Lecture
advertisement

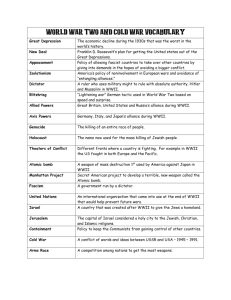
Origins of the Cold War IB History: The Cold War About the Unit... • • In the unit we will explore various aspects of the Cold War which was a global political and economic conflict between the United States and the Soviet Union (USSR) that lasted from Topics • • • • • • Nature of the Cold War Origins of the Cold War (How it began?) The First Cold War Fluctuating Relations From Detente to Second Cold War End of the Cold War Distrust to Cooperation • • • Distrust between Capitalist and Communist countries had been present since the Soviet Union was founded during WWI, but those differences were not a priority in the face of Hitler’s Germany during WWII. Distrust between the capitalist “West” and the Soviet Union existed since the Bolshevik Revolution (the revolution that founded by the Soviet Union) in 1917, especially because they had very different views of the world economically and politically. When Hitler’s Germany invaded the Soviet Union during WWII in 1941 the distrust and differences had to be put aside. Both the United States and Soviet Union cooperated in the “Grand Alliance” (USA, USSR, UK, and France) against Hitler’s Germany. Art depicting the Bolshevik or “October” Revolution through which the Soviet Union was founded. Leaders of the “Grand Alliance” against Hitler, From left: Winston Churchill (UK), Harry Truman (USA), and Josef Stalin (USSR) Map of Hitler’s Invasion of the Soviet Union Return to Distrust and beginning of Disagreement • As the end of WWII neared signs of tension emerged over strategy to end the war, how to deal with Germany following the war, and the use of nuclear weapons against Japan. • • • Signs of a strained relationship emerged at a conference in Tehran, Iran in 1943 where Stalin (USSR) pressured the USA to do more to end the WWII, and disagreed with the USA and UK on plans for Germany and Poland after the war. The differences grew in 1945 during the closing stages of WWII where the USA, UK, and USSR could not cooperate and chose to partition areas of post-war Germany into zones of occupation and Europe into spheres of influence at the Yalta and Potsdam Conferences. Finally, as the WWII drew to a close the USA became concerned with the USSR’s dominating influence in Eastern Europe and the USSR became concerned when the USA used nuclear weapons on Japan and refused to share the technology with them. Map of planned occupation of Germany by USA, UK, France, and USSR as decided by negotiations at Potsdam Conference in 1945. Images of nuclear weapons used Political cartoon depicting the by the USA against Japan during planned spheres of influence in WWII in 1945. The USA refused to Europe and Asia as decided by share nuclear weapon technology negotiations at Yalta with the USSR. Conference in 1945. Summary • • Distrust between Capitalist and Communist countries had been present since the Soviet Union was founded during WWI, but those differences were not a priority in the face of Hitler’s Germany during WWII. As the end of WWII neared signs of tension emerged over strategy to end the war, how to deal with Germany following the war, and the use of nuclear weapons against Japan.