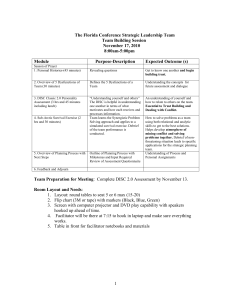
INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTERS 1

INTRODUCTION TO
COMPUTERS 1
BPC 101AA
The Pearson Custom Program for CIS,
BPC101AA, Introduction to Computers I,
Phoenix College; Copyright 2011 by
Pearson Learning Solutions
IDENTIFYING COMPUTER
COMPONENTS and THEIR FUNCTIONS
CHAPTER 2
LESSON ONE:
IDENTIFYING BASIC INPUT and
OUTPUT COMPONENTS
MONITORS:
Cathode Ray Tube (CRT)
On older computers
Uses a glass picture tube, similar to picture tubes in older televisions
Liquid Crystal Display (LCD)
Uses a fluorescent light behind a flat panel
Electrical charges make picture elements, or pixels
The number of pixels per inch displayed on the screen determines the resolution, or level of detail
More pixels per inch = higher resolution
THE MOUSE:
A device that controls a pointer on the screen
Mouse with a rubber ball
The rubber ball presses against 2 rollers that are perpendicular to each other
This action allows the pointer to move according to left-to-right position and the up-and-down position
Optical mouse
Uses reflected beams of light instead of rollers
Thumb mouse
The user moves a track ball directly to control the pointer
See Table 2 on page 51 for mouse instructions
Practice using the mouse on pages 52 - 53
Mouse Alternatives for
Notebook Computers
Pointing stick
A small knob that responds to sideways pressure
Touch pad
A small, rectangular, flat area that senses the position of your finger when you touch it
KEYBOARD:
Each keystroke is converted to a binary number that the computer understands
Function keys at the top can be programmed to perform special functions
Control Key, Alternate Key, Shift Key
Used in combination with other keys for special commands
Num Lock Key
A key that toggles the numeric keys’ function between the navigation arrows and numbers
Control, Alt, Delete Keys
Brings up a dialog box that enables you to close the program if it is not responding
OPTICAL DISCS:
Disks – Media used to store information using magnetic methods
Discs – Media used to store information using optical methods
Compact disc (CD) – Media used to store information as binary numbers (burning a pit for 0 and an unmarked surface, land, for 1)
Read-only drives – reads data on a disc, but can’t alter or write data on a blank disc
Writable drives – can write to writable discs
TYPES OF OPTICAL DISCS:
CD (compact disc)
CD-ROM: read-only memory
CD-R: blank disc that can be recorded on
CD-RW: can be written to and erased many times
DVD (digital video disc)
DVD-ROM: read-only that can be on 2 different layers and on both sides of the disc
DVD-R: can be written on once
DVD-RW: can be written on and erased many times
BLU-RAY – ability to store 25 gigabytes on a single-layer disc and 50 gigabytes on a double-layer disc
BD-ROM: read-only
BD-R: write once
BD-RE: erased and recorded many times
FLASH MEMORY
A type of memory that is not as fast as RAM, but does not require constant power
Compact flash cards – used in expensive cameras
Secure Digital (SD) cards & MicroSD cards – used in cameras, cell phones, smartphones, PDA’s
Flash drives, Thumb drives, USB drives – transports files from computer to computer and plugs into a USB port
Flash hard drives – used in notebook computers and don’t use as much energy as magnetic hard drives
EXTERNAL HARD DRIVE:
All computers come with an internal hard drive, which is the main storage unit in the computer
External hard drives are additional storage when the internal drive is full and to backup important data files.
PRINTERS:
Impact printer – typewriter technology in which a metal rod struck an ink-fused ribbon, and the impact transferred the ink to the paper to make a dot.
Dot matrix printer – produces patterns of dots that form text characters.
Laser printer – transferring powdered ink to paper, then heating the ink to make it stick to the paper.
Toner – powdered ink that is melted into the paper
Ink-jet printer – liquid ink that is directed to the paper using electric fields. Four colors (black, magenta, cyan, yellow) combine to produce all the other colors.
SPEAKERS:
Speakers are used to play music, videos, sound effects, speaking content of documents
External speakers
Monitors with built-in speakers
Subwoofer – a large speaker to play low bass notes
Speakers inside the computer’s system unit
To alert the user of a hardware problem
MICROPHONES:
Microphones pick up sounds and convert them to analog signals
The computer uses A to D converter to change the sounds into binary numbers
Voice recognition – computer programs that translate what you say into text for a document or e-mail
LESSON TWO:
IDENTIFYING SPECIALIZED INPUT
DEVICES
GAME CONTROLLERS:
Gamepad – a specialized input device to control the action in a computerized game
Joystick – a game controller that uses a rotating ball inside the case
Nintendo Wii – a wireless controller that enables you to play golf, tennis, the guitar, etc.
DIGITAL CAMERAS:
STILL and VIDEO
Uses light-sensitive detectors that convert the image into electrical signals and fed into an A to D converter
Megapixels (millions of pixels) – the higher number of megapixels means better resolution and larger picture sizes when the image is printed
1,280 x 960 = 1.2-megapixel image
4,000 x 3,000 = 12-megapixel image
DIGITAL CAMERAS:
STILL and VIDEO
Docking station – a place where the camera sits to transfer images to the computer
Flash memory or SD cards – removed from the camera and placed in a card reader that is connected by a wire to the computer to transfer images
DIGITAL CAMERAS:
STILL and VIDEO
Point-and-shoot camera – smallest and least expensive with automatic focus and shutter speeds
Digital single lens reflex (DSLR) camera – more expensive and larger. The photographer controls the settings.
DIGITAL CAMERAS:
STILL and VIDEO
Frames per second – the number of pictures taken by a digital video camera in one second.
It takes 30 frames per second to simulate smooth motion
It takes 15 frames per second for transmission over the
Internet
Web cams – video cameras that are attached to a computer for videoconferencing or monitoring
SCANNERS:
Scanners convert an image into digital data so a picture can be input into a computer
Flatbed scanner – a document is placed on a pane of glass and a fluorescent lamp travels the length of the document.
The reflected light converts to numbers using an A to D converter
Document scanner – uses a stationary lamp and the paper moves past the lamp. Used when many sheets of paper need to be scanned.
Optical character recognition (OCR) program – a computer program that recognizes the image and converts it to ASCII or Unicode number.
GRAPHICS TABLETS:
Used by architects, mechanical engineers, photographers, and animation artists to create drawings and process photographs
BAR CODE READER:
A narrow beam of light and sensor that converts the flickering reflection into binary numbers the computer can read.
They are used in conjunction with a database for pricing and inventory control for objects such as groceries, clothes, music CDs, etc.
RADIO FREQUENCY ID
(RFID)
A device that uses radio frequencies to remotely retrieve data
An example is in cars on toll highways. An
RFID device is attached to the windshield and the signal is read to deduct the toll amount from the driver’s account.
TOUCH SCREEN:
Monitors that act as input devices
Used in some stores to allow customers to check out
Stylus – a penlike device that is used to tap the screen
SENSORS and PROBES:
Sensor – detects the status of something and responds to changes in a predictable manner by producing an electric signal
Alarm systems
Probes – sensors that explore hard to access places
Oxygen sensor in the exhaust pipe of a car, probes that sense the movement of the earth
REMOTE CONTROLS:
Wireless devices used for appliances such as music
CD players, TVs, etc.
Infrared light – an invisible light that transmits the binary number to the appliance. The remote must be pointed to the infrared sensor on the appliance.
Radio waves – waves that transmit the binary number to the appliance. The waves spread out in all directions and do not have to be pointed at the appliance.
SECURITY DEVICES:
Passwords
Swipe cards
Biometric device – matches a user’s biological information such as fingerprint or retinal scan with patterns stored in a database to identify authorized users.
SPECIALIZED INPUT
DEVICES:
Adaptive computer devices – for use by people with special needs
Miniature keyboards
Keyboards with tactile surfaces
One-handed keyboards