vlan
advertisement

Chapter 8
VLAN
&
VPNs
By Dr.Sukchatri P.
VLAN & VPNs
Objectives
Upon completion of this chapter, you will
be able to perform the following tasks:
• Configure a VLAN
• Configure VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP)
• Configure a switch for trunking
• Verify VLAN connectivity
• Verify spanning-tree operations
VLAN & VPNs
Contents
• A switch connecting three segments
• Configuration VLAN (Cisco)
• Private network
• Hybrid network
• Virtual private networks
• VPN techniques
• Authentication
• Encryption
• Tunneling
• Addressing in VPN
VLAN & VPNs
VLAN Overview
• Segmentation
3rd floor
• Flexibility
2nd floor
• Security
1st floor
SALES
HR
ENG
A VLAN = A broadcast domain = Logical network (subnet)
VLAN & VPNs
A switch connecting three segments
VLAN & VPNs
A switch using VLAN software
VLAN & VPNs
Two switches
in a backbone
using VLAN
software
VLAN & VPNs
VLAN Operations
Switch A
Red
VLAN
Black
VLAN
Green
VLAN
• Each logical VLAN is like a separate physical bridge
VLAN & VPNs
VLAN Operations
Switch A
Switch B
Trunk
Fast Ethernet
Red
VLAN
Black
VLAN
Green
VLAN
Red
VLAN
Black
VLAN
Green
VLAN
• Each logical VLAN is like a separate physical bridge
• VLANs can span across multiple switches
• Trunks carries traffic for multiple VLANs
VLAN & VPNs
VLAN Membership Modes
Static VLAN
Dynamic VLAN
Trunk
Port e0/4
Port e0/9
VLAN5
VLAN10
VMPS
1111.1111.1111 = vlan 10
MAC = 1111.1111.1111
VLAN & VPNs
ISL Tagging
ISL trunks enable VLANs across a backbone
• Performed with ASIC
VLAN Tag added
by incoming
port
• Not intrusive to client
stations, client does not see
the ISL header
Inter-Switch
Link carries
VLAN identifier
• Effective between switches,
routers and switches,
switches and servers with
ISL network interface cards
VLAN Tag
stripped by
forwarding port
VLAN & VPNs
ISL Encapsulation
ISL Header
26 bytes
DA
Type User
Encapsulated Ethernet frame
CRC
4 bytes
SA LEN AAAA03 HSA VLAN BPDU
BPDU INDEX RES
VLAN
BPDU
• Frames encapsulated with ISL header and CRC
• Support for many VLANs (1024)
• VLAN field
• BPDU bit
VLAN & VPNs
VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP)
• A messaging system that advertises VLAN configuration information
• Maintains VLAN configuration consistency throughout a common
administrative domain
• VTP sends advertisements on trunk ports only
• Support mixed media trunks (Fast Ethernet, FDDI, ATM)
VTP Domain “ICND”
3.Sync to the latest vlan information
2
1.“new vlan added”
VLAN & VPNs
VTP Modes
• Create vlans
• Modify vlans
• Delete vlans
• Sends/forwards
advertisements
• Synchronize
• Saved in NVRAM
• Sends/forwards
advertisements
• Synchronize
• Not saved in
NVRAM
Transparent
VLAN & VPNs
• Create vlans
• Modify vlans
• Delete vlans
• Forwards
advertisements
• Does not
synchronize
• Saved in NVRAM
How VTP Works
• VTP advertisements are sent as multicast frames
• VTP servers and clients synchronized to latest revision number
• VTP advertisement are sent every five minutes or when there is a change
VLAN & VPNs
How VTP Works
• VTP advertisements are sent as multicast frames
• VTP servers and clients synchronized to latest revision number
• VTP advertisement are sent every five minutes or when there is a change
1.Add new VLAN
2.Rev 3 --> Rev 4
3
Server
3
4.Rev 3 --> Rev 4
5.Sync new vlan info
4.Rev 3 --> Rev 4
5.Sync new vlan info
Client
Client
VLAN & VPNs
VTP Pruning
•
Increases available bandwidth by reducing unnecessary flooded traffic
•
Example: Station A sends broadcast, broadcast is only flooded toward
any switch with ports assigned to the red VLAN
Port 2
Switch 4
Flooded
traffic is
pruned
B
Switch 2
Red
VLAN
Switch 5
Port 1
Switch 6
Switch 3
VLAN & VPNs
Switch 1
A
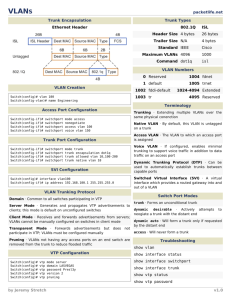
VLAN Configuration
Guidelines
• Maximum number of VLANs is switch-dependent
• Catalyst 1900 supports 64 VLANs with a separate
spanning tree per VLAN
• VLAN1 is One of the factory default VLANs
• CDP and VTP advertisements are sent on VLAN1
• Catalyst 1900 IP address is in the VLAN1 broadcast
domain
• Must be in VTP server or transparent mode to
create, add, or delete VLANs
VLAN & VPNs
VLAN Configuration Steps
• Enable VTP (optional)
• Enable trunking
• Create VLANs
• Assign VLAN to ports
VLAN & VPNs
VTP Configuration Guidelines
• VTP domain name
• VTP mode (server/client/transparent)—VTP server
mode is the default
• VTP pruning
• VTP password
• VTP trap
Use caution when adding a new switch into an existing domain.
A new switch should be added in client mode to prevent the new
switch from propagating incorrect VLANs information
Use the delete vtp command to reset the VTP revision number
VLAN & VPNs
Creating a VTP Domain
wg_sw_a(config)#
vtp [server | transparent] [domain domain-name] [trap {enable | disable}]
[password password] [pruning {enable | disable}
VLAN & VPNs
Creating a VTP Domain
wg_sw_a(config)#
vtp [server | transparent] [domain domain-name] [trap {enable | disable}]
[password password] [pruning {enable | disable}
wg_sw_a#conf terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z
wg_sw_a(config)#vtp transparent
wg_sw_a(config)#vtp domain switchlab
VLAN & VPNs
Verifying VTP Configurations
wg_sw_a#show vtp
VLAN & VPNs
Verifying VTP Configurations
wg_sw_a#show vtp
wg_sw_a#show vtp
VTP version: 1
Configuration revision: 4
Maximum VLANs supported locally: 1005
Number of existing VLANs: 6
VTP domain name
: switchlab
VTP password
:
VTP operating mode : Transparent
VTP pruning mode
: Enabled
VTP traps generation : Enabled
Configuration last modified by: 10.1.1.40 at 00-00-0000 00:00:00
VLAN & VPNs
Defining a Trunk
wg_sw_a(config-if)#
trunk [on | off | desirable | auto | nonegotiate]
• On = Set trunk on and negotiate with other side
• Off = Set trunk off and negotiate with other side
• Desirable = Negotiate with other side.
Trunk on if other side is on, desirable, or auto
• Auto = Will be a trunk only if the other side is on or desirable
• Non-negotiate = Set trunk on and will not negotiate
VLAN & VPNs
Defining a Trunk
wg_sw_a(config-if)#
trunk [on | off | desirable | auto | nonegotiate]
• On = Set trunk on and negotiate with other side
• Off = Set trunk off and negotiate with other side
• Desirable = Negotiate with other side.
Trunk on if other side is on, desirable, or auto
• Auto = Will be a trunk only if the other side is on or desirable
• Non-negotiate = Set trunk on and will not negotiate
wg_sw_a#conf terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z
wg_sw_a(config)#interface f0/26
wg_sw_a(config-if)#trunk on
First trunk port(Port A)
VLAN & VPNs
Verifying a Trunk
wg_sw_a#show trunk [A | B]
VLAN & VPNs
Verifying a Trunk
wg_sw_a#show trunk [A | B]
wg_sw_a#show trunk a
DISL state: On, Trunking: On, Encapsulation type: ISL
VLAN & VPNs
Adding a VLAN
wg_sw_a(config)#
vlan vlan#
[name vlan-name]
VLAN & VPNs
Adding a VLAN
wg_sw_a(config)#
vlan vlan#
[name vlan-name]
wg_sw_a#conf terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z
wg_sw_a(config)#vlan 9 name switchlab2
VLAN & VPNs
Verifying a VLAN
wg_sw_a#show vlan [vlan#]
VLAN & VPNs
Verifying a VLAN
wg_sw_a#show vlan [vlan#]
wg_sw_a#sh vlan 9
VLAN Name
Status Ports
------------------------------------------------9 switchlab2
Enabled
------------------------------------------------VLAN Type
SAID MTU Parent RingNo BridgeNo Stp Trans1 Trans2
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------9 Ethernet
100009 1500
0
1
1
Unkn 0
0
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
VLAN & VPNs
Modifying a VLAN Name
wg_sw_a(config)#
vlan vlan# name vlan-name
wg_sw_a#conf terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z
wg_sw_a(config)#vlan 9 name switchlab90
wg_sw_a#show vlan 9
VLAN Name
Status Ports
-----------------------------------------------9 switchlab90
Enabled
------------------------------------------------
VLAN & VPNs
Assigning Switch Ports to a
VLAN
wg_sw_a(config-if)#
vlan-membership {static {vlan#} | dynamic}
VLAN & VPNs
Assigning Switch Ports to a
VLAN
wg_sw_a(config-if)#
vlan-membership {static {vlan#} | dynamic}
wg_sw_a#conf terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z
wg_sw_a(config)#interface ethernet 0/8
wg_sw_a(config-if)#vlan-membership static 9
VLAN & VPNs
Verifying VLAN Membership
wg_sw_a#show vlan-membership
VLAN & VPNs
Verifying VLAN Membership
wg_sw_a#show vlan-membership
wg_sw_a#show vlan-membership
Port VLAN Membership Type
-------------------------------------------1
5
Static
2
1
Static
3
1
Static
4
1
Static
5
1
Static
6
1
Static
7
1
Static
8
9
Static
Port VLAN Membership Type
----------------------------------------13
1
Static
14
1
Static
15
1
Static
16
1
Static
17
1
Static
18
1
Static
19
1
Static
20
1
Static
Note: port 1=e0/1, port 2=e0/2 .....
VLAN & VPNs
Verifying Spanning Tree
wg_sw_a#show spantree {vlan number}
VLAN & VPNs
Verifying Spanning Tree
wg_sw_a#show spantree {vlan number}
wg_sw_a#show spantree 1
VLAN1 is executing the IEEE compatible Spanning Tree Protocol
Bridge Identifier has priority 32768, address 0050.F037.DA00
Configured hello time 2, max age 20, forward delay 15
Current root has priority 0, address 00D0.588F.B600
Root port is FastEthernet 0/26, cost of root path is 10
Topology change flag not set, detected flag not set
Topology changes 53, last topology change occured 0d00h17m14s ago
Times: hold 1, topology change 8960
hello 2, max age 20, forward delay 15
Timers: hello 2, topology change 35, notification 2
Port Ethernet 0/1 of VLAN1 is Forwarding
Port path cost 100, Port priority 128
Designated root has priority 0, address 00D0.588F.B600
Designated bridge has priority 32768, address 0050.F037.DA00
Designated port is Ethernet 0/1, path cost 10
Timers: message age 20, forward delay 15, hold 1
VLAN & VPNs
Visual Objective
SUBNET
10.1.1.0
10.2.2.0
10.3.3.0
10.4.4.0
10.5.5.0
10.6.6.0
10.7.7.0
10.8.8.0
10.9.9.0
10.10.10.0
10.11.11.0
10.12.12.0
10.13.13.0
VLAN
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
POD
wg_ro_x, wg_sw_x, core_sw_a
wg_pc_a, core_server
wg_pc_b, core_server
wg_pc_c, core_server
wg_pc_d, core_server
wg_pc_e, core_server
wg_pc_f, core_server
wg_pc_g, core_server
wg_pc_h, core_server
wg_pc_i, core_server
wg_pc_j, core_server
wg_pc_k, core_server
wg_pc_l, core_server
ISL
VLAN2
wg_pc_a
10.2.2.12
fa0/26 e0/1
(port A)
e0/2
wg_sw_a
10.1.1.10
VLAN13
fa0/26 e0/1
(port A)
...
fa0/1
fa0/24
core_ server ISL
10.x.x.1
e0
core_sw_a
10.1.1.2
VLAN & VPNs
wg_sw_l
ISL 10.1.1.120
fa0/12
wg_ro_a
10.1.1.11
wg_pc_l
10.13.13.12
e0/2
e0
wg_ro_l
10.1.1.121
Visual Objective
SUBNET
10.1.1.0
10.2.2.0
10.3.3.0
10.4.4.0
10.5.5.0
10.6.6.0
10.7.7.0
10.8.8.0
10.9.9.0
10.10.10.0
10.11.11.0
10.12.12.0
10.13.13.0
VLAN
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
POD
wg_ro_x, wg_sw_x, core_sw_a, core_sw_b
wg_pc_a, core_server
wg_pc_b, core_server
wg_pc_c, core_server
wg_pc_d, core_server
wg_pc_e, core_server
wg_pc_f, core_server
wg_pc_g, core_server
wg_pc_h, core_server
wg_pc_i, core_server
wg_pc_j, core_server
wg_pc_k, core_server
wg_pc_l, core_server
wg_pc_a
10.2.2.12
VLAN2
fa0/26 e0/1
(port A)
fa0/27
(port B)
wg_sw_a
10.1.1.10
wg_pc_l
10.13.13.12
VLAN13
fa0/26
(port A) e0/1
fa0/27
(port B)
wg_sw_l
10.1.1.120
...
ISL
fa0/1
fa0/24
core_ server
10.x.x.1
ISL
core_sw_a
10.1.1.2
VLAN & VPNs
ISL
...
fa0/12
fa0/13
fa0/1
ISL
fa0/12
fa0/13
fa0/14
ISL fa0/14
core_sw_b
10.1.1.4
ISL
Private network
VLAN & VPNs
Hybrid network
VLAN & VPNs
Virtual private networks
VLAN & VPNs
VPN techniques
VLAN & VPNs
Authentication
VLAN & VPNs
Encryption
VLAN & VPNs
Tunneling
VLAN & VPNs
Addressing in VPN
VLAN & VPNs
Summary
After completing this chapter, you should
be able to perform the following tasks:
• Configuring VLAN
• Configuring VTP
• Configuring a trunk
• Verifing Spanning Tree Operations
VLAN & VPNs
Review Questions
1. What are the three VTP modes?
2. Over what type of port can VTP
advertisements be sent?
3. VLAN ID is carried in the ________
header.
4. How do we assign a VLAN to a port?
VLAN & VPNs