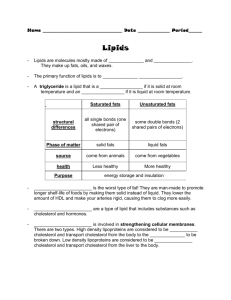
Macronutrient Q and A
advertisement

Macronutrients Question Revision Mrs Keillor Nat 5 HFT • What are the 5 main nutrients? • Proteins, Carbohydrates, Fats, Vitamins, Minerals • Explain what macro- nutrients are and identify them. • Nutrients needed by the body in relatively large amounts • Protein, Carbohydrates and Fats • Name the two main functions of protein. • Growth and repair of body cells • Maintenance of body cells •What is the secondary function of protein? •To provide energy •What are proteins made up of? •Amino Acids (some of these are essential) • Proteins can be divided into two groups, what are they? • HBV and LBV proteins • High biological value and low biological value • What is the difference between HBV proteins and LBV proteins? • HBV contain all the essential amino acids • LBV lack one or more essential amino acids •Give examples of HBV proteins. •Meat, fish, eggs milk, cheese, soy beans • Give examples of LBV proteins. • Cereals (wheat rice oats), pulses (peas lentils) , nuts • Also gelatine (animal sources) • What can happen if you do not eat enough protein? • Growth in children slowed down • Cuts and wounds take longer to heal • What can happen if you eat too much protein? • Converted to fat and lead to obesity if it is not used up as a secondary source of energy • What are the two main functions of carbohydrates in the body? • To provide energy • To provide warmth and so help maintain normal body temperature • Carbohydrates can be divided into two groups what are they? • Sugars and Starches(TCC’s) •Give examples of starchy carbohydrates (TCC’s) •Bread, pasta, cereals, potatoes • Give examples of Sugary carbohydrates. • Cakes, biscuits, sweets, chocolate, jams. Fizzy drinks • Why is it recommended that we get most of our energy from the starchy group (TCC’s)? • Starches are a good source of other nutrients • They bulk out the diet, make you feeler for longer • They do not encourage tooth decay • Starches are also a good source of NSP. What is NSP? • Non starch polysaccharide also known as fibre • What can happen if you eat too much carbohydrate? • Can be converted to fat in the body and can lead to obesity • Too much sugar can lead to diabetes or tooth decay • What can happen if you don’t have enough carbohydrate? • Lack of energy leading to tiredness • Protein may be used as a source of energy instead of its main function for growth and repair • What is the difference between intrinsic and extrinsic sugars? • Intrinsic are naturally occurring sugars in food e.g fruit • Extrinsic are sugars added to food known as NMES (non-milk extrinsic sugars) • What are the 5 functions of fat? • To provide warmth • To provide energy • To provide essential fatty acids • To provide fat-soluble vitamins ADEK • To surround and protect the organs • What are the two main types of fats? • Saturated and Unsaturated • Give examples of saturated fats. • Meat and meat products • Fats e.g. butter • Milk and dairy products- cream, cheese • Give examples of unsaturated fats. • Olive Oil, rape seed oil, avocados, nuts and seeds, vegetable oil • What does LDL and HDL cholesterol stand for and which one is the good/bad cholesterol. • Low density lipoprotein (Bad) • High-density lipoprotein (Good) • What effect do saturated fats have on cholesterol? • High level saturated fats raise blood cholesterol especially LDL. • This sticks to arteries leading to blood clots and blockages of artery • What effect do unsaturated fats have on cholesterol? • Help lower LDL cholesterol • Slightly increase HDL cholesterol • This cholesterol helps ferry the cholesterol away from the arteries to the liver where is broken down into bile • What are essential fatty acids? • Necessary fats that humans cannot make. They must be obtained through the diet • What is the main essential fatty acid? • Omega 3 fatty acids • What is omega 3 fatty acids needed for in children? • For brain development in babies and young children's • What does omega 3 fatty acids help reduce in adults? • The risk of blood clots, heart attacks and rheumatoid arthritis • What happens if you have too much fat? • Can lead to obesity • Can lead to high blood pressure and CHD • What happens if you don’t have enough fat? • The intake of essential fatty acids such as omega 3 fatty acids may be reduced • Fat soluble vitamins may be reduced • What are trans -fatty acids or hydrogenated fats? • Polyunsaturated fats which have been artificially hardened by adding extra hydrogen • What can they increase the risk of? • Heart disease, rheumatoid arthritis and some cancers • Where are they found? • Hard margarine, biscuits, cakes, commercially fried foods • What are the effects of storage on fats? • Exposure to air causes fats to deteriorate and become rancid • Fats become rancid due to oxidation- oxygen is absorbed by the fat molecules and reacts to produce an unpleasant flavour and colour • Oxidation is accelerated by light and any impurities in fat • What are the effects of preparation on fats? • High concentration of fat is difficult to digest. Is easier to digest when surface of food is broken down e.g. grated cheese • Combine a starchy food with the fatty food will make it easier to digest e.g. macaroni cheese • What is the effect of cooking on protein? • Protein COAGULATE or set when heated e.g. egg whites set • protein in milk forms a skin • Protein in meat shrinks • Heating the protein in wheat(gluten) helps bread to hold its structure • What is the effect of cooking on fats? • Solid fats melt to liquid • If oil continues to be heated a blue haze will be given off and the fat will ignite • When fat reaches smoking point, it will go rancid and smell • What is the effect of dry heat on starches? • Dextrin is formed. Known as dextrinisation. Gives baked items a brown colour. Overheating causes charring and burning. • What is the effect of moist heat on starch? • Starch grains soften and swell. They then absorb the moisture which causes the grain to rupture. This releases starch • What is the effect of dry heat on sugar? • Sugar melts the caramelises, going brown then burning • The caramelisation of the sugar forms a golden crust on bakes items • What is the effect of moist heat on sugar? • Sugar dissolves and becomes a syrup which caramelises then chars when the water has evaporated