
both answers are required for the mark
1
(c)
[5]
Page 36
if more than one line is drawn from any fact about the diet, award no mark for that fact
3
M6.
(a) No if more than one box is ticked, award no mark and any one from both the answer and the explanation are required for the mark
• sulphuric acid did not cure scurvy accept ‘some acids did not cure scurvy’
• not all the sailors recovered accept ‘only pair 5 totally recovered’
• only two pairs recovered
• only those that had fruit- related additions recovered
• some with acid failed to recover
• a week is not long enough to show the effect accept ‘a week is not long enough’
‘only those who received vitamin C recovered’ is insufficient
1
Page 37
[6]
(b) (i) any one from
• addition to their diet do not accept ‘type of food or drink’
• food or drink supplements do not accept ‘kind of meal’
• type of acid accept ‘the acid’ accept ‘amount of acid’ do not accept conclusions such as
‘4 out of 6 pairs of sailors had scurvy’
(ii) any one from
• whether they recovered
• return to health
• recovery from scurvy accept ‘scurvy is cured’
• effect after one week do not accept ‘time to recover’
(c) any one from
• there must be a different substance or something present in fruits that cures scurvy accept ‘fruits will cure scurvy’ accept ‘vitamin in the fruit would cure scurvy’ accept ‘vitamin C will cure scurvy’ accept any named vitamin for vitamin C accept ‘vitamins would have an effect’
‘the acids in oranges and lemons cure scurvy’ is insufficient
‘oranges and lemons will cure scurvy’ is insufficient
1
1
1
(d) any one from
• effects due to diet may take more than a week to reveal themselves accept ‘one week is too short’
Page 38
or ‘you need to see long term effects’
• the body takes time to adjust to the diet
• time is needed for the results to reveal themselves
• the effects do not take place before a week
• the longer the time the more reliable the results accept ‘oranges or lemons might be a short term cure’
1
M7.
(a) any two from
• it or the villus has a large surface accept ‘they have a large surface area’
• the microvilli have a large surface area
• it has a good blood supply or lots of capillaries
• the lining is one cell thick accept ‘the lining is thin’ or ‘the blood is close to the surface’
or ‘the blood vessels are close to the surface’
2
(b) (i) enzymes accept ‘acid’ or ‘alkali’ or ‘HCl’ or ‘protease’
(ii) any one from
• lubricates the food
• makes food pass along the intestine easily
• prevents food sticking in the intestine accept ‘it is part of the immune system’
1
1
(c) any one from
• emulsifies them
Page 39
[5]
accept ‘emulsifies it’
• breaks down large globules into smaller globules do not accept ‘digests fat’
or ‘breaks it into smaller molecules’
or ‘breaks them down’
• increases the surface area
1
M8.
(a) (i) an enzyme accept ‘enzymes’ or ‘pepsin’ or ‘protease’ accept ‘acid’ or ‘hydrochloric acid’
(ii) any one from
• it is the temperature at which enzymes work best
• it is the temperature of the body do not accept ‘this is the body heat’ or ‘to make a fair test’
1
1
(b) (i) any one from
• for growth accept ‘for new cells’
• for repair
• for making other protein or enzymes accept ‘to supply amino acids’ do not accept ‘for energy’
1
(ii) one mark is for the products of digestion getting through the barrier between intestine and blood, and the other mark is for the method of transport they pass through the intestine wall accept ‘they are absorbed or pass into the blood’ or ‘they pass through the gut wall’
Page 40
[5]
they are carried by the blood or plasma or blood stream accept ‘they go through the blood vessels
or arteries or veins’
M9.
(a) LHS = water
RHS = glucose
(b) any three from:
• (measure) temperature ignore reference to fair test
• to check that the temperature isn’t changing
• rate of reaction changes with temperature
• temperature is a variable that needs to be controlled allow lamp gives out heat
(c) (i) 10 correct answer = 2 marks allow 1 mark for: allow 1 mark for correct calculation without removal of anomalous result ie 15
(ii) graph: allow ecf from (c)(i) label on yaxis as ‘number of bubbles per minute’ three points correct = 1 mark allow ± 1 mm four points correct = 2 marks line of best fit = smooth curve
Page 41
1
1
[5]
1
1
2
1
2
3
1
(iii) as distance increases, rate decreases – pro allow yes between 20 – 40 but should be a straight line / but line curves – con / not quite pro allow not between 10 – 20 if line of best fit is straight line, allow idea of poor fit
1
1
(d) any four from:
• make more profit / cost effective
• raising temp. to 25 °C makes very little difference at 0.03% CO
• (at 20 °C) with CO
2
at 0.1%, raises rate
2
• (at 20 °C with CO
2 at 0.1%) → >3x rate / rises from 5 to 17
• although 25 °C → higher rate, cost of heating not economical
• extra light does not increase rate / already max. rate with daylight accept ref to profits c.f. costs must be favourable
M10.
(a) protein
(b) (i) (more) magnesium gives more growth / more leaves / more duckweed if converse must be clear that less magnesium gives less growth
1
1
4
[17]
(ii) A gave highest number of leaves / plants or more than others it equals ’A’ use of numbers must compare A with at least one other or
A gave most growth / most duckweed or more than others allow faster / fastest / better / best growth allow more growth with nitrate / less growth without nitrate do not allow ‘no’ growth without nitrate
(c) (i) mark (c) as a whole
Page 42
sensible method: e.g. mass / weighing ignore dry or fresh allow other sensible method involving measuring eg length of roots – ignore ‘size’ of roots or measure roots unqualified
1
(ii) corresponding explanation: ignore accuracy e.g. includes roots / includes whole plant or leaves vary in size or (length / mass / surface area given in c(i)) is a continuous variable
1
[5]
M11.
(a) less carbon dioxide used or higher carbon dioxide (concentration) in jar do not allow no carbon dioxide used or no change in carbon dioxide
1 because less photosynthesis or light was a limiting factor do not allow no photosynthesis
1
(b) magnesium / Mg do not allow manganese / Mn allow iron / Fe ignore nitrates
1
[3]
M12.
(a) 7.15 to 7.45 am and 7.15 to 7.45 pm
both required, either order accept in 24 hr clock mode
1
Page 43
(b) (i) 11
1
(ii) 32.5 to 33 allow answer to (b)(i) + 21.5 to 22
1
(c) any two from:
• more photosynthesis than respiration
• more biomass / carbohydrate made than used allow more food made than used
• so plant able to grow / flower accept plant able to store food
2
M13.
(a) (i) increase (and then level off) and max / up to at 0.15 (%) (carbon dioxide) ignore references to oxygen concentration only ignore mention of 23
1
(ii) CO
2
is limiting at low CO
2
/ at first ignore specific numbers
1 light is limiting at high CO
2
/ at end
1
(b) mark both parts together effect: (oxygen) falls
1
Page 44
[5]
explanation: (oxygen) used for respiration
if no other marks awarded allow (effect) no change and
(explanation) no photosynthesis for 1 mark
(c) more chlorophyll / chloroplasts
1
1
1
[7] allows more photosynthesis / description for both marks must refer to more at least once
M14.
(a) any one from:
• (type of / amount of) soil / minerals / nutrients / pH
• amount of water / time of watering
• space between plants / plants and wall
• time for growth list principle ignore carbon dioxide / same number of plants / food do not allow temperature / light / exposure to wind
(b) (i) North wall
(ii) nugget list principle
(c) has not tested all varieties / nugget / champion against all walls do not allow repeat experiment
Page 45
1
1
1
1
[4]
M15.
(a) xylem and phloem either order allow words ringed in box allow mis-spelling if unambiguous
(b) (i) movement / spreading out of particles / molecules / ions / atoms ignore names of substances / ‘gases’ from high to low concentration accept down concentration gradient ignore ‘along’ / ‘across’ gradient ignore ‘with’ gradient
(ii) oxygen / water (vapour) allow O
2
/ O2 ignore O
2
/ O allow H
2
O / H2O ignore H
2
O
M16.
(a) + light = + photosynthesis
+ light = + photosynthesis to a limit limit depends on temp/CO
2
levels
+ CO
2
= + photosynthesis
+ temp = + photosynthesis each for 1 mark
(b) need to raise optimum levels when one other raised
Page 46
5
1
1
1
1
[4]
to get max/economic yield each for 1 mark
2
[7]