NUR 101 Skills Lab Week 2
advertisement

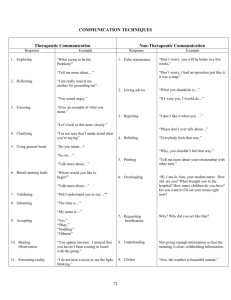
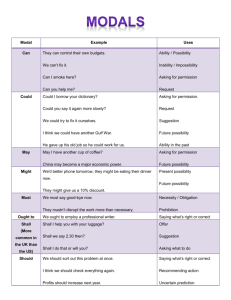
Communication in Nursing Therapeutic vs. Nontherapeutic Levels of Communication Intrapersonal Interpersonal Transpersonal Small-Group Public Basic Elements of Communication Process Referent Sender and Receiver Message Channels Feedback Forms of Communication Verbal Vocabulary Denotative and Connotative Meaning Pacing Intonation Clarity and Brevity Timing and Relevance Forms of Communication Nonverbal Personal Appearance Posture & Gait Facial Expressions Eye Contact Gestures Territoriality and Personal Space Zones of Personal Space and Touch Intimate (0-18 inches) Personal (18 in to 4 ft) Social (4-12 ft) Public (over 12 feet) Social Consent Vulnerable Intimate Professional Nursing Relationships Nurse-Patient Helping Relationships Nurse-Family Relationships Nurse-Health Care team Relationships Nurse-Community Realtionships Phases of the Helping Relationship Preinteraction Phase Orientation Phase Working Phase Termination Phase Elements of Professional Communication Courtesy Use of Names Privacy and Confidentiality Trustworthiness Autonomy and Responsibility Assertiveness Therapeutic Communication Techniques Active Listening (SOLER) Sharing Observations Shared Empathy Sharing Hope Sharing Humor Sharing Feelings Use of touch Therapeutic Communication Techniques Using Silence Asking Relevant Questions Paraphrasing Clarifying Focusing Summarizing Self-Disclosure Confrontation Non-Therapeutic Communication Techniques Asking personal questions Giving personal opinions Changing the subject Automatic responses False Assurance Sympathy Asking for Explanations Non-Therapeutic Communication Techniques Approval or Disapproval Defensive Responses Passive or Aggressive Responses Arguing Special Needs Communication Clients who cannot speak clearly (Aphasia, Muteness) Clients who are cognitively impaired Clients who are unresponsive Language barriers Hearing Difficulties Children Developmental Aspects of Communication Infants Toddlers & preschoolers School age children Adolescents