The Plasma Membrane
advertisement
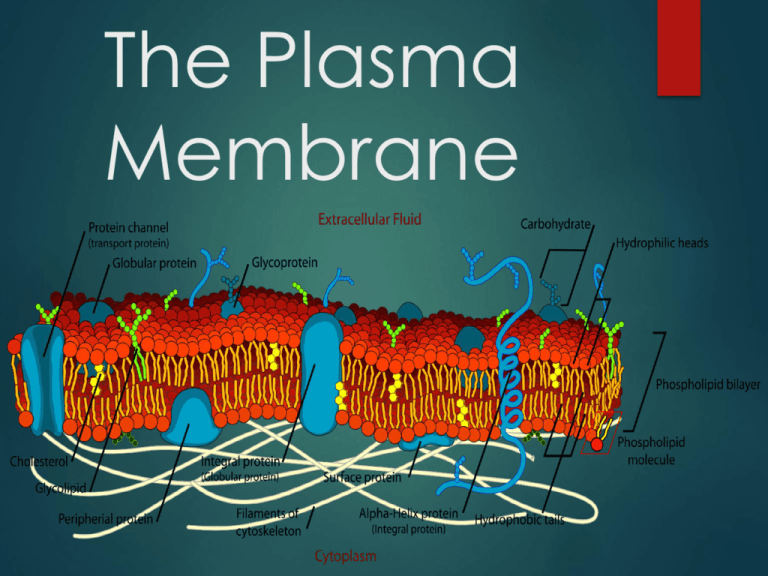
The Plasma Membrane The Plasma Membrane Also called cell membrane Cell’s boundary Maintains cell’s shape Protects the cell Controls what goes in and out of the cell Plasma membrane Termed the phospholipid bilayer Made of phospholipids A bilipid layer – 2 layers Fluid Mosaic Model Structure Flexible membrane Phospholipids can move side to side or flip-flop Acts like an oil Composition Other molecules in the membrane are like a mosaic Different “textures” and “patterns” (proteins and carbs, etc) Phospholipids Polar head (phosphate) Can form hydrogen bonds Hydrophilic Nonpolar tails (fatty acids) Hydrophobic Phospholipids Water inside the cell and water outside the cell Orient themselves Heads face water Tails face inside The Plasma Membrane Within it there are: Proteins Cholesterol Carb chains Within the cell there is: Cytoskeleton – Why? For structure/support Protein Channels – What do they do? Transports substances in/out of the cell Normally they can’t get in (ex: glucose or sodium) Receptors – What do they do? detect and respond to a signal Intracellular Within the cell Carries signal to an area of the cell Ex: steroids affect DNA/genes Membrane Signal molecule binds to a receptor Receptors starts a chain of events Causes a response Cholesterol – What does it do? Makes membrane more fluid able to change shape Less rigid/more flexible More space = more fluid (liquidlike) Carb Chains – What do they do? Carbs attached to: The membrane (glycolipid) A protein (glycoprotein) Tells immune system that these are “self” cells All cells have them as “identifiers” Selective Permeability What does this mean? Some substances can get in and out Small and/or uncharged = Large and/or charged = can get in/out without help can’t get in without help How does this relate to homeostasis? Plasma Membrane Videos https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6fhbbFd4icY (Amoeba Sisters – Homeostasis) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=S7CJ7xZOjm 0 (Bozeman Science) Building the Membrane! Build your own plasma membrane! Use foam shapes, pipe cleaners, markers, and more to make a model of what the plasma membrane could look like. This will vary between students, but make sure to include carb chains (glycoproteins, glycolipids, and carbohydrates), proteins (channels and receptors), cholesterol, and phospholipids







