WordIdassessmentJJ
advertisement

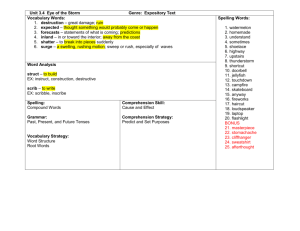
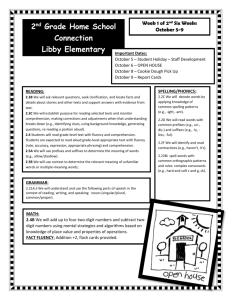
Assessment: A Literacy Perspective Julie A. Jeffery Agenda: Saturday • • • • • • News and announcements Email addresses/myLesley “business” Confidence check Writing up results Writer’s Workshop Digging Deeper: Word Identification and Spelling Agenda: Sunday • • • • • Assessment Tool Review Assignment Emergent Reader Report Comprehension assessment Writer’s workshop/conference with JJ road map for the next three weeks Assessment Tool Review (for March 24-25 weekend) • Tool name, author, publishers information • Administration specifics: time, whole group, 1:1, materials needed • Type of assessment: formal or informal, criterion or standardized • What it aims to test • Types of information yielded • Reliability and validity as applicable • Your thoughts on this test Reading Assessment in the News …What’s the latest? …What’s YOUR elevator speech for Literacy Assessment? …watch Animal School …how does this change your elevator speech? Your Case Study Student • What key things did you learn in their background? • What things did you learn in preliminary info? • What did you learn from the QRI so far? • K-W-L Running Record & Miscue Analysis • (RW) Number of running words • (E) Number of errors –meaning changing miscues • (SC) Number of self-corrections • Accuracy rate- 100-(E/RW *100) • Error ratio- RW/E • Self-correction ratio- SC/E+SC • WCPM = (RW-E)/Time (in seconds); take number and multiply by 60 to get WCPM Writing It Up • Text: level, familiar or not, genre, topicWhat type of text did the student read? • Accuracy, self- correction, error ratio-How difficult was this text for the student? • Words correct per minute- How fast did the student read? • Self-corrections- Do they monitor & fix? • Types of miscues (substitutions), omissions, insertions, types of words-What types of mistakes do they make? • How did they sound as a reader? When writing up your findings… 1. Make a statement of performance 2. Back-up with selected information & examples 3. Write summary statement • Make a statement of performance Jace demonstrates strong self-correction skills when orally reading. Jace was asked to orally read a 2nd grade level expository passage from the QRI-4, Whales. The passage was unfamiliar to Jace. • Back-up with selected information & examples Jace read the passage at a rate of 67 words correct per minute. This is lower than would be expected for his grade, but is consistent with his word identification skills. Jace read with 92% accuracy, making this level passage (2nd grade) at the instructional level for him. He made 8 errors, 7 of which he self-corrected. All of his errors were substitutions, and most words were high-frequency words. (Examples)While reading he made many repetitions and pauses, which slowed down his overall reading. After reading, he was able to answer 5 out of 8 questions about the passage, but most answers came from his background knowledge. • Write summary statement Based on this miscue analysis, we can see that Jace is able to monitor and self-correct while reading. His slower pace is perhaps impacting comprehension. More information needs to be gathered to determine Jace’s difficulties within the area of word identification, specifically sight word knowledge and decoding abilities. Choose one skill you have assessed and write it up following this pattern: 1. Make a statement of performance 2. Back-up with selected information & examples 3. Write summary statement Preliminary Section Should Include: • Getting to know you activities/outer circle – Retelling, LEA, writing, reading • Observations you made • QRI • Initial Hypothesis of what is going onwhat is the pattern that you have found at this point Writing up the QRI: • Look at example reports- high light paragraph • Take your child’s information, put it on paper Word Identification Listening Comprehension Silent Reading Comprehension Compare the Student’s Performance on Tasks Across these Processes To Identify Relative Strengths and Weaknesses Weakness? Word Identification Strength? Weakness? Language Comprehension Strength? Weakness? Print Processing Strength? Case Student Jace • Initial Profile: – Word Identification: 1st grade – Listening Comprehension: 4th grade – Silent Reading Comprehension: 2nd grade Case Student Jace • Initial Profile: – Word Identification: 1st grade – Listening Comprehension: 4th grade – Silent Reading Comprehension: 2nd grade • • • • Could identify through decoding 50% of the words up to 3rd grade Spelling mistakes are phonetic Misspelled several high frequency words in writing tasks Fluency rates averaged around 45 words per minute; accuracy was 80-85% on 1st and 2nd grade level passages • Attempts to ‘sound out’ words considered high frequency • Need to distinguish between sight words and decoding Stage II Assessment • The Stage I assessment provides an overall picture of a student’s relative strengths and weaknesses in the major areas. • A Stage II assessment is only completed in the areas of relative weakness to provide a more sophisticated understanding of the nature of the relative weakness. Going Deeper: Analysis within Area of Weakness • Using our Preliminary Information and Stage I assessment we will: • Go to appropriate area of manual based on profile • Design an assessment model that will answer the questions and hypothesis that come from ‘outer circle’ work • Only test in the areas that are weaknesses; do not test strengths when time is of essence • Keep smaller constructs in the context of the whole: silent reading comprehension Nick • • • • • Word Identification: 2nd grade Listening Comprehension: 4th grade Silent Reading Comprehension: 4th grade What area of the manual would you look in? What would you do next? Josie • Word identification: 1st grade – Could decode words up to the 3rd grade level • Listening Comprehension: 3rd grade • Silent Reading Comprehension: 2nd grade level • What area of the manual would you look in? • What would you do next? Potential Profiles from Initial Assessment Weakness Word Identification Word Identification Language Comprehension Language Comprehension Print Processing Print Processing Middle Language Comprehension Print Processing Word Identification Print Processing Word Identification Language Comprehension Strength Next? Print Processing Go to A Language Comprehension Print Processing Go to A Word Identification Go to B Language Comprehension Word Identification Go to C Go to B Go to C WORD IDENTIFICATION Automatic word recognition and Mediated word identification • Both are required for successful silent reading comprehension • We are not allowed to make instructional decisions based on our philosophical beliefs or skills - we must find a way to teach both. Questions/Levels of Word Identification Assessment • Does the child have more automatic sight words or rely more on decoding? – Ratio of automatic words to decoded words • What level of words is the child able to decode? – Single syllable, two-syllable, multi-syllabic – Onset-rime knowledge, particular patterns, word families – Affixes, prefixes, suffixes • What does the child’s encoding(spelling) look like? – Developmental Spelling (Gentry) – Spelling Patterns(Words Their Way) • If the child shows significant difficulty with decoding, and does not have an adequate sight word bank, – look at phonemic awareness, letter-identification, hearing sounds in words, early developmental spelling Student #1 • QRI – L1-10 Automatic 3 Decoding – P- 18 automatic- 1 Decoding • Decoding Test – Passed List A, 7 out of 12 on List B • Z Test – 20 out of 37, missed silent e rule words • Up, And & Out Test – 17 out of 42 words, trouble with /and/ words, consonant digraphs Student #2 QRI PP- 3 automatic, 6 decoding P- 4 automatic- 5 decoding Decoding Test List A- 3 out of 8 Z Test 30 out of 37- with a lot of time Fry Word List 22 out of first 100 http://www.literacyconnections.com/ Dolch.html High Frequency Word Lists Onset-Rime Knowledge • • • • • • Decoding Test Z Test (cd-rom and pg. 143) Up, And, & Out Real Word Test Test of Onset Knowledge (pg. 146) Names Test of Decoding (cd-rom, and article) Tests in McKenna & Stahl • In pairs: – Read about one test of word identification – Determine what question(s) it answers – Show class briefly how to give – Pros and cons of assessment Spelling Assessment Gentry & Gillet (1993) Monster Test Developmental Spelling Test (11-year-old, multiple disabilities) BECA ML LCA SK FT [back] [mail] [lake] [stick] [feet] SCRVL SOUA PATP D TS [sink] [dress] [peeked] [side] [test] Developmental Spelling Test (adult, severe speech and physical impairments) back mail lake stack feet light [back] [mail] [lake] [stick] [feet] [light] sta dress peeked side test s [sink] [dress] [peeked] [side] [test] [dragon] Developmental Spelling Test (9-year-old girl with Down syndrome, 3rd grade inclusion) bake mall lake stik feet light [back] [mail] [lake] [stick] [feet] [light] sinek drsse pekd side test baran [sink] [dress] [peeked] [side] [test] [dragon] Words Their Way Example Student Spelling 1. fan 2. pet 3. deg 4. robe 5. hop 6. watte 7. gum 8. suled 9. stik 10. shi 11. dreame 12. bulade 13. koach 14. frite 15. cheewed 16. krawle 17. whishes 18.thern 19. shot 20. spol 21. grwl 22. thered 23. kampped 24. trys 25. cliping 26. rideing 1.Fan 2. Pet 3. Dig 4. Rob 5. Hope 6. Wait 7. Gum 8. Sled 9. Stick 10. Shine 11. Dreme 12. Blaid 13. Coche 14. frieght 15. chewed 16. krawl 17. wishs 18. thern 19. showted 20. spoyle 21. growel 22. therd 23. camped 24. trys 25. claping 26. riddeing Questions/Levels of Word Identification Assessment • Does the child have more automatic sight words or rely more on decoding? – Ratio of automatic word to decoded words • What level of words is the child able to decode? – Single syllable, two-syllable, multi-syllabic – Onset-rime knowledge, particular patterns, word families – Affixes, prefixes, suffixes • What does the child’s encoding(spelling) look like? – Developmental Spelling (Gentry) – Spelling Patterns(Words Their Way) • If the child shows significant difficulty with decoding, and does not have an adequate sight word bank, – look at phonemic awareness, letter-identification, hearing sounds in words, early developmental spelling Yopp Singer Phonemic Awareness Test Yopp Singer Example: 5 year old Jake Yopp-Singer Test of Phoneme Segmentation Phonemic Awareness Assessment https://dibels.uoregon.edu/ Video Clip: DIBELS Phoneme Segmentation Fluency Phoneme Segmentation Fluency https://dibels.uoregon.edu/ Phonemic Awareness Assessment Nonsense Word Fluency When Writing About One Test • State the name of the test/task performed – Jace was given the Developmental Test of Word Recognition (McKenna & Stahl 2003). • State the purpose of the test and what it addresses – This test assesses the areas of word concepts, initial and final sounds, vowel coding, consonant blends, and polysyllabic word reading. • State the range of scores the child achieved (full scores go in table) – Jace’s performance on the word concepts, initial and final sounds was excellent with 100% accuracy in all three areas (5 out of 10, and 10 out of 10). On the vowel and long-vowel coding sections he had more difficult and scored 3 and 4 out of 10 respectively. • State backup information or observations made. – Jace made several attempts to get the right answers and commented on how hard he was trying. It was observed that Jace attempted a decoding strategy that was introduced in class while taking this test. • Summary Statement – Therefore, Jace’s performance on this assessment indicates he has solid skills in the areas of word concepts,and initial and final sounds for decoding, but is still struggling with vowel and long-vowel coding. • Make connection to other testing situations/tasks if applicable – This is consistent with information seen in his spelling and running records. Jace was given the Developmental Test of Word Recognition (McKenna & Stahl 2003). This test assesses the areas of word concepts, initial and final sounds, vowel coding, consonant blends, and polysyllabic word reading.Jace’s performance on the word concepts, initial and final sounds was excellent with 100% accuracy in all three areas (5 out of 10, and 10 out of 10). On the vowel and long-vowel coding sections he had more difficult and scored 3 and 4 out of 10 respectively. Jace made several attempts to get the right answers and commented on how hard he was trying. It was observed that Jace attempted a decoding strategy that was introduced in class while taking this test.Therefore, Jace’s performance on this assessment indicates he has solid skills in the areas of word concepts,and initial and final sounds for decoding, but is still struggling with vowel and long-vowel coding. This is consistent with information seen in his spelling and running records. DIBELS • • • • • • Oral Reading Fluency Retell Fluency Nonsense Word Fluency Phoneme Segmentation Fluency Letter Naming Fluency Initial Sound Fluency DIBELS Investigation • • • • • • Find videos Read about 3 of the subtests What are the pros & cons? What grades is it given to? What information does it yield? How would you use the information in your teaching? Looking at Student Data Sets