Shapes of Molecules Me
advertisement

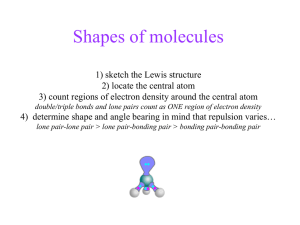
Shapes of Molecules •be able, in terms of electron pair repulsion, to predict the shapes of, and bond angles in, simple molecules and ions. Molecules • The shape of a molecule is determined by the no. Of electron groups around the central atom ‘Groups’ might be a bonding pair of electrons, a single, non-bonding electron, a double pair of bonding electrons, etc... 3.9 Molecular and ionic shapes VSEPR theory: Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion theory. States that pairs of electrons arrange themselves around the central atom so that they are as far apart from each other as possible. Which of these shapes contains a central atom with a lone pair? http://liakatas.org/chemblog/?page_id=17#Vi deos SUPER IMPORTANT SUB-RULE!!! Any lone pairs of non-bonding electrons will be closer to the nucleus of the central atom There is no second atom attracting/sharing the lone pair This increases the repulsion between the lone pair of electrons on A and any other electron groups on A (bonding or non-bonding) As the lone pair – ‘other pair’ repulsion increases, the angle between these pairs decreases. The X-A-X angle will be slightly reduced compared to what we would expect from the simple geometry of the shape VSEPR summary Place these in order of increasing repulsion: Lone pair - bonding pair Bonding pair- bonding pair Lone pair - Lonepair Complete worksheet 3.9 ** Linear AX2 Examples •BeCl2 •CO2 •Bond Angle 180° Trigonal Planar AX3 Example •BF3 •Bond Angle = 120° Bent AX2 Example •H2O •Bond Angle = 104.5° Tetrahedral AX4 Example •CH4 •Bond Angle = 109.5° Trigonal Pyramidal AX3 Example •NH3 •Bond Angle = 107° Trigonal Bipyramidal AX5 Example •PCl5 •Bond Angles = 120° and 180° Working it all out 1. Work out the central atom (the one with the smallest number in the formula) 2. Count the number of bonding pairs to the central atom 3. Count the number of lone pairs on the central atom 4. Arrange the atoms so the electrons are as far apart as possible 5. Lone pairs squash bond angles by around 2.5 degrees 6. Treat multiple bonds as single covalent bonds Total Electro n Pairs Bonding Pair Geometry Bonding Pairs Lone Pairs Molecular Geometry 2 180⁰ 3 120⁰ 120⁰ 4 109.5⁰ 107⁰ 104.5⁰ 5 120⁰ & 90⁰ 90° & 117° 90° 180⁰ 6 90⁰ 88⁰ 90⁰