Assessment of the Older Adult
advertisement

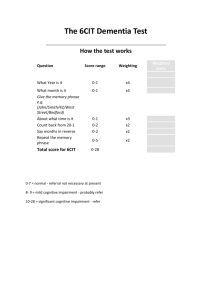
Utilizing Standardized Tools for Recreational Therapy Treatment With Geriatric Clients Jo Lewis, MS/CTRS Megan Janke, Ph.D., LRT/CTRS Upon successful completion of this session, the participant will be able to: Identify 3 standardized assessment tools that may be utilized in Recreational Therapy treatment with older adults. Verbalize 2 benefits of utilizing standardized assessments during Recreational Therapy treatment Utilize internet resources for standardized assessment tools in Recreational Therapy practice with older adults. Validity ◦ Does it measure what it is intended to measure? External Internal Reliability ◦ Does it consistently measure what is intended? Internal Consistency Inter-rater Reliability Responsiveness Can it detect real change when it happens? Measure what you intend to measure Justification of Services Accepted across discipline boundaries Brief Interview for Mental Status Short Portable Mental Status Questionnaire Blessed Orientation-Memory-Concentration Test Global Deterioration Scale Brief Cognitive Rating Scale Clock Drawing Test Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) Utilized for the MDS 3.0 Areas measured: ◦ attention ◦ orientation ◦ the ability to register and recall new information Maximum Score: 15 ◦ 13-15 ◦ 8-12 ◦ 0-7 Cognitively intact Moderate impairment Severe impairment 10 Items Maximum Score: 10 ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ 0-2 errors 3-4 errors 5-7 errors 8-10 errors Intact Mild impairment Moderate impairment Severe impairment 5-10 minutes to administer Domains assessed ◦ Orientation ◦ Immediate and delayed episodic recall ◦ Working memory 6 Items Maximum Score- 28 Higher score indicates greater impairment 3-6 minutes to administer Rating scale 1: 2: 3: 4: 5: 6: 7: No cognitive impairment Very mild cognitive decline Mild cognitive decline Moderate cognitive decline Moderately severe cognitive decline Severe cognitive decline Very severe cognitive decline Used with Brief Cognitive Rating Scale 5 Axes ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Concentration Recent Memory Past Memory Orientation ADL & Functional Abilities Each axis is measured on a scale of 1-7 ◦ Scores from each axis added then divided by 5 Higher scores indicate higher level of impairment Correlates well with other cognitive assessment instruments Visuospatial Assessment of Cognitive Functioning 6 point scoring system The higher the score, the greater the degree of impairment Score of 3 or more indicative of cognitive loss Completed in about 5 minutes Screening tool for mild cognitive dysfunction Cognitive Domains ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Attention and concentration Executive functioning Memory Language Visuoconstructional skills Conceptual thinking Calculations Orientation 10 Minutes to Administer Possible score of 30 ◦ 26 or above is considered normal Barthel Index Berg Balance Scale Katz Index of Independence in Activities of Daily Living Lawton Instrumental Activities of Daily Living Tinetti Mobility Scale ◦ Performance-Oriented Assessment of Balance ◦ Performance-Oriented Assessment of Gait Get-Up & Go Test Self-report ◦ 2-3 minutes Trained observation ◦ 10-15 minutes 3 point scale for each item Assesses: Feeding Grooming Bowel & Bladder Continence Dressing Toileting Walking Stairs Bathing Performance measure ◦ Self-report ◦ Trained observer Scoring ◦ Letter score from A-G A= Most independent G= Most dependent Bathing Dressing Toilet use Transfer ability Feed self Maintenance of bowel & bladder continence Self-report of Performance Scoring ◦ O= Low functioning ◦ 8= High functioning Gender bias◦ transportation Telephone usage Housekeeping* Food preparation* Laundry* Transportation Medications Money management 5 point scale Higher score indicates more difficulty with gait and balance Scoring 1 2 3 4 5 = = = = = Normal Very slightly abnormal Mildly abnormal Moderately abnormal Severely abnormal Score of greater than 3 at risk for falling Can be performed as a timed assessment 14 item scale 5 point scale, ranging from 0-4 Completion time: 15-20 minutes Equipment needed: Ruler Two standard chairs Footstool or step Stopwatch or wristwatch Scoring 41-56: Low fall risk 21-40: Medium fall risk 0-20: High fall risk 3 point scale per item Used in conjunction with Gait Assessment Assessment Process: Nudge on sternum Sitting in chair Rising from chair Immediate standing balance Standing balance Balance with eyes closed Turning balance Neck turning One leg standing balance Back extension Reaching up Bending down Sitting down 8 Items ◦ 2 point scale Assessment Process Initiation of gait Step height Step length Step symmetry Step continuity Path deviation Trunk stability Walk stance Turning while walking PHQ-9 Geriatric Depression Scale Zung Self-Rating Depression Scale Cornell Scale for Depression in Dementia Zung Self-Rating Anxiety Scale WHOQOL-BREF Part of the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ) ◦ PHQ-9- Depression Module Self-report Multiple choice Measures severity of depression Implemented in the MDS3.0 30 Questions ◦ Short version available- 15 questions Administration ◦ Self –administered ◦ Rater-administered Questionable with older adults with severe dementia Scoring ◦ >5 indicates potential depressionShould have a comprehensive assessment ◦ => 10 almost always indicative of depression Screening tool Self-report 20 items ◦ 4 point scale ◦ Half of the items are positively worded; half negatively Respondents rate frequency of occurrence Older adults score higher than other age groups Administration ◦ Observation ◦ Interview Patient Caregiver 3 Point Scale ◦ 0- Absent ◦ 1- Mild or intermittent ◦ 2- Severe Assessment Areas ◦ Mood related signs ◦ Behavioral disturbances ◦ Physical signs ◦ Cyclic functions ◦ Ideational disturbance Self-report 20 items ◦ 5 affective ◦ 15 somatic Score range: 20-80 Administration Time: 10-15 minutes Used in psychiatric and medical patients and with normal older adults Measures the impact of disease ◦ Impact of disease and impairment of daily activities and behavior ◦ Perceived health measures ◦ Disability/ functional status measures 26 Questions Self-Administered Interviewer assisted or administered Manual is recommended to score the assessment Faces Pain Scale Numeric Scale Pain Thermometer Brief Pain Inventory Checklist of Nonverbal Pain Indicators Pain Assessment in Advanced Dementia Scale Originally developed for pediatrics No verbal component ◦ Language impairments ◦ Difficulty with expression 7 point scale Self-rating Scale of 0-20 ◦ O= No pain ◦ 20= Pain as bad as it could be Scores can be averaged over time Widely used in clinical and research settings Originally developed for used with cancer patients Currently used with individuals experiencing chronic nonmalignant pain 16 items ◦ Measures pain and impact on daily function Completion time: 5 minutes (short form) Measures pain in older adults with cognitive impairment Observation during movement and at rest Scoring: 0 or 1 6 items Nonverbal, vocal complaints Facial grimacing Bracing Restlessness Rubbing Verbal, vocal complaints Observation Score ranges from 0-10 points 1-3 Mild pain 4-6 Moderate pain 7-10 Severe pain 5 Areas Assessed Breathing Negative vocalization Facial expression Body language Consolabilty BANDI-RT Utilizes information from MDS 3.0 Guides the therapist ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Identified problems Care plan Physician’s Orders RT treatment Flow sheet Iowa Geriatric Education Center Geriatric Assessment Tools ◦ http://www.healthcare.uiowa.edu/igec/tools/ Hartford Institue of Geriatric Nursing Try This ◦ http://hartfordign.org/practice/try_this/ Dementia Practice Guidelines for Recreational Therapy ◦ Buettner & Fitzsimmons (2003) Available through the ATRA Bookstore