Blood Typing
advertisement

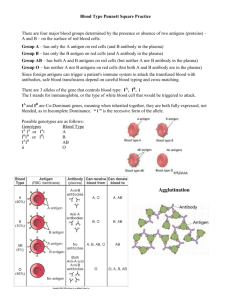
What is Blood Made Of? •Red Blood Cells •White Blood Cells •Plasma •Platelets Erythrocytes Erythro: red Cytes: cells Transport oxygen Carry away carbon dioxide No nucleus Leukocytes Leuko: white Cytes: cells Important aspect of immune system “Eat” bacteria and other foreign substances Formed from stem cells in bone marrow Plasma Mostly water Proteins, electrolytes, hormones, and clotting factors Proteins used to fight infection Provides means of transportation for the other blood cells Thrombocytes Thrombo: blood clotting Cyte: cell Sticky, have irregular shape Form blood clots No nucleus Formed in bone marrow History of Blood Typing 1900-1901 Karl Landsteiner of Austria Noted agglutination of patients’ red blood cells when they received serum from someone else Determined this was due to red blood cell antigens and serum antiobodies A blood group and B blood group O for “ohne” AB blood group 1910: Blood type is inherited The ABO Blood Group System Group A – has only the A antigen on red cells (and B antibody in the plasma) Group B – has only the B antigen on red cells (and A antibody in the plasma) Group AB – has both A and B antigens on red cells (but neither A nor B antibody in the plasma) Group O – has neither A nor B antigens on red cells (but both A and B antibody are in the plasma) http://www.redcrossblood.org/learn-about-blood/blood-typesm Rh Factor Another antigen found on red blood cells is the Rh factor If present, indicated as (+) If not present, indicated as (-) Example: A+ A antigens on red blood cells, B antibodies in plasma, Rh factor present OK, So What Are Antigens? Antigens cause immune response Red blood cells have millions of antigens These recognized and ignored by body’s immune system When red blood cells with unfamiliar antigens enter body, immune system attacks it Blood Type is Inherited A, B, AB, O determined by a sugar Rh (+) or (-) determined by a protein DNA determines the sugars and proteins your body produces DNA is inherited Phenotype Genotype A AA or AO B BB or BO AB AB O OO Determining Blood Type Simple test Drop of blood combined with an anti-A chemical and anti-B chemical If reacts with anti-A, blood is type A If reacts with anti-B, blood is type B If reacts with both, blood is AB If no reaction, blood is type O Similar test for Rh factor If blood clots, Rh (+) If no clot, Rh (-) Who Gets What? Group A Group A or Group AB Group B Group B or Group AB Group O All blood groups Universal donor Group AB Only Group AB Universal acceptor Donor Recipient O O A A B B AB AB