MC D27 WS - Parkway C-2
advertisement

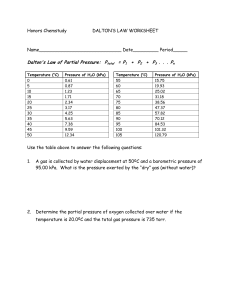
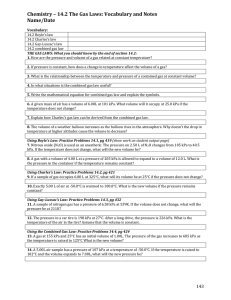
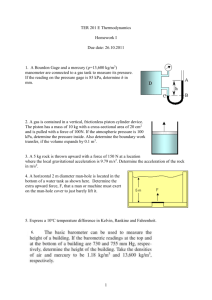
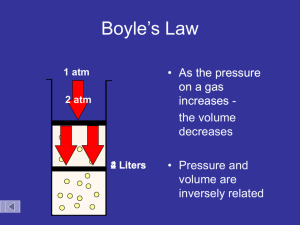
MC D27 WS Block: ____ Name: ________ Items for the test: There will be two one step and two multi step conversions. Practice these skills and make sure you remember the metric staircase. This time with scientific notation! Know how to set up a data table and properly plot pressure vs temperature, pressure vs volume, and volume vs temperature. Know how to determine the density of liquids and solids. Know the names and symbols for the first 18 elements (I will test you on 10). Be able to describe and identify the physical and chemical properties of a substance. Be able to distinguish between chemical and physical changes. Be able to identify and describe the five common states of matter. Be able to use KMT to explain the behavior of solids, liquids, and gases. Be able to explain pressure of a gas from a KMT viewpoint and predict changes in gas pressure due to changes in temperature, volume, and number of particles. Be able to explain and use the gas laws (combined, Charles’, Boyle’s, Gay-Luccas’) in solving simple gas law problems. You should have the combined gas law memorized. Be able to identify and describe phase changes using KMT and energy changes (endothermic or exothermic). Need to practice? Go back to your old worksheets and rework problems (the solutions are on the web in our handout section). Convert (use scientific notation in your answers): 1. 43.21 kg to g 2. 65.0 x 105 s to ks 3. 5.32 x 1075 mm to miles 4. 78 y to mm 5. Complete the table below for the three common states of matter found on earth. State Description 6. Identify (and compute if necessary) the chemical and physical properties below. A dull metal is in the shape of a rectangle with sides measuring 2.5 cm, 54 mm, and 2.75 cm. It has a mass of 0.069 kg. It is not easy to bend and will scratch surfaces. When placed on a hot plate with medium heat, it will heat up very quickly. Electrical current will also pass through the block of metal. When a flame is applied to the metal, it will not burn, but it will change shape and turn into a liquid. When placed in hydrochloric acid, the metal fizzes and makes tiny bubbles. List the physical properties of the solid List the chemical properties of the solid 7. For each gas law (combined, Charles’, Boyle’s, and Gay-Luccas’), provide the mathematical equation for the law. Draw graphs for Charles’, Boyle’s, and Gay-Luccas’ Laws. What type of relationship does each graph show? 8. Detail the six phase changes below. Name From To Type of Energy change KMT description 9. Describe the heating curve of a liquid as it goes from the liquid phase to the gas phase. 10. A gas has an initial volume of 30 L and is initially at a pressure of 200 kPa. It has a temperature of 300 K. The pressure is then changed to 50 kPa with the temperature remaining at 300 K. What is the new volume of the gas? 11. A gas has a volume of 20 L and a pressure of 103 kPa, and a temperature of 20 oC. The volume is reduced to 0.5 L and the temperature rises to 90 oC. What is the new pressure of the gas? 12. A gas has a volume of 5.5 L and a temperature of -7 oC. If the temperature is raised to 75 oC, what is the new volume if the pressure remains constant? 13. A sickly yellow gas fills a 15 L clear reaction vessel at 300 K. The vessel is closed and has a pressure of 110 kPa. The vessel is then heated to 900 K but the volume of the vessel does not change. What is the new pressure of the system now? 14. At 700 oC, the final pressure of a gas in a five L container was found to be 510,000 Pa. If the initial temperature of the gas was 105 oC, what was its initial pressure? (Note that the volume was constant). 15. Suppose a gas in a stretchy balloon is initially at 25 oC and occupies a volume of eleven liters at 202 kPa. The temperature is increased to 50 oC and the pressure is increased to 303 kPa. What is the new volume of the gas? 16. A bicycle tire has a constant air volume of 310 mL. It initially is at 4.95 x 105 Pa at 295 K. Once the tire is warmed up by being ridden, it has a temperature of 375 K. What is the new pressure of the tire?