Density
advertisement

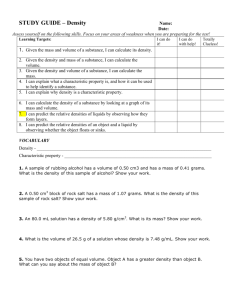
Density • Is a physical property of matter • Every pure substance has its own density • Is important for the identification of a sample of matter • Is an intensive property of matter Density • Density can be described as the concentration of mass in an area of space OR is described as the mass of a given substance per unit volume • The more concentrated the mass is in an object, the greater is its density. Density • Since Density is defined as mass per unit volume. • The relationship can be written mathematically as: mass density = volume units: solids [ g / cm3 ] liquids[ g / mL] gases [ g / L] OR m d = v Comparison of Densities Each cube represents a volume of 1.00 cm3. The mass of each sample increases while the volume remains constant. Determining the Volume • In order to figure the density we need to determine the volume: • For regularly shaped objects we use direct measurement: • Block I • Mass = 79.4 grams • Volume=29.8 cubic cm. • D = 79.4 g ÷ 29.8 cm3 = 2.66443 = 2.66 g/ cm3 • Block II • Mass= 25.4 grams • Volume=29.8 cubic cm • D = 25.4 g ÷ 29.8 cm3 = .85235 = .852 g/ cm3 Which block is more dense? • • • • • Cylinder 1 Radius = 3.5cm Length = 7.25 cm Mass = 32.3 g What is the volume? V = π X radius2 X height π = 3.14 What is the density? Sphere • Diameter = 7.0cm • Radius = 3.5cm • Mass = 32.3 g • What is the volume? V = 4/3 π X radius3 π = 3.14 What is the density? Determining Volume for an Irregular object • Done by displacement • We did this in the Scientific Measurement lab earlier in the quarter. Question for you- Why does ice float? • Solid H2O (ice) is less dense than liquid H2O (water). • Rivers never become completely frozen because as soon as water freezes, it floats up to the surface. • Fish live in the unfrozen, denser liquid water below the layer of ice. • Example: Calculate the volume of a 100. g ice cube with a density of 0.92 g /mL. • Solution: The density translated as a conversion factor is: 0.92 g = 1 mL 100. g x 1.0 mL = 108.7 mL = 110 mL 0.92 g • Comparison of: Liquid water Mass = 100 g Volume = 100 mL Density = 1.0 g/mL Ice Mass = 100 g Volume = 110 mL Density = 0.92 g/mL Density • Can also be used as a means of separating components of matter • Ex: if 2 solids of a different density are mixed together, the solid with the greater density will gravitate to the bottom • When a solid object is placed in a liquid that has a great density, the solid object will float. Density Gradient THE DENSITY CONCEPT • The picture illustrates a density gradient. • Each item (solid or liquid) is arranged in the cylinder according to its density. • The samples are arranged with the greater densities toward the bottom and the lowest density on the top. The Concept of Density for Liquids and Solids Which kind of matter is more dense? Density - Review • The concentration of mass in an area of space OR • The mass of a given substance per unit volume • The more concentrated the mass is in an object, the greater is its density. mass density = volume