NATIONAL-SUPREMACY
advertisement

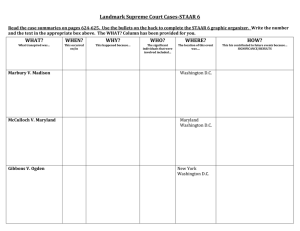
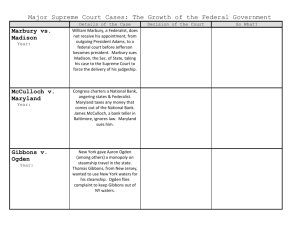
NATIONAL SUPREMACY • Facts of the Case: • Associations of companies that create, publish, distribute, sell and/or rent video games brought a declaratory judgment action against the state of California in a California federal district court. The plaintiffs brought the claim under the First and Fourteenth Amendments seeking to invalidate a newly- enacted law that imposed restrictions and labeling requirements on the sale or rental of "violent video games" to minors. • The district court found in favor of the plaintiffs and prevented the enforcement of the law. • On appeal, the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Ninth Circuit affirmed, holding that: (1) violent video games did not constitute "obscenity" under the First Amendment, (2) the state did not not have a compelling in interest in preventing psychological or neurological harm to minors allegedly caused by video games, and (3) even if the state had a compelling interest, the law was not narrowly tailored enough to meet that objective. Supremacy Clause • Article VI, Paragraph 2 • Federal GOV trumps state Gov, and states cannot make laws to counter national law. McCulloch v. Maryland • National Banks were creating competition with state banks. • Maryland starting taxing a branch of the national bank. • Cashier, McCulloch, refused to pay the tax. • State courts decided in favor of Maryland, it went to the Supreme Court on appeal Strict Constructionists v. Loose Constructions • To read the Constitution strictly • Or to read it openly • WHAT DOES NECESSARY AND PROPER MEAN? The Supreme Court Decision • Marshall decided to read the constitution openly • Determined that if it was necessary for the federal government to open a bank, to carry out its actions, they could. • Therefore, not allowing the states to tax the federal GOV. • McCulloch wins! GIBBONS v. OGDEN • Odgen was given the sole job of running steamboats out of New York • Gibbons ran boats illegally without the permission of New York • Odgen sued Gibbons • Odgen won in the state courts, Gibbons appealed to The Supreme Courts. SUPREME COURT DECISION • Defined and broadened the meaning of commerce. • Commerce included all business dealings, such as steamboat travel. • Ruled against Ogden, saying Gibbons had to have the right to compete. United States v. Lopez • Lopez 1990, was charged in violation of the Gun-Free School Zones act… • Federal lawyers argued Interstate Commerce? How? • Lopez’s lawyers argued criminal statues… How? • Who won?