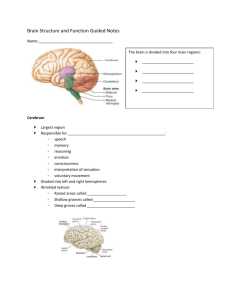
Brain
advertisement
Anatomy of the Brain and Cranial Nerves 1 The Nervous System can be divided in: Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain and Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Cranial and spinal nerves, ganglia, sensory receptors 2 Division of the Peripheral Nervous System Sensory or afferent Somatic Visceral Motor or efferent Somatic - voluntary Visceral or Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) - involuntary Sympathetic Parasympathetic 3 Major regions and landmarks Six regions in the adult brain Cerebrum Diencephalon Mesencephalon Pons Cerebellum Medulla oblongata Brain contains extensive areas of neural cortex Layer of gray matter on the surface of the cerebellum and cerebrum 4 The Cerebrum 5 The cerebral hemispheres Surface contains gyri, sulci, fissures Fissures Longitudinal fissure separates two cerebral hemispheres Transverse fissure separates cerebellum from cerebrum 6 The Cerebrum 7 The cerebral hemispheres Sulci Parieto-occipital sulcus separates parietal from occipital lobe Lateral sulcus separates temporal from parietal lobe Central sulcus separates frontal and parietal lobe 8 The cerebral hemispheres Gyri Precentral gyrus Poscentral gyrus 9 The cerebral lobes Frontal Precentral gyrus Primary motor area – conscious control of voluntary movements. Premotor cortex – memory bank for skilled motor activities or of patterned and repetitious nature. Broca’s area Located on the left hemisphere. Controls speech. 10 The cerebral lobes Prefrontal cortex – responsible for personality, cognition, intellect. Lesion cause mental and personality disorder Parietal Primary Somatosensory Area – touch, pressure, temperature, vibration, and pain from body wall Somatosensory association area – interprets stimulus sent by the above area. Ex: recognizes objects by touch. 11 The cerebral lobes Temporal Primary Auditory area – temporal lobe. Primary association auditory area – interprets the sound heard by above area Wernicke’s area – only on left hemisphere, between parietal and temporal lobes. Area responsible for understanding spoken language Olfactory area –uncus. Smell area. 12 The cerebral lobes Occipital Primary visual area – perception of light Visual association area – interprets the images seen on the area above Insula Gustatory cortex 13 Cerebral hemispheres - internal structures Gray matter Cell bodies of the neurons Dendrites Small unmyelinated axons Neuroglias 14 Cerebral hemispheres - internal structures White matter Tracts Association – connects 2 areas of the same hemisphere Projection – connects upper and lower brain. Ex: internal capsule Commissure – connects the 2 hemispheres. 15 Tracts 16 Sagittal Section 17 Cerebral hemispheres - internal structures Corpus callosum Connects the 2 hemispheres Fornix Connects limbic system areas Septum pellucidum Separates the 2 lateral ventricles 18 Cerebral hemispheres - internal structures Basal Nuclei – regulation of voluntary motor activities. Allows smooth movements. Caudate Nucleus Putamen Globus pallidus 19 The Diencephalon 20 21 22 Diencephalon: external view Olfactory tract Olfactory bulb Optic nerve Chiasma optic Pituitary gland or hypophysis Mammilary bodies – relay for olfaction 23 The diencephalon is composed of Epithalamus Hypothalamus Thalamus 24 Sagittal Section 25 Figure 14.12b The Epithalamus Roof of the third ventricle Contains choroid plexus Contains pineal gland Regulates sleep-awake cycle 26 The thalamus Relay area for impulses Two large lobes of gray matter Interthalamic adhesion or intermediate mass 27 The hypothalamus Autonomic center for regulation of body temperature, water balance, etc Secretes hormones Mammilary bodies – relay station for olfaction Pituitary glands – secretes hormones Optic chiasm 28 The Brain Stem Midbrain Cerebral Aqueduct – connects third and forth ventricles Cerebral peduncles – connects pons to cerebrum Corpora quadrigemina Superior colliculi – visual reflex center Inferior colliculi – auditory reflex center 29 The Brain Stem Pons Consists of tracts and nuclei Connects brain to lower CNS • Medulla Oblongata • Tracts • Decussation of the pyramids • Autonomic reflex centers – heart rate, blood pressure, vomiting, swallowing, respiratory rhythm • Olives 30 PART 2 31 Cerebellum Two hemispheres connected by the vermis Arbor vitae – white matter Cortex of gray matter 32 The Cerebellum 33 The Cerebellum 34 The cranial meninges Dura mater Falx cerebri-formed by dura mater that dips into the longitudinal fissure and separates the 2 hemispheres Falx cerebelli – separate the two cerebellar hemispheres 35 The cranial meninges – dura mater Superior sagittal Sinus – collects blood from the brain Tentorium cerebelli – separates the cerebrum from the cerebellum 36 The cranial meninges Arachnoid Subarachnoid space Filled with CSF Arachnoid villi – projections of the mater that protrude through the dura For the CSF to drain back to the venous circulation 37 The cranial meninges Pia mater Highly vascular Covers the entire brain Meningites 38 The Relationship among the Brain, Cranium, and Meninges 39 Ventricles of the brain Filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) Lateral ventricles Septum pellucidum Interventricular foramina or foramen of Monro 40 Ventricles of the brain Third ventricle Cerebral aqueduct Forth ventricle 3 Apertures 41 Ventricles of the Brain 42 Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) CSF cushions delicate neural structures Supports the brain Pathway of CSF Produced at the Choroid plexus Travels through the apertures on the 4th ventricle to the subarachnoid space Diffuses across the arachnoid villus (granulation) into the superior sagittal sinus 43 The Circulation of CSF 44 Cranial Nerves 12 pairs of cranial nerves To help to remember “Old Opie Occasionally Tries Trigonometry And Fells Very Gloomy Vague And Hypoactive” 45 The Cranial Nerves PLAY 46 Cranial Nerves Number I II III IV V Name Olfactory (sens) Optic (sens) Oculomotor (mot) Trochlear (mot) Major Functions Smell Vision Eye movement Eye movement Trigeminal (mix) Chewing muscles, head and face sensation 47 Cranial nerves VI Abducens (mot) Eye movement VII Facial (mix) Face expression, taste VIII Vestibulocochlear (sen) Vestibular: posture and balance Cochlear: hearing 48 Cranial Nerves IX X XI XII Glossopharingeal Swallowing, taste, general (mix) sensation for pharynx Vagus (mix) Visceral muscle movement and taste sensation Accessory (mot) Swallowing, and head movement Hypoglossal Movement of tongue for (mot) speaking, swallowing and mixing food 49 Brain Dissection Whole Brain Pia-Arachnoid Gyrus Sulcus Fissure Transverse Longitudinal Cerebrum 50 Brain Dissection Pons Medulla Oblongata Cerebellum Cranial nerves: I (bulb, tract) II (nerve, chiasma) III 51 Brain Dissection Colliculi Superior Inferior Pineal Gland 52 Brain Dissection Sagittal Cut Diencephalon Epithalamus Thalamus Hypothalamus Ventricles Lateral, third, forth 53 Brain Dissection Septum pellucidum Corpus callosum Fornix Arbor vitae (cerebellum) 54