Fluidity of Cell Membranes Discussion Questions
advertisement
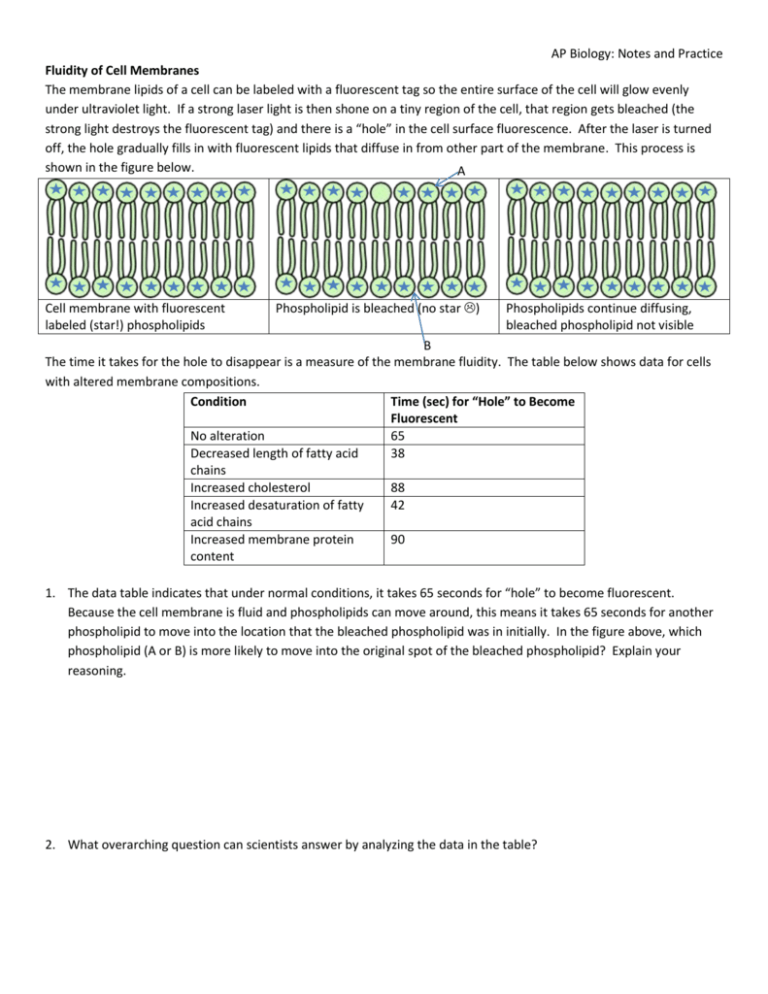
AP Biology: Notes and Practice Fluidity of Cell Membranes The membrane lipids of a cell can be labeled with a fluorescent tag so the entire surface of the cell will glow evenly under ultraviolet light. If a strong laser light is then shone on a tiny region of the cell, that region gets bleached (the strong light destroys the fluorescent tag) and there is a “hole” in the cell surface fluorescence. After the laser is turned off, the hole gradually fills in with fluorescent lipids that diffuse in from other part of the membrane. This process is shown in the figure below. A Cell membrane with fluorescent labeled (star!) phospholipids Phospholipid is bleached (no star ) Phospholipids continue diffusing, bleached phospholipid not visible B The time it takes for the hole to disappear is a measure of the membrane fluidity. The table below shows data for cells with altered membrane compositions. Condition Time (sec) for “Hole” to Become Fluorescent No alteration 65 Decreased length of fatty acid 38 chains Increased cholesterol 88 Increased desaturation of fatty 42 acid chains Increased membrane protein 90 content 1. The data table indicates that under normal conditions, it takes 65 seconds for “hole” to become fluorescent. Because the cell membrane is fluid and phospholipids can move around, this means it takes 65 seconds for another phospholipid to move into the location that the bleached phospholipid was in initially. In the figure above, which phospholipid (A or B) is more likely to move into the original spot of the bleached phospholipid? Explain your reasoning. 2. What overarching question can scientists answer by analyzing the data in the table? AP Biology: Notes and Practice 3. In addition to lipids, the cell membrane contains proteins. a. Based on the data in the table, does protein add to a cell membrane’s fluidity, or make the membrane more rigid? Explain your answer. b. Based on your knowledge of protein structure, why does your response to part a make sense? 4. Which alterations to the cell membrane allow for faster repair after a hole is made? For each alteration listed, propose an explanation as to why it allows for faster repair.








