The Third Estate
advertisement

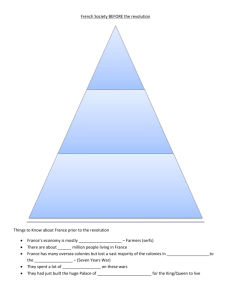
Understanding Influences • For this activity, you will work with a group and analyze a section of the Declaration of Independence. • Your group will need to put the excerpt into your own words. • Your group will also need to determine what documents or philosophes influenced the ideas included in your assigned section. Thoughts on the Declaration of Independence • What was the worst thing the king required of or did to the colonists? Why? • Do you think the British acts warranted rebellion? • Will these events influence the French Revolution? Why? The French Revolution King Louis XVI & Queen Marie Antoinette • Lived at Versailles • Very wealthy • Absolute power The Nobility & Clergy • Also very wealthy • Enjoyed special privileges from the King • Clergy paid no taxes The Rest of France: Commoners • Many in France lived in poverty • There was a small middle class, but they did not have any power • The commoners in France paid high taxes and struggled in hard times The Estates General • An historical group that represented the three main groups in French society • The three groups were: – First Estate (representing the clergy) – Second Estate (representing nobles) – Third Estate (representing commoners/the majority of France) • Called together by the King at the urging of his financial minister Jacques Necker The Estates General • One vote per estate • Clergy and nobility usually joined together to out-vote the Third Estate • Met in Versailles in May 1789 • Voting controversy A meeting of the Estates General The Estates General are divided • First and Second Estate want to keep their privileges, pay no taxes, and have the Third Estate pay more • The Third Estate wants taxes to be more evenly distributed among all French citizens, meaning all the estates would have to pay taxes How would you vote? Do you think the vote should be taken by estate or by person? Vote by Estate Vote by Person The King decides... • Clergy and nobility enjoy many privileges; King Louis XVI is a devout Catholic and he does not want to anger the nobility • King Louis decides to vote on the proposals by estate, rather than by person • Third estate creates the National Assembly to vote on matters independently. • King Louis locks them out of the meeting hall The Tennis Court Oath “I swear an oath to God and nation never to be separated until we have formed a solid and equitable Constitution as our constituents have asked us to.” The National Assembly is born • The result of the Tennis Court Oath is the creation of a Constitutional Monarchy • The King must now rule with the new National Assembly, a group that represents all of France. (Louis reversed his previous position) • However, King Louis XVI still has the power to veto any proposed law France is starving Despite the creation of a new government, the financial situation in France gets worse: •Bread prices skyrocket •Nobles begin to flee France as commoners begin to grow restless •The public begins to distrust the King more and more Storming of the Bastille • Rioting in Paris in early July • Firing of Finance Minister Necker (who supported the people) • July 14th: a mob storms and takes the Bastille • French soldiers refuse to stop the attack The Great Fear • Rebellion spreads • Peasants destroy the countryside • End of feudal privileges The Declaration of the Rights of Man and Citizen • Adopted by National Assembly on August 27th, 1789 • Enlightenment ideals • Outlined basic freedoms held by all • Asserted the sovereignty of the people • “Liberté, Egalité, Fraternité” The March of Women • Lower classes still unsatisfied • Thousands of starving women and peasants march on Versailles • Louis forced to return to Paris Civil Constitution of the Clergy Cartoon depicting the confiscation of Church lands • Financial crisis • National Assembly confiscates and sells off church lands • Church also secularized, reorganized • Clergy oath of loyalty Flight of the King • Émigrés • Louis XVI and his family attempted to flee France • They were arrested at Varennes The capture of Louis XVI at Varennes Reaction from Other Countries • Declaration of Pillnitz • Possible foreign intervention Illustration depicting Prussian King Frederick William III, Austrian Emperor Leopold II, and the Comte d’Artois, Louis XVI’s brother New Constitution • Constitutional monarchy • New Legislative Assembly • Sans-culottes Painting depicting the 1791 constitution War With Austria • France declares war • War of the First Coalition • Levee en masse Painting of the Battle of Valmy, 1792 The Radicals Take Over • Paris mob stormed Tuileries • Louis and family seek aid of Legislative Assembly • Arrested and deposed Paris crowds storm the Tuileries The National Convention • First met on September 21, 1792 • Revolutionary Calendar • Monarchy abolished; France officially becomes a republic • Factions: Jacobins vs. Girondins A Jacobin club Robespierre • Lawyer • Radical Jacobin • Most controversial figure of the French Revolution The unfortunate fate of Louis XVI and his family The Committee of Public Safety • Created to cease an internal rebellion in 1793 • Given dictatorial power • Ruled France for nearly a year A citizen petitions the Committee of Public Safety The Reign of Terror • July 1793– July 1794 • Executions • Death of Robespierre The execution of Marie Antoinette But peace and democracy don’t follow… • Reign of Terror: Over 40,000 people are guillotined for “acting against the revolution” • The Reign of Terror is led by Maximilien Robespierre • He is eventually guillotined as well The Thermidorean Reaction • Robespierre overthrown on 9 Thermidor • Committee of Public Safety dismantled • Jacobin clubs disbanded • New constitution adopted in August 1795 • Executive branch known as the Directory 9 Thermidor meeting of the National Convention The Directory • 1794 - 1799 • Promoted middle class interests • Financial crisis • Food shortages • Riots in Paris • Rise of Napoleon Cartoon depicting the errors and bad judgment of the Directory And then… • A general named Napoleon Bonaparte comes to power • He builds France’s army and conquers much of Europe • He crowns himself emperor in 1802 Legacies of the French Revolution • End of absolutism • Power of nobles ended • Peasants became landowners • Enlightenment ideals • Nationalism