ссылка для скачиваний
advertisement

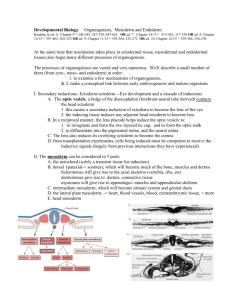
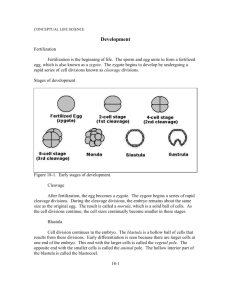
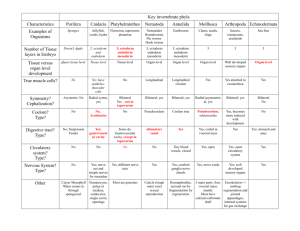
The test on the subject of "Human Embryology" 1. What are the initial period of development of the individual: a) Phylogeny. b) Embryogenesis. c) Ontogenesis or development of biology. d) - Gametogenesis. 2. What is the initial stage of embryogenesis? a) Cleavage; b) Gastrulation; c) Fertilization; d) Organogenesis. 3. Call the transition from unicellular to multicellular stages of development: a) Cleavage; b) Gastrulation; c) Fertilization; d) Histogenesis. 4. What are the final stages of embryogenesis? a) Cleavage; b) Gastrulation; c) Fertilization; d) Histogenesis and organogenesis; e)Neurulation; 5. What are the main characteristics of mature germ cells? a) Diploid; b) Haploid; c) Undifferentiated; d) The ability to divide. 6. What are derivatives of the skin formed from the ectoderm of the embryo? a) Striated muscle tissue; b) The epithelium of the skin; c) Amnion epithelial lining; d)Smooth muscle tissue 7. Indicate that develops from the ectoderm of the embryo? a) The epithelium of the stomach; b) The dermis of the skin; c) The epithelium of the umbilical cord; d) The epithelium of the trachea, bronchi and lungs 8. What are embryonic beginnings occur during gastrulation? a) the embryonic disc; b) blastula; c) the zygote; d) tissue; e) organs. 9. Specify the components of the blastocyst: a) Trophoblast; b) The ectoderm; c) The mesoderm; d) The endoderm. 10. Call the process by which the embryo communicates with the body of the mother. a) Gastrulation; b) Implantation; c) Histogenesis; d) Fertilization; 11. What are the usual times of implantation in a human after fertilization? a) 1-3 days; b) 3-5 days; c) 5-6 days; d) 7-8 days; 12. When finish the embryonic and begins fetal period human development? a) At the end of the first month; b) At the beginning of the third month; c) At the end of the third month; d) At the beginning of the fourth month 13. Specify which tissues and organs develop from the intestinal endoderm: a) Epithelium of the oral cavity; b) Epithelium of the nasal cavity; c) Renal epithelium; d) Epithelium of the gastrointestinal tract. 14. What are tissues and organs develop from neuroectoderm? a) Organ of taste; b) Organ of hearing; c) Eyesight; d) Olfactory organ. 15. Specify which tissues and organs develop from the mesoderm, somites dermatomes: a) The epidermis; b) Kidney; c) Mesothelium; d) The connective tissue of the skin; 16. What are tissues and organs develop from the mesoderm myotomes? a) Smooth muscle; b) Vessels; c) Striated (skeletal) muscle tissue; d) Bones and bone. 17. Specify which tissues and organs develop from the mesoderm sclerotome: a) Striated (skeletal) muscle tissue; b) Spinal cord; c) Skins eyes; d) Cartilage tissue and cartilage; 18. What are tissues and organs develop from the ventral mesoderm leaves (splanchnotome)? a) Striated muscle tissue; b) Smooth myocyte; c) Blood cells; d) Cardiomyocyte; 19. What is the function of cortical granules egg? a) Launch of crushing the zygote; b) The accumulation of nutrients; c) Facilitate the penetration of sperm into the egg; d) Formation of the fertilization membrane; 20. What capacitation? a) Formation of the fertilization membrane; b) Loss of sperm flagellum; c) Activation of sperm; d) Isolation of sperm enzymes; 21. Where is the fertilization of an egg? a) The uterine cavity; b) B distal oviduct; c) In the abdomen; d) In the vagina; 22. What acrosome? a) Derivative of the Golgi complex; b) Nemembranny organelle; c) Contains the proteins; d) Located in the neck of the sperm; 23. Where there should be a human embryo for 5-6 day development? a) In the oviduct; b) Add to the uterus; c) In the vagina; d) Abdominal; 24. Specify the dimensions of human sperm? a) 1-2 microns; b) 10-20 microns; c) 60-70 microns; d) 1-2 mm; 25. Specify the dimensions of human eggs? a) 1,5-2 microns; b) 30 microns; c) 150 microns; d) 1-2 mm; 26. From what sources develops human amnion wall? a) Extraembryonic ectoderm and the extraembryonic mesoderm; b) Germ extraembryonic ectoderm and mesoderm; c) Germ extraembryonic mesoderm and mesoderm; d) Extraembryonic mesoderm and endoderm; 27. What does amniotic membrane in mammals? a) Breathing; b) Excretory; c) Hematopoietic; d) Protective; 28. What type of food fetal development in human chorionic villi? a) Gematotrofic; b) Gistiotrofic; c) Epiteliotrofic; d) Yolk; 29. From which germ layers develop epithelial tissue? a) Only from the ectoderm and mesoderm; b) Only from the ectoderm and the endoderm; c) Only from the ectoderm; d) Out of all three germ layers; 30. What is the source of embryonic development of blood? a) The ectoderm; b) Mesenchyme; c) Extraembryonic ectoderm; d) Endoderm; 31. What is the source of the epithelium of the mucous membrane of the digestive tube? a) The ectoderm; b) The endoderm; c) The mesoderm and endoderm; d) The ectoderm and endoderm; 32. What is the origin of the epithelium of the oral cavity? a) The mesoderm; b) Ectoderm; c) Mesenchyme; d) Visceral layer splanchnotome; 33. Sources of the epithelium (parenchyma) of the liver in embryogenesis? a) The ectoderm; b) The embryonic mesoderm; c) Trunk gut endoderm; d) Visceral layer splanchnotome; 34. Specify the source of the urinary system? a) Trunk somites; b) Splanchnotome; c) The embryonic ectoderm; d) Segmental leg mesoderm; 35. Fertilization - is: a) merger of the egg and sperm; b) the formation of the mesoderm; c) the formation of 3 germ layers; d) the formation of the epiblast and hypoblast. 36. From the cellular material of the primitive streak is formed: a) the endoderm and the notochord; b) the neural tube and the endoderm; c) mesoderm; d) intestinal tube. 37. What are the types of cleavage the birds: a) complete, uniform; b) complete, uneven; c) incomplete, discoid; d) incomplete, uneven; 38. Zygote - the embryo is: a) multicellular; b) unicellular; c) three-layer; d) single layer. 39. What is fertilization? Fertilization - is: a) the formation of a multicellular organism; b) the formation of the mesoderm c) the formation of 3 germ layers; d) the formation of the epiblast and hypoblast. 40. Embryogenesis - is: a) development of the embryo from the moment of fertilization until birth (viviparous) or up to hatching (in egg-laying b) the science of the development of the embryo; c) development and education of germ cells; d) the science of tissue development. 41. Type of cleavage in mammals: a) complete, uniform; b) complete, uneven; c) incomplete, discoid; d) incomplete, uneven; 42. Provisory organs – is: a) definitive organs; b) interim authority; c) embryonic organs; d) normal body; 43. Types egg cell in mammals: a) telolecithal, sharply telolecithal; b) mezoletsital, moderately telolecithal; c) secondary oligoletsital, izoletsital; d) secondary mezoteloletsital. 44. What features are sex cells: a) contain the haploid number of chromosomes, multiplies, high metabolic rate; b) contain a haploid number of chromosomes, not breed, low level of metabolism (suspended animation); c) contain the diploid number of chromosomes, multiplies, low metabolism; d) contain the diploid number of chromosomes, not breed, high metabolic rate. 45. Call of provisional bodies of birds: a) the yolk sac, allantois, serosa; b) the placenta, amnion, serosa; c) the allantois, the amnion, serosa, yolk sac; d) the placenta, allantois, yolk sac. 46. Blastula - is: a) a single-celled embryo; b) three-layer embryo; c) multicellular embryo, having a cavity; d) single-layer embryo. 47. The egg cells are classified according to: a) the duration of the external environment; b) the distribution of the yolk; c) the number of yolk and its distribution; g) the conditions of an animal (the external or internal environment) and the number of yolk; d) the type of crushing. 48. Call oogenesis periods: a) reproduction, growth, maturation, the formation; b) the reproduction, growth, maturation; c) reproduction, growth, formation; d) growth, maturation, reproduction. 49. What is formed from the primitive streak: a) the endoderm and the notochord; b) the neural tube and the endoderm; c) mesoderm; d) intestinal tube. 50. List of spermatogenesis periods: a) reproduction, growth, maturation, the formation; b) the reproduction, growth, maturation; c) reproduction, growth, formation; d) growth, maturation, reproduction 51. What day comes implantation human embryo a) the 1st day; b) 3-4th day; c) b-7th day; d) 10-14th day; e) 12-21th day of embryogenesis. 52. What happens when a capacitation: a) activation of sperm; b) recovering the enzyme from the spermatozoa; c) the formation of fertilization membranes; d) the loss of sperm flagellum; 53. Formation of human amnion starts with education: a) amniotic folds; b) the trunk folds; c) the amniotic bubble; d) extraembryonic mesoderm; 54. Fertilization of the egg takes place in a person: a) the abdominal cavity; b) uterus; c) the ampullary part of the oviduct; d) isthmic portion of the uterus; 55. Differons - is: a) the germ of embryonic tissue; b) the smallest unit of the structure of the living body; c) collection of cells constituting a tissue lineage; d) the collection of highly cells; e) the cell organelles. 56. The phase reproduction spermatogenesis occurs:: a) reduction division spermatocytes; b) the reduction division of spermatogonia; c) dividing mitotic spermatogonia; d) DNA replication in spermatocytes; 57. In the growth phase of spermatogenesis occurs: a) the prophase of the first meiotic division; b) the formation of sperm; c) dividing mitotic spermatogonia; d) reduction division spermatotsigov; 58. In the phase of maturation of spermatogenesis occurs: a) the formation of sperm; b) the mitotic division of spermatogonia; c) replication of DNA in spermatocytes; d) meiotic division spermatocytes; 59. In the phase of forming spermatogenesis occurs: a) conjugation of chromosomes in spermatocytes; b) crossing over; c) the formation of tetrads; d) transformation of spermatids. 60. The formation of male germ cells takes place in: a) straight tubules of the testis; b) network tubules of the testis; c) the convoluted tubules of the testis; d) efferent tubules of the testis; 61. List the stages of spermatogenesis in order? a) reproduction, growth, maturation, the formation; b) the reproduction, growth, maturation; c) reproduction, growth, formation, maturation; d) growth, maturation, reproduction, formation/ 62. In some periods of human life begins spermatogenesis and oogenesis a) newborn; b) coming of age; c) sexually mature; d) old 63. What stage of embryogenesis, which is formed by a single-celled fetus. a) blastula; b) gastrula; c) the zygote; d) morula 64. What are the stages of embryogenesis, in which a single layer is formed multicellular embryo. a) blastula; b) gastrula; c) the zygote; d) morula. 65. What stage of embryogenesis, which is formed multicellular embryo of a single layer. a) blastula; b) gastrula; c) the zygote; d) morula. 66. List all components of the spermatozoa: a) the head, the tail section; b) the tail section, neck; c) the head, terminal part; d) the head, bonding department. 67. What kind of blastula is characteristic of mammals? a) coeloblastula; b) disk blastula; c) a blastocyst; d) amfiblastula. 68. What are the sources of germ cells: c) mesoderm cells; b) gonocytes (gonoblast); c) cells of the ectoderm; d) endoderm cells. 69. Acrosome - is: a) binding of the head and tail of the spermatozoa department; b) a modified Golgi complex; c) the core of the spermatozoa head; g) terminal of the caudal region of the spermatozoa. 70. What constitutes the wall of the amnion: a) extraembryonic ectoderm, mesoderm visceral leaf; b) extraembryonic ectoderm, mesoderm extraembryonic parietal leaf; c) extraembryonic endoderm, visceral piece splanchnotome; d) extraembryonic endoderm, parietal leaf splanchnotome. 71. What is the function of the yolk sac: a) the gas exchange, secretory, trophic; b) blood-forming, education, primary germ cells, trophic; c) respiratory, trophic; d) excretory, gas exchange. 72. The period ends with the formation of cleavage: a) morula; b) two germ layers; c) blastula; d) zygote. 73. Progenez - is: a) the period from the moment of fertilization until birth, hatching out of the egg membranes, the end of metamorphosis; b) the science of the development of the embryo; c) the process of formation and development of germ cells; d) education gonoblast. 74. What shell egg mammals: a) the egg shell, under the egg shell, tunica; b) under the egg shell, shiny; c) shiny, radiant crown, oolemma; d) egg shells, radiant crown. 75. The inner shell of the yolk sac is formed by: a) the embryonic endoderm; b) embryonic ectoderm; c) extraembryonic endoderm; d) extraembryonic mesoderm. 76. Select the correct order of embryonic development a) fertilization, gastrulation, organogenesis, histogenesis, crushing b) fertilization, crushing, gastrulation, organogenesis, histogenesis c) fertilization, gastrulation, organogenesis, histogenesis d) fertilization, crushing, gastrulation, histogenesis, organogenesis 77. What is the source of a piece of embryonic spinal cord development a) endoderm; b) mesoderm; c) ectoderm; d) mesenchyme; 78. Any tissue develops from the mesoderm sclerotome? a) muscle tissue b) connective tissue a) Skeletal tissue g) blood 79. what days is happening implantation in? a) 7-8 days b) 5-6 days c) 1-5 days g) 48 hours 80. at what time is the development of germs and the formation of the placenta a) 3-8 weeks of development b) 15-20 weeks of developmentc) 20-24 weeks of development d) 7-8 days of development 81. What is happening in terms of the stage of accelerated growth of the brain a) 3-8 weeks of development b) 15-20 weeks of developmentc) 20-24 weeks of development d) 7-8 days of development 82. in which extraembryonic organs first formed blood vessels a) allantois b) the placenta c) the amnion d) the yolk sac 83. what kind of these tissues is characteristic of the umbilical cord a) reticulum b) mucosal tissue c) adipose tissue g) pigment tissue 84. from which embryonic rudiments of developing retina and optic nerve a) endoderm b) mesoderm c) the neural tube d) mesenchyme 85. as is called chorionic villi, they vascularized a) stem villi; b) anchor villi; c) tertiary villi; d) mature villi 86. The paramesonephric ducts in female embryos give rise to the: a) uterine tubes and uterus b) ovarian ligament c) inferior fifth of the vagina d) round ligament of the uterus 87. Capacitation of the sperm: a) is caused by the zona pellucida b) occurs in the male c) prevents polyspermy d) is essential for fertilization 88. The early stages of cleavage are characterized by: a) formation of a hollow ball of cells b) formation of the zona pellucida c) increase in the size of the cells in the zygote d) increase in the number of cells in the zygote 89. The first two intraembryonic germ layers to differentiate are the: a) ectoderm and hypoblast b) epiblast and hypoblast c) ectoderm and endoderm d) ectoderm and mesoderm 90. The blastocoele becomes the: a) amniotic cavity b) extraembryonic coelom c) the primary yolk sac d) chorionic cavity