DNA PPT
advertisement

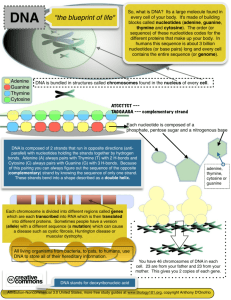
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) What is DNA? DNA is an encoded molecule that determines traits by giving instructions to make proteins. Discovery of DNA Structure • 1953 – James Watson and Francis Crick (Nobel Prize) • Rosalind Franklin Structure of DNA • Very long molecule Structure of DNA • Made of nucleotides – Each nucleotide: • Sugar (deoxyribose) • Phosphate group (negatively charged) • Nitrogen base adenine (A) guanine (G) cytosine (C) thymine (T) Structure of DNA • Double helix – 2 strands connected like a ladder and twisted Structure of DNA • Base pairing rules – In DNA … • Adenine (A) always pairs with thymine (T) • Cytosine (C) always pairs with guanine (G) Calculating % of Bases • If you know % of one base, you can calculate the rest. – Example: % of adenine = 34% – Because A & T pair up, # adenine = # thymine – So, thymine = 34% – So, adenine and thymine make up 68% (34 + 34) – So, cytosine and guanine together make up 32% (100 – 68) – Because C & G pair up, just divide 32 by 2. – So, cytosine = 16% and guanine = 16%. Importance of Base Sequences • Sequence = order of bases • Sequence of bases determines the proteins made by the cell • We can also use sequence to determine: – How closely 2 organisms are related – If 2 people are related (paternity) – If crime scene DNA matches suspect’s DNA