Development
advertisement

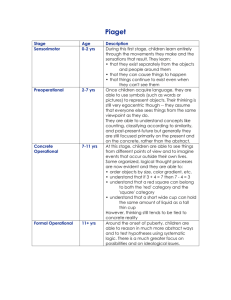
Development QuickTime™ and a Photo - JPEG decompressor are needed to see this picture. Great Debates Nature vs. Nurture Discontinuity (“steps”) vs. Continuity (“waves”) Cross-Sectional vs. Longitudinal Designs How do we study babies? We use what they can do, such as . . . Sucking Looking Habituation Language Development Babbling Single Words Overgeneralization Word / Naming Explosion Grammar Errors tell us children are paying attention “Went” -> “Goed” -> “Went” Cognitive Development Jean Piaget (1896 - 1980) Studied cognitive development by looking at the errors (his own) children made Theorized distinct, discontinuous stages of development Schemes - Mental Representations Assimilation Accommodation Sensorimotor Stage Move from reflexes to problem solving, discover object permanence Six Substages: Reflex Primary Circular Reactions Secondary Circular Reactions Coordination of Secondary Schemes Tertiary Circular Reactions Symbolic Thought / Insight Preoperational Stage Thinking is intuitive, inflexible, based on appearances Characterized by several errors "A-not-B" Error Egocentrism Centration Special guest demo . . . Concrete and Formal Operations Concrete Operations The child can deal with concrete, perceptually visible objects, conservation mastered Formal Operations The child masters abstract thinking and logic Criticisms and Re-evaluations Case study method Strict stage view Phrasing of questions Operationalizations Cultural variations Evidence that these transitions happen much sooner than Piaget thought Gender and Stereotyping “Welcome him with fresh flowers & love. Rambunctious yellows, creams, blues and pinks, for a soon-to-be rambunctious baby boy.” ($41.99) “Flowers as pink and delicate as baby's cheeks. It's a girl! And she's pink and pretty and peaceful, like this perfect bouquet in a glass vase.” ($48.99) (actual quotes and prices from FTD.com) Culture and Child-Rearing Great variability in Sleeping arrangements Amount of movement allowed Beliefs about independence vs. interdependence Aging Quiz n n n n n 1. At least one tenth of the aged are living in longstay institutions such as nursing homes and hospitals 2. Old people usually take longer to learn something new 3. A person’s height tends to decline in old age 4. As women enter the workforce in greater numbers, the gender difference in life expectancy is getting smaller 5. More than 20% of older people are senile Aging Quiz n n n n n 6. Older people are seldom bored 7. The majority of old people are socially isolated and lonely 8. The elderly are more fearful of crime than people under 65. 9. Older people are more politically conservative than younger people 10. People are happiest in their 20’s, and happiness decreases with age It gets better from here . . .