Academy Conference 2010
Frisco, Texas
Teaching VLSM
Barry Charter ~ North Arkansas College ~ Newly Retired
Shawn Dennis ~ Arkansas State University Mt. Home Arkansas
CCNA CCAI
July 19, 2010
© 2010 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
1
Introduction
Contact Information
Barry Charter
bc_charter@yahoo.com
and
Shawn Dennis
sdennis@asumh.edu
© 2010 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
2
Importance of understanding VLSM
IPv4 address availability
CCNA exam
Further networking classes
Networking careers
What about IPv6?
© 2010 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
3
Note:
INTRODUCE IP ADDRESSING AND BINARY THE
FIRST DAY!!
Do not wait until the chapter on IP Addressing & Subnetting
(D1 = Ch 5, E1 = Ch 6) to begin discussing the basics of IP
addressing and what a subnet mask is.
Review IP Addressing and Binary daily
Practice makes perfect!!
© 2010 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
4
Binary & IP Addressing
Understanding binary is extremely important
VLSM
Wildcard masks
IP Addresses
32 bits
Dotted decimal format – 4 octets
Conversion for each octect
Practice converting IP Addresses from binary to
decimal and vice versa.
Introduce binary system to students early in first
course. I start the second day of class.
© 2010 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
5
Dividing Address Space
The “Great Divide”
Where the division occurs between host bits and network bits
The “Magic Number”
Decimal value of the bit to the immediate left of “Great Divide”
Subnets will be in increments of the “Magic Number”
Example
Subnet Mask: /27 or 255.255.255.224
The “Great Divide”
The “Magic Number”
128
64
32
16
8
4
© 2010 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
2
1
6
Subnetting vs. VLSM vs. CIDR
Subnetting
Dividing network address space into equal size subnets
VLSM – Variable Length Subnet Mask
Divide network address space into unequal size subnets
Maximize use of IP address space
CIDR – Classless Inter-domain Routing
Subnet Mask specified using the prefix size
255.255.255.0 = /24
Use of VLSM requires use of routing protocols that support
CIDR
RIPv2
EIGRP
OSPF
© 2010 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
7
Teaching Methods
Magic Box
© 2010 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
8
Magic Box Method
© 2010 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
9
What Length Subnet Mask Should You Use? –
Practice, Practice, Practice...
Number of Hosts
Required
# of Host Bits
Needed to
Support the
Required # of
Hosts
Subnet Mask
(CIDR Prefix)
Subnet Mask
(Dotted Decimal)
Number of Usable
Hosts Created
100
2
25
50
900
5
10
80
500
15
© 2010 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
10
What Length Subnet Mask Should You Use? –
Practice, Practice, Practice...
Number of Hosts
Required
# of Host Bits
Needed to
Support the
Required # of
Hosts
Subnet Mask
(CIDR Prefix)
Subnet Mask
(Dotted Decimal)
Number of Usable
Hosts Created
100
7 bits
/25
255.255.255.128
126
2
2 bits
/30
255.255.255.252
2
25
5 bits
/27
255.255.255.224
30
50
6 bits
/26
255.255.255.192
62
900
10 bits
/22
255.255.252.0
1022
5
3 bits
/29
255.255.255.248
6
10
4 bits
/28
255.255.255.240
14
80
7 bits
/25
255.255.255.128
126
500
9 bits
/23
255.255.254.0
510
15
5 bits
/27
255.255.255.224
30
© 2010 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
11
Determine Network Portion of Subnets
Start with largest LAN
Working down in LAN size to point-to-point links
Determine number of bits needed to address the hosts
Larger LANs will have smaller CIDR prefixes
/30 prefix for point-to-point links
Formula: 2n – 2
n – number of bits
2 unusable addresses
Network address – first address in subnet
Broadcast address – last address in subnet
© 2010 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
12
Teaching Method
Subnetting in a Box
© 2010 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
13
Subnetting in a Box Method
Divide a piece of paper into smaller subnets
Value in top left corner of each section – network
address
Value in bottom right corner of each section –
broadcast address
Last network address is the value of the appropriate
octet for subnet mask
As bits are borrowed the network is divided into smaller
subnets.
New subnet mask is indicated by first address of last
© 2010 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
14
Value in top left corner of each section – network address
Value in bottom right corner of each section – broadcast address
0
255
© 2010 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
15
Value in top left corner of each section – network address
Value in bottom right corner of each section – broadcast address
0
128
7 host bits /25
126 hosts
127
255
© 2010 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
16
Value in top left corner of each section – network address
Value in bottom right corner of each section – broadcast address
0
128
6 host bits /26
62 hosts
7 host bits /25
126 hosts
191
192
127
255
© 2010 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
17
Value in top left corner of each section – network address
Value in bottom right corner of each section – broadcast address
0
128
6 host
bits /26
62 hosts
7 host bits /25
126 hosts
191
192
224
4 host
bits /28
239
5 host
bits /27
240
30 hosts
248
243
251
247
255
244
127
223
© 2010 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
18
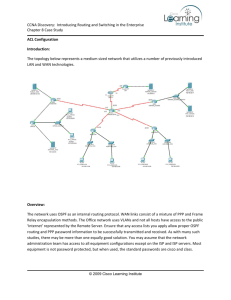
Here is an example VLSM Exercise 1
© 2010 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
19
Start with largest LAN
Working down in LAN size to point-to-point
links
Example:
list LANS in descending order
60 hosts
28 hosts
12 hosts
12 hosts
There are 3 WAN links
© 2010 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
20
Start with largest LAN
Working down in LAN size to point-to-point
links
Example:
Determine number of host bits needed
60 hosts – 6 host bits /26
28 hosts – 5 host bits /27
12 hosts – 4 host bits /28
12 hosts – 4 host bits /28
There are 3 WAN links – 2 host bits /30
© 2010 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
21
Start with the largest LAN
Working down in LAN size to point-to-point links
0
128
62 hosts
192.168.10.0 /26
63
64
60 hosts – 6 host bits /26
28 hosts – 5 host bits /27
12 hosts – 4 host bits /28
127
255
12 hosts – 4 host bits /28
There are 3 WAN links – 2 host bits /30
© 2010 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
22
Start with the largest LAN
Working down in LAN size to point-to-point links
0
128
62 hosts
192.168.10.0 /26
63
64
96
30
hosts
60 hosts – 6 host bits /26
192.168.10.64 /27
28 hosts – 5 host bits /27
12 hosts – 4 host bits /28
95
127
255
12 hosts – 4 host bits /28
There are 3 WAN links – 2 host bits /30
© 2010 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
23
Start with the largest LAN
Working down in LAN size to point-to-point links
0
128
62 hosts
192.168.10.0 /26
63
64
96
14 hosts
192.168.10.96 /28
30
hosts
60 hosts – 6 host bits /26
111
192.168.10.64 /27
112
14 hosts
28 hosts – 5 host bits /27
12 hosts – 4 host bits /28
192.168.10.112 /28
95
127
255
12 hosts – 4 host bits /28
There are 3 WAN links – 2 host bits /30
© 2010 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
24
Start with the largest LAN
Working down in LAN size to point-to-point links
0
128
136
131
132
160
139
140
62 hosts
192.168.10.0 /26
135
143
144
63
64
96
159
191
192
14 hosts
192.168.10.96 /28
30
hosts
60 hosts – 6 host bits /26
111
192.168.10.64 /27
112
14 hosts
28 hosts – 5 host bits /27
12 hosts – 4 host bits /28
192.168.10.112 /28
95
127
255
12 hosts – 4 host bits /28
There are 3 WAN links – 2 host bits /30
© 2010 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
25
Practice
Packet Tracer
Activities
Exercise 2
20 min
© 2010 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
26
Start with the largest LAN
Working down in LAN size to point-to-point links Ex 2
© 2010 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
27
Practice
Packet Tracer
Activities
Exercise 3
20 min
© 2010 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
28
Start with the largest LAN
Working down in LAN size to point-to-point links Ex 3
© 2010 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
29
Practice
Packet Tracer
Activities
Exercise 4
20 min
© 2010 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
30
Start with the largest LAN
Working down in LAN size to point-to-point links
© 2010 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
31
Teaching
Resources
© 2010 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
32
Cisco Learning Institute
© 2010 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
33
Other Resources
Presentations
http://www.cisco.com/web/learning/le31/le46/cln/clp/fastlane/Su
bnet_Calculator/index2.htm
www.learntosubnet.com
Subnet Calculators
http://www.cisco.com/cgi-bin/Support/IpSubnet/home.pl
www.solarwinds.com
www.subnet-calculator.com/cidr.php
http://www.subnetonline.com/pages/subnet-calculators/ipsubnet-calculator.php
http://www.wildpackets.com/resources/free_utilities/ipsubnetcalc
© 2010 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
34
Questions?
Thank you for attending!
DON’T FORGET TO TURN IN EVALUATION
© 2010 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
35