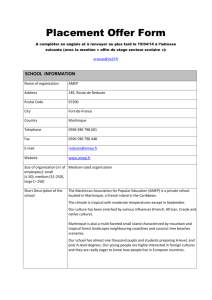
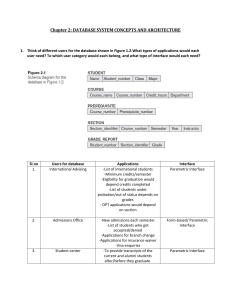
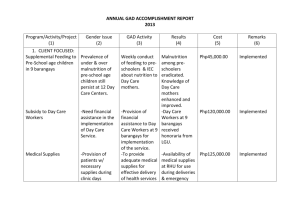
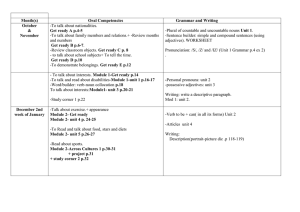
TYPES OF ECONOMIES
advertisement

TYPES OF ECONOMIES WHO AND WHY? Who makes economic decisions? Who owns resources? Who provides goods and services? Why? Either ... or ... FREE MARKET ECONOMY WHO makes economic decisions? WHY? COMMAND ECONOMY (PLANNED ECONOMY) Either ... or ... FREE MARKET ECONOMY COMMAND ECONOMY (PLANNED ECONOMY) WHO makes economic decisions The market: -supply and demand -sellers-buyers -producers – consumers The state WHY? -to allow competition and thus make the economy more efficient ↓ -to provide better quality products at lower costs -to redistribute wealth in the country more fairly -to care for public needs Group the following expressions: government interference privately-owned companies market mechanism market reliance state-owned companies central planners laissez-faire government-run business central planning system privately-run companies government intervention USSR PLANNED E. government interference state-owned companies central planning government intervention USSR vs. MARKET E. market mechanism market reliance privately-owned companies privately-run companies laissez-faire ... or both... FREE MARKET ECONOMY (FREE ENTERPRISE ECONOMY) WHO The market: makes -supply and economic demand decisions COMMAND ECONOMY (PLANNED ECONOMY) MIXED ECONOMY The state Both the market and the state -to redistribute wealth in the country more fairly -to care for public needs To benefit from both economic systems -sellers-buyers -producers – consumers WHY -to allow competition and make the economy more efficient -to provide better quality products at lower costs Identify the advantages and disadvantages of the market economy as opposed to the command economy (R: p.13). - Assignment FREE MARKET ECONOMY advantages disadvantages COMMAND ECONOMY (PLANNED ECONOMY) “The market has a keen ear for private wants, and a deaf ear for public needs.” (R. Heilbroner) MIXED ECONOMY PUBLIC SECTOR VS. PRIVATE SECTOR Who provides goods and services? Why? (What is their interest?) What do the two sectors consist of? WHO AND WHY? PUBLIC SECTOR The government, local authorities (e.g. municipalities, counties) Care for socially important issues of public interest (e.g. protecting environment, consumers, education) Less profitable and unprofitable businesses VS. PRIVATE SECTOR Private owners Making a profit Profitable businesses WHAT DOES IT CONSIST OF? PUBLIC SECTOR State services: e.g. education, defence, social welfare, public safety, utilities Government-owned industries: e.g. public corporations* (e.g. electricity company) Municipal enterprises: local government, e.g. bus company VS. PRIVATE SECTOR Privately-owned companies The division is not always so clear ... PRIVATE S.→PUBLIC S. →PRIVATE S. → ?... nationalisation denationalisation privatisation ... and there may be cases of cooperation .... PPP nationalisation vs. privatisation Are the following arguments in favour of nationalisation or privatisation? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. The sale of an industry raises money for the government. Competition makes an industry more efficient. It is socially right. These companies are more likely to innovate and develop desirable products than these owned by … . The government has a better control of the economy. Consumers are offered more choice and better quality. An industry is more efficiently managed by that sector. What is privatization, anyway? (Read the text, find answers - R:p.24) in the broadest sense contractor seek though leap state enterprise issue vouchers general public auctions public stock offering contradictory goals raise money attract layoffs proponents argue Homework: 1. R: p.27a) fill in b)heading for each pg. 2. MK:pp.129 and 130 Compare the two texts The Role of Government: Galbraith vs.Friedman Make clearly structured notes based on the two texts. (Use graphics to show the structure:e.g., bullet points, vs., etc., …)-Wed group: TO BE SUBMITTED IN CLASS (HANDWRITTEN) Free market economy or state intervention in times of crisis (1)? “Ten short days saw the nationalisation, failure or rescue of what was once the world’s biggest insurer, two of the world’s biggest investment banks, and two giants of America’s mortgage markets” “The bankruptcy of Lehman Brothers and the sale of Merrill Lynch to Bank of America” “government rescue of American International Group (AIG)” The Economist, 20 Sept 2008 Free market economy or state intervention in times of crisis (2)? “Regulation is necessary and much must now be done to improve the laws of finance”: better oversight more transparency supervision of giants accounting that values risk better safer financial transactions (derivatives) The Economist, 20 Sept 2008