Chemistrypp
advertisement

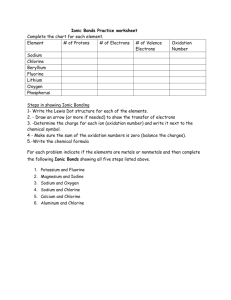
• Make two columns on a sheet of paper. Title 1 column Physical Changes and the 2nd column title Chemical Changes. • From the next slide, categorize each item either physical or chemical change. PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL Change? Candle wax melting Wood burning Cake baking Ice freezing Iron rusting Salt dissolved in water Fireworks exploding Leaves Cooking an egg changing colors Breaking an egg Cutting paper Water boiling Mixing baking soda and water Tarnished silver Battery corrosion Chemistry Background • In order for elements to be completely stable (or un-reactive) they need to have 8 electrons in their outside energy level. • An element with 8 electrons on its last level is a happy element. The “happiest” elements on the table are the noble gases. • Exception: Helium is happy with two electrons in its outer energy level. Selection Process • Sodium contains 1 valence electron on its outside shell. It is very unhappy and unstable. It needs a “partner” to balance it out. But, only one type of “partner” will do. It must have 7 valence electrons! Match • Chlorine looks like a good partner because it has 7 valence electrons! • Draw a Lewis Dot Diagram for Sodium and Chlorine. Chemistry of Sodium and Chlorine • If sodium gives away its last electron, it will be left with 8 on its last shell! Therefore it will be happy! 8 1e- 2 11P+ positive The sodium atom then becomes a ____________ion. Chemistry of Sodium and Chlorine • If chlorine accepts the electron from sodium it will now have 8 electrons on its outside shell therefore it will be happy! 8 7e- 1e- 2 17P+ negative The chlorine atom then becomes a ___________ ion. Ion an atom that has an electrical charge because it no longer has an equal number of protons and electrons. 6P+ 6N 2e- 3e- Rule of Eight 7e- 1e- 11P+ 8e1e1e- 17P+ Sodium Chloride 8e- Molecule Copy the table and identify if each of the following compounds is possible. Explain why! LiF HHe BeO NaCl KI CaS MgO FAr KCl Possible Not Possible Models of Compounds • Make the following compounds by fitting the puzzle pieces together. Use the names of the compounds as clues. – – – – – Sodium chloride Calcium oxide Carbon dioxide Calcium chloride Aluminum oxide • Draw the compounds in your notebook and write the name of the compound and its chemical formula. Include the Lewis Dot Diagram for each atom Chemical Equations • Shorthand way that scientists use to represent what takes place in a chemical reaction. • Chemical equations consist of many different components (parts). Components of a Chemical Equation 2Na2O2 + 2H2O -> 4NaOH + O2 Copy the chart and fill in the spaces. Chemical Formula NaCl CO2 H3PO4 2H2SO4 H2O 2C6H12 Total # of Elements in the Formula Total # of Atoms in the Formula Symbol Ex: H, Na 1 or 2 letters used to represent an element Place of discovery, scientist, or other language such as Latin or Greek. First letter capitalized, second letter lower case. Chemical Formula Ex: NaCl, H2O A combination of symbols and numbers that represent the number and types of elements(atoms) present in a compound. Subscript Ex: CO2, H2O2 Small number written to the right and below the normal line of letters. Shows how many atoms of each element are present in a substance. No subscript means there is only one atom present. Chemical Reaction • Ex: H2 (g) + O (g) H2O (liquid) • When substances interact to form one or more new substances with different properties than the original substance Chemical Equation • Ex: 2H2 + 2O2 2H2O2 • A combination of chemical formulas used to describe what happens in a chemical reaction. • The equation identifies the reactants and resulting products. Coefficient • 2Na + 2Cl 2NaCl • A number written in front of a chemical formula to show how many molecules of that substance are present. Reactants • 2CO2 2C + 2O2 • Formulas written on left side of arrow ( ) • Starting substance or substances in a chemical reaction Product • 2Fe + O2 2FeO • Formulas written on the right side of arrow ( ) • New substance or substances formed in a chemical reaction Yields • H2 + O2 H2O2 • Arrow shows a reaction has taken place. • The reactants have reacted to produce a new substance (the product) Compound H2O, CO2, CO A substance composed of two or more elements chemically combined in a definite proportion Physical Change • A change in which the characteristics of a substance are only changed physically and the original properties stay the same. • Physical properties of matter are characteristics that you can observe about the matter. • EX: color, shape, size, density, melting point, boiling point, freezing point, specific heat, state, metal, nonmetal, metalloid, evaporation, condensation, crystallization, conductivity, magnetism, luster, malleability, taste, dissolving, odor, texture, volume, mass, length, temperature Physical Properties Chemical Changes • A change in which a substance or substances is changed into one or more new substances with different properties than the original substances Chemical Properties • Chemical properties of matter are the properties that indicate whether an object can undergo a chemical reaction. • EX. flammable, reactive, corrosive, tarnishing, rusting oxidation … Law of Conservation of Mass • Matter is neither created or destroyed, only changed. • The number of atoms in the reactants must be equal to the number of atoms in the product. Precipitate • A solid that forms as a result of a chemical reaction • It will pull out and fall to the bottom of the container Law of Conservation of Mass • Reactants • NaHCO3 + HC2H3O2 yields Products CO2 + H2O + NaC2H3O2 • 1 sodium, 5 hydrogens, 3 carbons, 5 oxygens • BALANCED!!! • Number and kind of atoms on the reactant side must equal the number and kinds of atoms on the CHEMICAL CHANGES Occur When: Different substances with new properties are formed. Chemical Equations • You can explain a chemical reaction on paper by using a chemical equation. yields • reactants • What you START with with products What you end up Chemical Reactions Involve the breaking or forming of chemical bonds causing atoms to become rearranged into a new substance or substances. What to look for in a chemical change: • New substance with new properties • Energy involved (heat being released, heat being absorbed) • Gases released • Color change • A precipitate( a solid that separates out of a reaction)