Curved Mirrors
advertisement

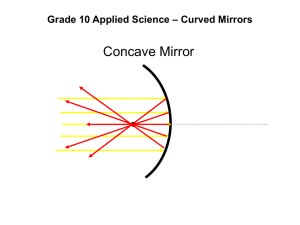
Mirrors that are not flat are called curved mirrors. Depending on whether the reflective coating is on the inside or outside of the curve will decide if it is a concave or convex type of mirror. If the mirror is coated on the inside of the curve it is called a concave mirror. Those which reflect from the outside of the curve are called convex mirrors. A curved mirror is a cut out section of a circle. In mathematics the distance from the curve to the centre of the circle is referred to as a radius (r). For the purpose of curved mirrors, the centre of the circle is called the centre of curvature (C). Any circle is an example of both a concave and convex mirror. Note the solid line is the reflected surface and the hatched side is the back of the mirror. The principal axis is a line through the centre of curvature that strikes the mirror at a 90o angle. The vertex (V) of a curved mirror is where the principal axis meets the mirror. The centre of curvature and vertex both lie along the principal axis. Half the distance between the centre of curvature (C) and mirror is called the focus or focal point (F). Therefore, if the focus (F) has a distance of 4 cm from the curved mirror, the centre of curvature(C) is 8 cm. This is why the focus is given the symbol of F and the centre of curvature is located at 2F. 1. _______ 2. _______ 5. 1. 2. 3. 3. _______ 5. 4. 4. 3. 4. _______ 2. 1. 5. _______ 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Principal Axis Vertex Focal Point (F) Centre of Curvature Focal Length To determine the location of any image in a concave mirror you need to draw at least two incident rays. The following rules will help you to draw the incident and reflected rays for objects with a concave mirror. (i) A ray of light, which is parallel to the principal axis of the concave mirror, will reflect off of the mirror and pass through the principal focus (F) C F V (ii) A ray of light passing through the centre of curvature (C) of a concave mirror will reflect back along the same path C F V (iii) A ray of light passing through the principal focus (F) of a concave mirror will reflect back parallel to the principal axis. C F V i) A ray of light, which is parallel to the principal axis of a convex mirror will reflect as if it had come from the principal focus. V F C ii) A ray of light going towards the centre of curvature(C) of a convex mirror is reflected back along the same path. V F C iii) A ray of light going towards the principal focus will reflect back parallel to the principal axis. V F C