World War II Begins
advertisement

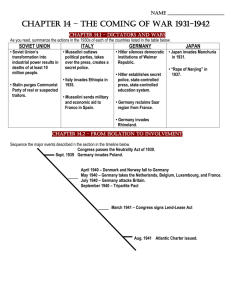
World War II Lesson 1: The Rise of Dictators Germans bitter- Treaty of Versaillesexpected Germany to pay for damages caused by World War I Worldwide depression (and Great Depression) affected countries around the world. Many Germans blamed other European nations and German Jews for their hardships. Didn’t have enough money to do this Adolf Hitler, leader of Germany during the 20’s, said Germany had been treated unfairly. What do you think? Worldwide Depression Countries short of supplies Still trying to recover from World War I Economic hard times worldwide Discuss reasons for the above facts with a partner. Georgia Performance Standards SS5H6 The student will explain the reasons for America’s involvement in World War II. a. Describe Germany’s aggression in Europe and Japan’s aggression in Asia. b. Describe major events in the war in both Europe and the Pacific; include Pearl Harbor, Iwo Jima, D-Day, VE and VJ Days, and the Holocaust. c. Discuss President Truman’s decision to drop the atomic bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki. d. Identify Roosevelt, Stalin, Churchill, Hirohito, Truman, Mussolini, and Hitler. e. Describe the effects of rationing and the changing role of women and African- Americans; include “Rosie the Riveter” and the Tuskegee Airmen. f. Explain the U.S. role in the formation of the United Nations. Other factors leading to WWII Germany-reduced size by the Treaty of Versailles League of Nations was organized French and Britain (ruled by Winston Churchill)-unsure U.S.- isolationist What does all of this mean? Hitler (leader of Germany) Believed only Germans with blond hair and blue eyes were “true Germans” Blamed Jews for many of the problems. Adolf Hitler took advantage of the unhappiness to lead his Nazi Party to power Hitler preached hatred of the Jews and promised to return Germany to greatness By 1933, he was firmly in power Hitler Continued Hitler wanted to expand his empire, which he called the Third Reich. What is this called (expanding an empire)? Invaded the Rhineland, Austria, and parts of Czechoslovakia. Since other European nations did not want another war, they did little to stop him. They chose appeasement- the belief that it is best to let an aggressive nation have what it wants-they hope that this will satisfy its leaders and stop aggression Hitler didn’t stop. Signed alliance with two other aggressive nations: Italy and Japan. In 1939, Germany invaded Poland, starting World War II in Europe. National Socialists or Nazis? Political party with Hitler in charge Grew in power and started an army and continued to build it – What is this called? Soldiers, called storm troopers attacked Jewish people and others opposed to Hitler Put prisoners into terrible prisons called concentration camps. Nazis in Control 1933 took control of German government Hitler ruled as a dictator, an allpowerful ruler. Rebuilt Germany’s economy by preparing for another war. Built tanks, guns, and other war supplies Wanted to Rule the World German Dictator, Adolf Hitler Click on the picture for A video. Other Dictators Dictatorship – a country ruled by one all-powerful person. Joseph Stalin ruled the Soviet Union. Francisco Franco ruled Spain. Benito Mussolini ruled Italy. Hirohito ruled Japan. Can you think of any mnemonics for remembering these names? Japan’s Aggression 1920’s- Japan decided to expand its territory in Southeast Asia. Emperor Hirohito did not desire war, but he didn’t have most of the power… Government fell under the control of the military Japan (tiny island nation) lacked natural resources Many in the military saw the invasion of other territories as the best way to solve this problem By the late 1930’s, Japan controlled most of the Chinese coast and was determined to conquer other territories as well. Sound familiar? What is this called? Discuss it with a neighbor. Lesson 2: The War Begins Japan, Italy, and Germany began taking over other countries. What is this called? Sept. 1, 1939 Germany invaded Poland. British and French leaders had had enough! Declared war on Germany on Sept. 3, 1939. British and French not able to stop Germany from taking over other countries. The United States Many thought we should stay out (Can you make a connection here?) President Franklin Roosevelt promised to keep us out of the war. Prepared for attack just in case 1st peacetime draft • Men ages 21-39 had to register. • Started making war supplies Japanese Invasion Spreads Japanese invaded Indochina, now what is Cambodia, Laos, and Vietnam. American leaders were afraid Japan would threaten the Philippines and other Pacific islands. What did the US own in the Pacific? They were RIGHT! Japan’s Aggression Continued United States was very concerned about Germany and Japan. Still, many citizens did not want the US to go to war. Then, in late 1941, everything changed. Japanese leaders believed that the US Pacific Fleet at Pearl Harbor, Hawaii, was anchored too close to Japan. Much of the harbor and surrounding lands is a United States Navy deepwater naval base. They felt it threatened Japan’s expansion. On December 7, 1941, Japanese planes launched a surprise attack on Pearl Harbor. U.S. Enters the War December 7, 1941- Japanese planes attacked Pearl Harbor in the Hawaiian Islands. Dropped bombs on American ships at the Pearl Harbor naval base. In less than two hours, Japan had destroyed most of the U.S. Pacific fleet. More than 2,000 sailors and 68 civilians were killed. Declaration of War Day after the attack at Pearl Harbor President Roosevelt asked Congress to declare war on Japan. Congress declared war that same day. Because Germany and Japan were allies, the United States soon found itself at war with Germany as well. The US had entered WWII. Italy and Germany, Japan’s allies, declared war on the U.S. three days later. Turn and tell a neighbor why the US entered WWII. The War in Europe North Africa and Italy In June 1941, Germany invaded the Soviet Union (USSR) After Pearl Harbor, the US, Great Britain, the USSR, and a number of other nations fought together as the Allies. Germany, Italy, and Japan formed the Axis Powers. Although the Soviet Union’s leader, Joseph Stalin, urged the US and Great Britain to invade Western Europe, President Roosevelt and Britain’s Prime Minister Winston Churchill decided to attack in North Africa first. Following the victory in North Africa, the British and US forces invaded and conquered southern Italy. Sides are Drawn Axis Powers Germany Japan Italy AXIS- The world spins on an axis, and Hitler (along with Japan and Italy) wanted to rule the world! Allies United States Britain France USSR Americans at War Produced more and more airplanes, tanks, and other war supplies Created new jobs World War II ended the Great Depression Discuss with a neighbor how this affected the economy. Women took over many of the jobs Power of the federal government grew Rationing, or limiting what Americans could buy occurred, so supplies could be sent overseas. Lesson 3: The War at Home While US soldiers were away fighting in Europe and the Pacific, citizens at home did their part to support the war effort Military needed weapons and supplies. Production increased, and the economy boomed. Citizens began to looking for ways to conserve goods so that more could go to the soldiers. Do you remember what this is called? People planted victory gardens in which they raised their own vegetables. The Role of Women Women’s role in society changed during the war. Over 275,000 women served in the United States military. The largest military division of women was the WAC (Women’s Army Corps). http://embodiedidentity.pbworks.com/f/1350757234/wac_women_group_shot_large.jpg Rosie the Riveter became the symbol of such women. It was the title of a song about a woman who went to work as a riveter while her husband went off to war. Posters of “Rosie” encouraged women to go to work and help production. The Role of Minorities in WWII Perhaps the most impressive was an army infantry regiment known as the 442nd Regiment It was made up totally of Japanese American soldiers. The 442nd fought in Europe and became the most decorated unit in US history. "Tuskegee Airmen" refers to the men and women, African-Americans and Caucasians, who were involved in the so-called "Tuskegee Experience", the Army Air Corps program to train African Americans to fly and maintain combat aircraft. The Tuskegee Airmen included pilots, navigators, bombardiers, maintenance and support staff, instructors, and all the personnel who kept the planes in the air. The War in Europe Italy’s Axis leader, Benito Mussolini, escaped to the north There he became the leader of a puppet government under Adolf Hitler (A puppet government is one that rules a country but answers to a stronger foreign government.) Whose government did he answer to???? D-Day Following the meeting between Stalin, Churchill, and Roosevelt, the Allies agreed that the time had come for an invasion of Western Europe. US General Dwight D. Eisenhower commanded the invasion. On June 6,1944, Allied troops launched a surprise attack on Northern France The invasion became known as D-Day. It was a huge success. As the Soviets marched toward Berlin from the east, the western Allies liberated France and other countries as they advanced from the west. Victory in Europe April 1945- Hitler realized he had lost As Soviet troops surrounded Berlin, Hitler committed suicide rather that be captured In May, Germany surrendered. The Allies celebrated VE Day (Victory in Europe Day) President Roosevelt did not see the day of victory. He died earlier that same month at his vacation home in Warm Springs, Georgia. Harry Truman became the new president. The Holocaust Allies are advancing through Europe They made a horrifying discovery They found concentration camps housing thousands of starving and tortured prisoners Most were Jewish At first, Hitler’s government simply passed discrimination laws against the Jews After invading Soviet Union, Hitler tried to exterminate the Jewish people He wanted to kill other people the Nazis felt were unfit to live These groups were Slavs, the mentally ill, gypsies, and Jehovah’s Witnesses. The Holocaust Jewish suffered the most Jewish people of all ages were arrested Many were executed immediately or shipped to camps where they were killed upon arrival Other were forced to work or were tortured in the camps before they were finally murdered Over six million Jewish people would perished. The horrible period became known as The Holocaust After the war, a number of German leaders stood trial for these crimes. Most were found guilty. Some received long prison sentences. Others were hanged. Lesson 4: Island Hopping The US military then used a strategy called island hopping US forces conquered one set of islands after another as they fought their way toward Japan Forces under the command of Admiral Chester Nimitz advanced across the Central Pacific Meanwhile, General Douglas MacArthur and Admiral William Halsey commanded forces that attacked from the south and retook the Philippines Island Hopping One of the fiercest battles occurred on the island of Iwo Jima It took more that 100,000 US soldiers nearly a month to defeat a Japanese force of 25,000 Japanese soldiers often believed it was more honorable to fight to the death rather than surrender One of the most famous images of the was that of the US Marines raising an American flag over Iwo Jima. The Atomic Bomb During the war, the US developed the atomic bomb It was the world’s first nuclear weapon It was far more powerful than any weapon ever invented When Japan refused to surrender unconditionally, President Truman ordered the bomb dropped on the Japanese city of Hiroshima On August 6, 1945, a US plane dropped the bomb IT DESTROYED HIROSHIMA Thousands of Japanese people were killed Thousands more died later from radiation caused by the explosion. The Enola Gay lands at a Mariana Island base after dropping the first atomic bomb on Hiroshima The Atomic Bomb When Japan still delayed in surrendering, the president ordered a second atomic bomb dropped on Nagasaki The death and destruction caused by these horrifying weapons forced Japan to surrender People in the US celebrated VJ Day (Victory over Japan Day). Problems for JapaneseAmericans Some military leaders distrusted Japanese Americans Were afraid they would help the “enemy” Roosevelt ordered 110,000 Japanese Americans into “relocation camps” • Like prisons, fenced in with barbed wire • Soldiers guarded the camps with guns • Had to sell their homes, businesses, and belongings. Problems Continue Moved to Utah, California, Arizona, Wyoming, Arkansas, and Idaho Had to wear identification tags Over 17,000 Japanese Americans served in Army units even though their friends and families were being locked away by their own country. The United Nations After WWII, countries established the League of Nations They hoped the League would encourage peace and avoid future wars The League had no power to enforce its decisions, however. The US and it allies led the way in establishing a new organization In 1944, the US hosted meetings to come up with a plan for the organization In April 1945, leaders from fifty countries met in San Francisco to draft a charter. In October, the United Nations (UN) was formed. The United Nations Its purpose was to maintain peace between countries & make sure nations obeyed international law and protect human rights Most of the decision-making power fell to five permanent members of the UN Security Council: the US, Soviet Union, China, Great Britain, and France.