File
advertisement

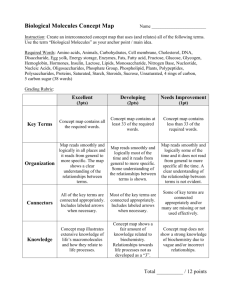
Parenteral Calculations Practice… Matching 1.1 Order : Cleocin (clindamycin) 0.3 g IM q6h Vial labeled 300 mg/2 ml. 1.2 Order : Vitamin B12 1.5 mg IM daily Vial labeled 1000 mcg/mL. A. 1.5 mL 1.3 Order: Heparin 6000 units subcut q12h Vial labeled 10,000 U/units/mL. B. 1.2 mL C. 2 mL 1.4 Order: Benadryl (diphenhydramine) 25 mg IM q4h prn Vial labeled 50 mg/2 mL. 1.5 Order: Nubain (nalbuphine) HCL 12 mg IM Vial labeled 10 mg/mL. D. 1 mL E. 0.6 mL The patient is admitted to the hospital in severe congestive heart failure. The physician orders Lasix 80 mg IV push stat followed by 30 mg po b.i.d. The label reads 40 mg in 4 milliliters. How many grams of Lasix will you administer? A. 0.8 g B. 0.08 g C. 1.2 g D. 0.4 g Morphine sulfate 8 mg subcut daily. The label reads 10 mg / 2.5 mL. How many milliliters will you prepare? A. 1/4 mL B. 1.5 mL C. 2 mL D. 1 mL The estrogen, DES, has been prescribed for a patient; 0.5 g IV once a week. The label reads 50 mg/mL. How many milliliters will you administer to the patient? A. 0.5 mL B. 7.5 mL C. 25 mL D. 10 mL The physician has written an order for Vit B12 200 mcg IM stat. The label on the vial reads 1 mg = 1 mL. How many milliliters of the Vit B12 will you administer to the patient? A. 4 mL B. 0.4 mL C. 0.2 mL D. 2 mL Esmolol, a beta adrenergic blocker, has been prescribed, 175 mg IV. The vial reads 250 mg = 10 mL. How many milliliters will you prepare for this patient? A. 5 mL B. 6 mL C. 8 mL D. 7 mL If an ampule of digoxin, a cardiac stimulant, is labeled 250 mcg = 10 mL, how many milligrams are in 1 mL? A. 2.5 mg B. 0.25 mg C. 0.025 mg D. 0.0025 mg The prescriber ordered 0.1 mg of digoxin I.M stat. The ampule reads 0.5 mg = 2 mL. How many mL will you prepare? A. 0.2 mL B. 0.4 mL C. 0.6 mL D. 0.8 mL The medication order is for 5 milligrams per kilogram of ritonavir (Norvir). Read the label in the figure above, and determine how many milliliters are contained in this dose if the patient weighs 48 kilograms? mL The order is for K-Lor 60 mEq po stat. Read the label in the figure, and determine the number of packets you would need. _____packets Case Study • A patient was admitted to the hospital with a diagnosis of type II diabetes Mellitus, congestive heart failure, hypertension, and a urinary tract infection. • Her vital signs are as follows: BP, 168/102; P, 92; R, 30; T, 101F. The patient responded well to her treatment and was discharged with the following orders: Visiting nurse qd x 3 with follow-up NPH insulin 44 units ac breakfast daily subcut Blood glucose levels q6h Diabenese 0.2 g b.i.d. po Doxazosin 0.004 g daily hs po Lasix 60 mg po daily K-Lor 30 mEq po daily Vistaril 20 mg po IM hs daily prn Antivert 0.025 g po q4h prn for nausea Zoloft 0.1 g daily po 1.) Lasix is supplied in 20, 40, and 80 mg tablets. Which strength tablets and how many would you administer to the patient? 2.) You have K-Lor tablets 10 mEq each. How many of these tablets equal the prescribed dose? 3.) How many tablets of Diabinese will you prepare for this patient if one tablet contains 100 mg? 4.) How many tablets of Doxazosin will you give to the patient if each tablet contains 2 mg? 5.) Calculate the number of milliliters that equals the prescribed dose of Vistaril if the label reads, 25 mg per mL.