1 - WLWV Staff Blogs
advertisement

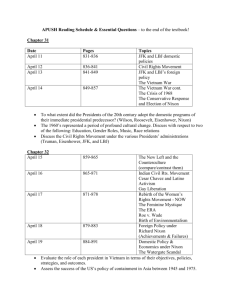
Homework Sheet Unit 16: Political Changes in America During the Cold War – 60’s, 70’s, and 80’s Date Class Activities Homework Due In Class Today Mon Kennedy Chapter 41 Part 1: 936-946 4/08 Split Doc 3 Documents 1,4 and 7 Tues Johnson and the 60’s 4/09 Presentations of Doc 3 Block 4/10 Mon 4/15 Tues Nixon, Ford, and the End of Vietnam Chapter 41 Part 2: 947-962 Documents 2,3, and 5 My part of Doc 3 is:_______ Chapter 42 Part 1: 964-980 Chapter 42 Part 2 and Chapter 43 Part 1: Carter + the Conservative Revolution 980-996 Documents 6 and 9 Reagan, Bush I, and the End of the Cold War Chapter 43 Part 2: 996-1009 Document 8 4/16 Block Go over old tests Work on your review!!! 4/17 DBQ Practice Bring DBQ supplies Friday 4/19 Unit 15 + 16 Test Receive Unit 17 HW Unit 15 + 16 Review Sources Used this Unit: Pageant (Your Textbook): Kennedy, David M., Lizabeth Cohen, and Thomas A. Bailey. The American Pageant: A History of the Republic. Boston: McDougal Littell/Houghton Mifflin. 11th Edition. Unit 16: Political Changes in America During the Cold War – 60’s, 70’s, and 80’s Content Covered Politics and Foreign Policy of the “Stormy Sixties”: The New Frontier; Berlin Wall; flexible response; Vietnam; Bay of Pigs; Cuban Missile Crisis; Kennedy assassinated; Johnson; War on Poverty; Great Society; Election of 1964; DOT, HUD, and NEA; Medicare and Medicaid; Immigration and Nationality Act of 1965; Dominican Republic; Operation Rolling Thunder in Vietnam; escalation in Vietnam; Trouble in the Middle East – 6 Day War; Anti-War Demonstrations; Tet Offensive; Summer of 1968; Election of 1968 and Nixon; Effects of LBJ; Vietnamization; Cambodia Politics and Foreign Policy in the “Stalemated Seventies”: Détente with China and Moscow; Changes on the Court; Philadelphia Plan; EPA and OSHA; Nixon in 1972; “Peace” in Vietnam; Watergate; War Powers Act; Impeachment and Resignation; Ford; Fall of Saigon; 1976 and Carter; Camp David Accord of 1978; China; SALT II; Iranian Hostage Crisis; Soviet Invasion of Afghanistan; Politics and Foreign Policy in the Conservative Eighties: Conservative Revolution of 1980; Judicial Attacks on Desegregation and Affirmative Action; Election of Reagan; Cutting Social Services and Taxes; Refueling the Cold War; Star Wars; Nicaragua; Election of 1984 and a Woman VP for Mondale!; Libya; Iran-Contra Fiasco; Democratic win in 1986; 1988 and Bush I; Tiananmen Square; Fall of the Soviet Union and the Cold War Economics: Kennedy’s attempts to revitalize the economy; Trade Expansion Act of 1962; Stagnation in the 1970’s; Oil Embargo and Energy Crisis; Federal Deficit; Reaganomics; Supply-Side; Economic Resurgence in the 80’s or income gap?; Economic Effects of Reagan; Black Monday; Civil Rights: Freedom Riders; Ole Miss; Birmingham; March on Washington; Civil Rights Act of 1964; EEOC; affirmative action; Voting Rights Act of 1965; 24th Amendment; Selma; Change from nonviolence to Black Power; Watts; Malcolm X; Black Panther Party; MLK shot; dejure and defacto segregation; Social Change: Cultural Consequences of the Struggles of the 1960’s; Free Speech Movement; Sexual Revolution; Roe v. Wade; Silent Spring; Yuppies; Primary Reading American Pageant; Chapters 41-42 &43 through page 1009 Secondary Reading Civil Rights: 1. Mississippi Freedom Summer: Student Workers – Section 34 AF V2 2. The Young Lords: Pablo Guzman – Section 35 AF V2 3. The Black Revolution Erupts – Documents 42-C-1,2,3,4,&5 (497-517) - split Social and Political Change: 4. Michael Harrington Discovers Another America (1962) – Document 42-B-1 TAS V2 (490-494) 5. Students for Democratic Society Issues A Manifesto (1962) – Document 42-E-1 (531-533) 6. Editor Irving Kristol Defines Neoconservatism (1983) – Document 44-D-1 (629-632) 7. Rachel Carson: Silent Spring (1962) Economics: 8. The Supply-Side Gospel (1984) – Document 44-A-1 TAS V2 (586-588) Crises: 9. An American Hostage in Tehran: Barry Rosen – Section 36 AF V2 Chapter 41: The Stormy Sixties, 196-1968 I. Identify and state the historical significance of the following: 1. 2. 3. 4. Robert S. McNamara Martin Luther King, Jr. Barry Goldwater Malcolm X II. Define and state the historical significance of the following: 9. flexible response III. Describe and state the historical significance of the following: 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. New Frontier Viet Cong Bay of Pigs War on Poverty Great Society Tonkin Gulf Resolution Civil Rights Act of 1964 Cuban missile crisis IV. Essay Questions: 26. What success and failures did Kennedy’s New Frontier experienced at home and abroad? 5. 6. 7. 8. 10. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. Stokely Carmichael Eugene McCarthy Hubert H. Humphrey George Wallace peaceful coexistence nuclear test-ban treaty Twenty-fourth amendment Voting Rights Act Operation Rolling Thunder Pueblo Incident Tet offensive counterculture 27. How did the civil rights movement progress from difficult beginnings to great success in 1964-1965 and then encounter increasing opposition from both black militants ad “white backlash” after 1965? 28. What were Johnson’s major domestic achievements, and why did they come to be overshadowed? 29. Why did the Vietnam War, and the domestic opposition to it, come to dominate American politics in the late 1960s? 30. How was the cultural upheaval of the 1960s related to the political and social changes of the decade? Is the “youth rebellion” best seen as a response to immediate events, or as a consequence of such longer-term forces as the population bulge and economic prosperity? What were the long-term results of the counterculture in all its varieties? Chapter 42: The Stalemated Seventies, 1968-1980 I. Identify and state the historical significance of the following: 1. 2. 3. Henry Kissinger Earl Warren Warren Burger II. Define and state the historical significance of the following: 6. détente III. Describe and state the historical significance of the following: 9. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. Vietnamization Nixon doctrine My Lai massacre Cambodian incursion Kent State killings Twenty-sixth amendment Pentagon Papers ABM treaty SALT IV. Essay Questions: 4. 5. 7. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. George McGovern shah of Iran executive privilege southern strategy Watergate scandal CREEP Saturday Night Massacre War Powers Act energy crisis Helsinki accords OPEC Iranian hostage crisis 26. What policies did Nixon pursue with Vietnam, the Soviet Union, and China, and what were the consequences of those policies? 27. In what ways did Nixon’s domestic policies appeal to Americans’ racial and economic fears, and in what ways did he positively address problems like inflation, discrimination, and pollution? 28. How did Nixon fall from the political heights of 1972 to his forced resignation in 1974? What were the political consequences of Watergate? 29. How did the administration of the 1970s attempt to cope with the interrelated problems of energy, economics, and the Middle East? 30. Why can the 1970s be characterized as a “decade of stalemate”? What caused the apparent inability of the federal government to cope with the new problems of the time? Chapter 43: The Resurgence of Conservatism, 1980-1996 IV. I. Identify and state the historical significance of the following: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Jimmy Carter Edward Kennedy Ronald Reagan John Anderson Walter Mondale Gary Hart Jesse Jackson II. Define and state the historical significance of the following: 14. 15. “supply side” economics affirmative action III. Describe and state the historical significance of the following: 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. NAFTA Moral Majority Chappaquiddick Reaganomics Solidarity 10. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 16. 22. 23. 24. 25. Geraldine Ferraro Sandra Day O’Connor Mikhail Gorbachev H. Ross Perot Newt Gingrich Clarence Thomas reverse discrimination Grenada invasion Strategic Defense Initiative Roe v. Wade boll weevils Essay Questions: 26. What caused the rise of Reagan and the “new right” in the eighties, and how did their conservative movement affect American politics? 27. What were the goals of Reagan’s “supply-side” economic policies, and what were their short-term and long-term effects? 28. What led to the revival of the Cold War in the early 1980s and to its decline and disappearance by 1991? 29. What were the successes and failures of George H.W. Bush’s administration? Was Bill Clinton’s election a positive mandate for change, or was it primarily a repudiation of the Bush record? 30. How did the antigovernment mood of the late 1990s affect both Bill Clinton and his Republican opponents? What were its larger consequences for U.S. society?