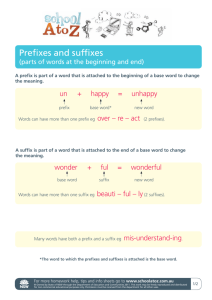
Suffixes
advertisement

Medical Terminology NURS 1103 or HLSC 2613 Learning Terminology 2 INTRODUCTION TO MEDICAL LANGUAGE (ML) Dr. Mohammed Qasim Baghdad College of Medicine Main Objective: Learn Medical Terminology New students to Medical Terminology often bewildered by strange spelling and pronunciation. Approximately 75% of Medical Terms are based on either Greek or Latin Medical Terminology Mispronunciations Artery - The study of fine paintings. Benign - What you are after you be eight. Coma - A punctuation mark. Morbid - A higher offer. Urine - opposite of you’re out. Tablet - A small table. Course Objectives Apply basic principles of medical word building. Correctly pronounce medical terms. Define common medical terms. Relate common medical terms to human anatomy and physiology; common disease states, pharmacological categories and diagnostic tests. Identify the medical terminology in medical record reports. A Busy Course! Are you feeling like a lot of information is about to come your way? The answer is YES. Now, lets begin Lecture 1 Basic Elements of Medical Word Medical Dictionary Use Look Up Unfamiliar Terms Building Medical Terms Word Root Prefix Suffix Combining forms 10 Forming Medical Terms Medical Term Word root Prefix Suffix Combining forms 11 Word Roots (WR) Usually derived form Greek or Latin Frequently indicates a body part Most medical terms have one or more word roots Examples of Word Roods Greek Word Word Root Kardia (heart) Cardi Gaster (stomach) Gastr Hepar (liver) Hepat Nephros (kidney) Nephr Osteon (bone) oste Combining Forms (CF) Combining Form (CF) is a Word Root (WR) plus a vowel, usually an “o” Usually indicates a body part Combining Forms Examples Cardi/ + o = cardi/o gastr/ + o = gastr/o hepat/ + o = hepat/o nephr/ + o = nephr/o oste/ + o = oste/o heart stomach liver kidney bone Suffixes Word Ending Suffix usually indicates a procedure, condition, disease, or part of speech Usually derived from Greek or Latin Examples of Suffix Arthr/o-centesis joint throac/o chest gastr/o puncture Arthrocentesis puncture of a joint -tomy incision Thoracotomy incision of the chest -megaly Gastromegaly stomach enlargement enlargement of the stomach Prefixes Word element located at the beginning of a word Changes the meaning of the word Usually indicates a number, time, position, direction, color, or sense of negation Examples of Prefix A- mast without breast -ia condition hyper- -ia condition therm excessive heat intra- in muscul muscle -ar relating to Basic Rule One A WR (word root) is used before a suffix that begins with a vowel. Scler/ + osis = sclerosis Basic Rule Two A combining vowel is used to link a WR to a suffix that begins with a consonant and to link a WR to another WR to form a compound word colon/o + scope = colonscope osteo/ o/ chondr/ itis = osteochondritis Defining Medical Words First, define the suffix or ending Second, define the prefix, or beginning Third, define the middle Word Roots and Combining Forms [CYT(O)] Combining Forms Meaning cyt(o) cell dextr(o) right dips(o) thirst dors(o) back erythr(o) red esthesio sensation, perception 23 Word Roots and Combining Forms Combining Forms Meaning galact(o) milk gluco glucose gero old age glyco sugars gyn(o) women home(o) same kin(o) movement 24 Combining Forms Meaning kinesi(o) motion lact(o) milk leuk(o) white lith(o) stone mio smaller; less narco sleep; numbness necro death; dying 25 Word Roots and Combining Forms [NOCT(O)] Combining Forms Meaning noct(i) night oncho tumor path(o) disease phago eating phon(o) sound; voice pseud(o) false pyo 26 pus Word Roots and Combining Forms [PYRO] Meaning Combining Forms pyro fever salping(o) tube schiz(o) split; division scler(o) hardening scolio crooked; bent somato body spiro breath; breathe 27 Word Roots and Combining Forms [TEL(O)] Combining Forms Meaning tel(o) distant; end; complete tono tension; pressure tropho food; nutrition xanth(o) yellow xeno stranger Xer(o) dry 28 Prefixes Prefix •Prefixes are attached to the beginning of words. •Modifies the meaning of the word or word root. •Indicates size, quantity, position of, and location. 29 Prefix 30 Prefixes (a–aut) Meaning a without ab away from ana up, toward ante before anti against aut(0) self Prefix 31 Prefixes (brachy–hypo) Meaning brachy short brady slow contra against dys abnormal; difficult hemi half hyper above normal hypo below normal Prefix 32 Prefixes (inter–peri) Meaning inter between iso equal; same mal bad; inadequate meta after micr(o) small olig(o) few; little; scanty peri around; about; near Prefix Prefixes (pro–un) Meaning pro before; forward re again; backward retro behind; backward semi half supra above; over tachy fast un not 33 Suffixes Prefix •Attaches to the end of the word and carries the underlying meaning of the word. •Suffixes can also be combining forms. 34 Suffix Suffixes (ad–crine) Meaning -ad toward -algia pain -asthenia weakness -blast immature; forming -cidal destroying; killing -clast breaking -crine secreting 35 Suffix Suffixes (crit–ectomy) Meaning -crit separate -cyte cell -cytosis condition of cells -derma skin -dynia pain -ectasis expanding; dilating -ectomy 36 removal of Suffix Suffixes (emesis–graphy) Meaning -emesis vomiting -emia blood -esthesia sensation -globin protein -gram a recording -graph recording instrument -graphy process of recording 37 Suffix Suffixes (ic–malacia) Meaning -ic pertaining to -ism condition; disease -itis inflammation -kinesia movement -logist one who practices -lysis destruction of -malacia softening 38 Suffix Suffixes (mania-pathy) Meaning -mania obsession -megaly enlargement -oid like; resembling -opia vision -ostomy opening -para bearing -pathy disease 39 Suffix Suffixes (penia-phrenia) Meaning -penia deficiency -pepsia digestion -pexy fixation -phage eating; devouring -phobia fear -phonia sound -phrenia 40 of the mind Suffix Suffixes (phylaxis-rrhaphy) Meaning -phylaxis protection -plasty surgical repair -plegia paralysis -pnea breath -ptosis falling down; drooping -rrhagia heavy discharge -rrhaphy 41 surgical suturing Suffix Suffixes (rrhexis-tropia) Meaning -rrhexis rupture -spasm contraction -stasis stopping; constant -stenosis narrowing -tomy cutting operation -trophy nutrition -tropia 42 turning Rules •Add s to words ending in any vowel or consonant except s,x,z, or y (ex. joint- joints) •Add es to words ending in s,x, or z (ex. reflex reflexes) 43 Rules Cont’d •Remove x and add `ces to Latin words ending in x (ex. appendix - appendices) •Remove the `y and add `ies to words ending in `y preceded by a consonant (ex. mastectomy- mastectomies) 44 Rules Cont’d •When an ending `y is preceded by a vowel, the usual plural suffix is `s (ex. boy - boys) •Add `e to Latin terms ending in a (ex. lamina laminae) 45 Rules Cont’d •Remove `us and add `i to Latin words ending in us (ex. bacillus- bacilli) •Change `sis to `ses in Greek words ending in sis (ex. psychosis - psychoses) 46 Rules Cont’d •Remove `on from and add `a to Greek words ending in `on (ex. criterion - criteria) •Remove `um from and add `a to Latin words ending in um (ex. diverticulum - diverticula) 47 Latin Greek Singular Plural Singular Plural •fossa fossae •neurosis neuroses •datum data •ganglion ganglia •radix radices •calyx calyces 48