Substitution reactions of benzene
advertisement

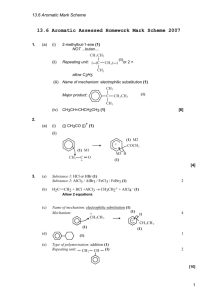
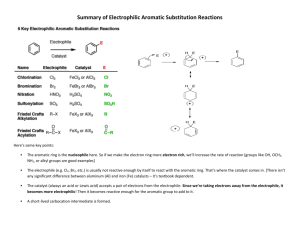
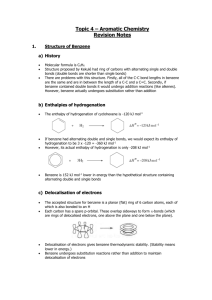
Substitution reactions of benzene L.O.: Outline the mechanism for mononitration and monohalogenation of benzene. Homework Q: 1&3 Extension: Q2 Recap questions • What are the three sources of evidence which led to the delocalised electron model of benzene? • Why is benzene less reactive than alkenes? Starter activity • What is the name for the reaction between bromine and ethene? • Draw the mechanism for it • Define the term “nucleophile” Reactions involving benzene • Benzene is more stable than alkenes, therefore less reactive • Won’t react with halogens at RTP without a catalyst • Will usually undergo electrophilic substitution reactions STRUCTURE OF BENZENE H H C H C C C C H C H H STRUCTURE OF BENZENE STRUCTURE OF BENZENE NITRATION NO2 + + HNO3 nitrobenzene Conditions conc HNO3 conc H2SO4 catalyst 50ºC H2O Electrophile curly arrow NITRATION – ELECTROPHILIC SUBSTITUTION Formation of electrophile + HNO3 + H2SO4 NO2 + HSO4- + H2O nitronium ion Reaction of electrophile with aromatic compound + NO2 + NO2 H + -H H+ + HSO4- → H2SO4 NO2 NITRATION CH3 CH3 NO2 Equation (name product) Conditions Mechanism NITRATION CH3 CH3 NO2 + HNO3 + 2-methylnitrobenzene Conditions conc HNO3 conc H2SO4 catalyst 50ºC H2O NITRATION Uses of nitro compounds: 1) as explosives 2) to make aromatic amines (used to make dyes) CH3 O2N NO2 NO2 1,3,5-trinitrotoluene TNT Name the mechanism for this reaction. Electrophilic substitution Reactions with halogens • React in the presence of a catalyst called a halogen carrier Benzene + Chlorine Chlorobenzene + Hydrochloric acid Common halogen carriers are FeCl3, AlCl3 and AlBr3 Reactions with halogens –mechanism of reaction • Electrophilic substitution Br2 + FeBr3 → Br+ + FeBr4- • The halogen carrier reacts with the halogen molecule to produce the halide ion which then goes on to react with the benzene o OCR past paper Q Reactivity of cyclohexene vs benzene (4 marks) Comparing benzene with alkenes o o o o benzene is more stable (1) benzene π electrons are delocalised (1) benzene has lower electron density (1) so bromine is less polarised /attracted to it / benzene is less susceptible to electrophiles (1) Finishing off • Draw the complete mechanism for the nitration of benzene. Include the reaction conditions and catalyst • Draw the complete reaction for the chlorination of benzene