Introduction to Photosynthesis—Online Notes Visit http://www
advertisement

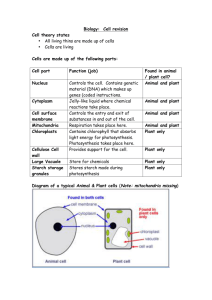
Introduction to Photosynthesis—Online Notes Visit http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/biocoach/photosynth/intro.html and proceed through the Photosynthesis—BioCoach Activity to complete this noteguide. ***Some questions may require you to use your textbook (pgs.*** An Overview of Photosynthesis Photosynthesis converts _______________ energy into the _________________energy of _____________ and other organic compounds. This process consists of a series of chemical reactions that require ______________________ (CO2) and _______________ (H2O) and store _______________ energy in the form of _______________. _____________ energy from the sun drives the reactions. __________________ (O2) is a _________________ of photosynthesis and is ____________________ into the ______________________. Write the equation which summarizes photosynthesis: Photosynthesis transfers ___________________from __________________ to energy-poor CO2 molecules, forming energy-rich ____________________ molecules. This electron transfer is an example of an ______________________________ process: the _______________is oxidized (_____________________) and the _______ is reduced (______________________). Photosynthesis uses light energy to drive the electrons from water to their more energetic states in the sugar products, thus converting solar energy into chemical energy. Label the diagram below: Extension Question (use textbook, p. 113): 1. What do you call the organisms that are able to make their own energy (food) through photosynthesis or by breaking down chemical bonds? 2. What do you call the organisms that must obtain their energy by consuming other organisms? Electromagnetic Energy The solar energy called ____________________________ drives photosynthesis. Solar radiation is composed of _______________________ energy that travels through space in a manner analogous to the motion of ___________ in water. The distance between the ______________ of waves is called the __________________. The ____________ the ___________________, the ____________ the _____________ for each unit (photon) of electromagnetic energy. __________________ cannot be created or destroyed. When light is _________________ by a green plant, a small portion of that energy is __________________ into chemical energy in the process of photosynthesis. The Action Spectrum for Photosynthesis A classic experiment reveals which _________________________work best for photosynthesis. The ______________ molecules (chlorophyll) in photosynthetic organisms ________________ specific __________________of light. In 1883, Thomas Engelmann devised an experiment to learn which _____________________ (__________) of light were the most effective in carrying out photosynthesis in the green alga ______________________. Extension Questions: 3. Which are the wavelengths (state the colors) of light that work best for photosynthesis, based on the graph of oxygen released by the Spirogyra? 4. Which wavelengths of light (state the colors) are absorbed by chlorophyll (used for photosynthesis)? Which wavelength (state the color) is transmitted by chlorophyll (color of the leaf that is visible to the human eye)? Read over the Structure of a Leaf and Structure of a Mesophyll Cell sections. Chloroplast Structure __________________________ are the sites of ____________________. These double-membrane bound organelles enclose additional membranes called _____________________. The disc-shaped ___________________ possess an interior space. The thylakoids are stacked to form _________________, which are suspended in the ______________ of the chloroplasts. Color and label the diagram of the chloroplast below (you may use your textbook to help you): Extension Question (use textbook): In which part of the chloroplast does photosynthesis occur? Chlorophyll ___________________ molecules embedded in the _______________ membrane absorb ___________ energy. These molecules are the most important __________________ for __________________ the light energy used in photosynthesis. Extension Questions (use textbook): 5. What are the two types of chlorophyll that absorb light energy for photosynthesis? 6. What are the different wavelengths of light absorbed by these two types of chlorophyll? How do these correspond with the wavelengths of light in Engelmann’s experiment in 1883? Cooperation of the Light Reactions and the Calvin Cycle Photosynthesis depends on an interaction between two sets of reactions: the _________________________ and the _______________________. ______________________ and the other molecules responsible for the light reactions are built into the_________________ membranes. The enzymes that catalyze the Calvin cycle are located in the __________________. Beginning with the ____________________ of light by ______________________, the light reactions convert ___________energy into _______________ energy in the form of ___________and _____________. The ATP provides the _____________, and the NADPH supplies the _________________ for the ______________________, which converts _____________________ to ______________. The ADP and NADP+ that result from the ___________________ shuttle back to the _____________________, which regenerate _________________ and ____________________. Complete the diagram below: Extension Questions (Click on “A Closer Look”, in the top right corner of your brower window): Step 1-Light Reaction: 7. What are the two pieces of “equipment” in the thylakoid membrane used to produce ATP and NADPH from light energy in the light reaction? 8. Where does the energy absorbed from light initiate a transfer of electrons to other molecules? Step 2-Dark Reaction (The Calvin Cycle): The Calvin cycle uses _______________ and _________________ to convert _____________ molecules of CO2 to ______________molecule of a ____-carbon sugar. The plant can then use this small sugar to make ___________________ such as glucose and many other organic compounds. The main role of the _______________ _____________ is to restock the stroma with the _________ and ________________ required for the Calvin cycle. Introduction to Photosynthesis—BioCoach Self Quiz Score: /24 Answer the questions on the BioCoach self quiz. You only need to answer the questions listed below (the other questions are important, but not directly related to our objectives). If you get the question wrong, put an X over that number. Write out the correct answers (DON’T use just letters). At the end of the quiz, record your score—your score will be out of 24. Raise your hand to show the teacher your score to get full credit for completing the self-quiz. 3. Most of the carbon dioxide used in photosynthesis is derived from the ______the atmosphere. 4. If photosynthesis on this planet were to stop____________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________. 5. Which of the following is not required for photosynthesis? 6. Which part of the leaf is most active during photosynthesis? 11. The conversion of light energy into chemical energy takes place in _______________________________. 12. The products of the light reaction of photosynthesis are___________________________________ 13. The most efficient wavelengths of light for photosynthesis are__________________________. 15. Oxygen released during photosynthesis comes from _____________________. 16. During photosynthesis, what is incorporated into existing organic molecules to build carbohydrates? 17. ATP __________________________________________________________________________________________ 19. Light reactions of photosynthesis cannot occur in the absence of ______________________________________. 25. During photosynthesis, electrons extracted from ____________ during the light reactions eventually turn up in ______________made during the Calvin Cycle. These electrons are transferred from the light reactions to the Calvin Cycle by ___________.