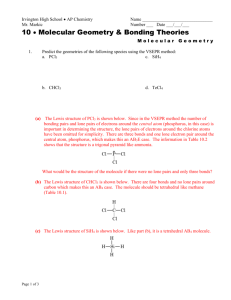
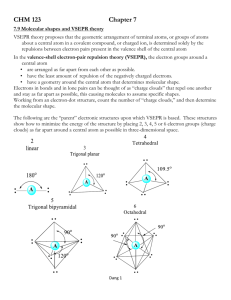
Ch. 8 Section 8.13 Powerpoint
advertisement

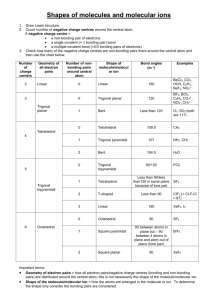
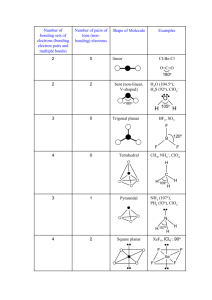
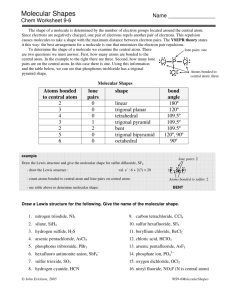
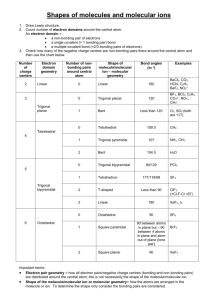
Valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) model: Predict the geometry of the molecule from the electrostatic repulsions between the electron (bonding and nonbonding) pairs. The idea here is that the bonding and nonbonding pairs around a given atom will be positioned as far apart as possible. This chart is NOT provided on the AP exam! VSEPR A = central atom B = atoms bonded to central atom E = lone pairs (non-bonding) of electrons on central atom Class # of atoms bonded to central atom # lone pairs on central atom AB2 2 0 Arrangement of electron pairs Molecular Geometry linear linear B Bond angle B Cl Be Cl lone pairs on to central atom 20 atoms bonded central atom VSEPR Class # of atoms bonded to central atom # lone pairs on central atom AB2 2 0 linear linear AB3 3 0 trigonal planar trigonal planar Arrangement of electron pairs Molecular Geometry VSEPR – Trigonal Planar arrangement Class # of atoms bonded to central atom # lone pairs on central atom Arrangement of electron pairs Molecular Geometry trigonal planar bent AB3 3 0 trigonal planar AB2E 2 1 trigonal planar VSEPR Class # of atoms bonded to central atom # lone pairs on central atom AB2 2 0 linear linear AB3 3 0 trigonal planar trigonal planar AB4 4 0 Arrangement of electron pairs tetrahedral Molecular Geometry tetrahedral VSEPR – Tetrahedral Arrangement Class AB4 AB3E # of atoms bonded to central atom # lone pairs on central atom 4 0 3 1 Arrangement of electron pairs Molecular Geometry tetrahedral tetrahedral tetrahedral trigonal pyramidal VSEPR – Tetrahedral Arrangement # of atoms bonded to central atom # lone pairs on central atom AB4 4 0 tetrahedral tetrahedral AB3E 3 1 tetrahedral trigonal pyramidal AB2E2 2 2 tetrahedral bent Class Arrangement of electron pairs Molecular Geometry O H H CH4 NH3 H2O Number of lone pairs 0 1 2 Bond angle 109.5o 107o 104.5o In these molecules, the arrangement of the electron pairs predict tetrahedral geometry. Why is the geometry different from predicted? Lone pairs require more room than bonding pairs and tend to compress the angles between the bonding pairs. VSEPR Class # of atoms bonded to central atom # lone pairs on central atom AB2 2 0 linear linear AB3 3 0 trigonal planar trigonal planar AB4 4 0 tetrahedral tetrahedral 0 trigonal bipyramidal trigonal bipyramidal AB5 5 Arrangement of electron pairs Molecular Geometry VSEPR – Trigonal Bipyramidal Arrangement Class AB5 AB4E # of atoms bonded to central atom # lone pairs on central atom 5 0 trigonal bipyramidal trigonal bipyramidal 1 trigonal bipyramidal See-Saw 4 Arrangement of electron pairs Molecular Geometry (distorted tetrahedron) VSEPR – Trigonal Bipyramidal Arrangement # of atoms bonded to central atom # lone pairs on central atom AB5 5 0 trigonal bipyramidal trigonal bipyramidal AB4E 4 1 trigonal bipyramidal See-Saw AB3E2 3 2 trigonal bipyramidal Class Arrangement of electron pairs Molecular Geometry T-shaped F F Cl F VSEPR – Trigonal Bipyramidal Arrangement # of atoms bonded to central atom # lone pairs on central atom AB5 5 0 trigonal bipyramidal trigonal bipyramidal AB4E 4 1 trigonal bipyramidal See-Saw AB3E2 3 2 trigonal bipyramidal T-shaped AB2E3 2 3 trigonal bipyramidal linear Class Arrangement of electron pairs Molecular Geometry I I I VSEPR Class # of atoms bonded to central atom # lone pairs on central atom AB2 2 0 linear linear AB3 3 0 trigonal planar trigonal planar AB4 4 0 tetrahedral tetrahedral trigonal bipyramidal octahedral Arrangement of electron pairs AB5 5 0 trigonal bipyramidal AB6 6 0 octahedral Molecular Geometry VSEPR – Octahedral Arrangement # of atoms bonded to central atom # lone pairs on central atom AB6 6 0 octahedral octahedral AB5E 5 1 octahedral square pyramidal Class Arrangement of electron pairs Molecular Geometry F F F Br F F VSEPR – Octahedral Arrangement # of atoms bonded to central atom # lone pairs on central atom AB6 6 0 octahedral octahedral AB5E 5 1 octahedral square pyramidal AB4E2 4 2 octahedral square planar Class Arrangement of electron pairs Molecular Geometry F F Xe F F Predicting Molecular Geometry 1. Draw Lewis structure for molecule. 2. Count number of lone pairs on the central atom and number of atoms bonded to the central atom. 3. Use VSEPR to predict the geometry of the molecule. What are the molecular geometries of SO2 and SF4? (In SF4, S uses an expanded octet of 10.) F S S F S F AB2E bent AB4E F See-Saw (distorted Tetrahedron) Dipole Moments and Polar Molecules electron poor region electron rich region H F d+ d- A molecule such as HF that has a center of positive charge and a center of negative charge is said to have a dipole moment. The dipole moment is often represented by an arrow pointing to the negative charge center with the tail of the arrow indicating the positive center of charge. Which of the following molecules have a dipole moment? H2O, CO2, SO2, and CH4 O S dipole moment polar molecule dipole moment polar molecule H O C O no dipole moment nonpolar molecule H C H H no dipole moment nonpolar molecule