CHAPTER 9: Chemical Names and Formulas
advertisement

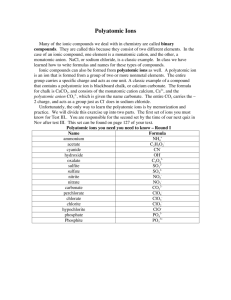
CHAPTER 9: Chemical Names and Formulas Objectives: 1. To be able to name ionic and molecular compounds, and acids. 2. To be able to write the formulas of ionic and molecular compounds, and acids. Different Types of Formulas and Names • Ionic compounds • Molecular compounds (molecules) • Acids (a special type of molecule) Ionic Compounds Monatomic ions are ions of a single atom with a positive or negative charge resulting from the loss or gain of one or more valence electrons. Monatomic cations: Na+, Ca2+ Monatomic anions: Cl-, N3- Naming monatomic cations: Cations for groups 1, 2, & 3 metals have the same name as the atoms, followed by ion or cation. Naming monatomic anions: Anion start with the same stem and end with -ide. This is followed by ion or anion. Na+ is sodium ion or sodium cation. Cl- is chloride ion or chloride anion. Other Names of Monatomic Ions Ion Symbol Ion Name Li+ lithium ion (or cation) Ca2+ calcium ion (or cation) Al3+ aluminum ion (or cation) F- fluoride ion (or anion) O2- oxide ion (or anion) N3- nitride ion (or anion) P3- phosphide ion (or anion) Naming Binary Ionic Compounds Binary Ionic Compounds are composed of ions of two elements. To Name Binary Ionic Compounds, place the cation name first, followed by the anion name. Formulas NaCl CaF2 Mg3N2 AlP K2Se Names sodium chloride calcium fluoride magnesium nitride aluminum phosphide potassium selenide Polyatomic Ions • Polyatomic ions are ions composed of more than one type of atom (usually nonmentals) covalently bonded. • Examples of Polyatomic ions: NH4+ PO43SO32- OH• For naming polyatomic ions, you can use your common ion table to get the name. Compounds Names NH4Cl ammonium chloride Na3PO4 sodium phosphate Al2(CO3)3 aluminum carbonate Cu(NO2)2 copper(II) nitrite Naming Ions & Ionic Compounds of Transition Metals • Since some transition metals may have more then one charge, the charges of the cations must be determined and represented when naming transition metal ions and compounds with transition metal ions. • For example, iron is a transition metal and can have two common charges, Fe2+ and Fe3+. • When naming these ions, we use the Stock system which uses Roman numerals in parentheses after the metal name. • If the charge of the metal is not given directly, you must determine it by using the formula given. Ion Name of Ion Ionic Compound Name of Compound Fe2+ iron(II) ion FeCl2 iron(II) chloride Fe3+ iron(III) ion FeCl3 iron(III) chloride Cu+ copper(I) ion CuF copper(I) fluoride Pb4+ lead(IV) ion PbI4 lead(IV) iodide 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Steps to Writing Formulas of Ionic Compounds Write the symbols of both ions including their charges remembering that the cation is placed first followed by the anion. sodium oxide Na+ O2Crisscross the value of the charges. This will make it so that the charges are balanced. Na+ O2Rewrite your new formula and make sure the charges cancel each other. Na2O two Na+ = +2 total charge one O2- = -2 is zero If the charge is 1- or 1+, leave the number 1 out the formula since it is understood to be there. If necessary, reduce the numbers of each atom by a common denominator since formula units represent the lowest ratio of ions in an ionic compound. If there is more then one polyatomic ion present, use ( ) around the ion and then place the subscript outside of the ( ). Formula Practice: Binary Ionic Compounds Name of Compound aluminum iodide calcium phosphide barium sulfide rubidium bromide strontium nitride copper(II) chloride chromium(III) oxide Ions Al3+ Ca2+ Ba2+ Rb+ Sr2+ Cu2+ Cr3+ IP3S2BrN3ClO2- Formula AlI3 Ca3P2 BaS RbBr Sr3N CuCl2 Cr2O3 Naming Ionic Compounds with Transition Metals • It is necessary to determine the charge of a transition metals that can have more then one charge in order to name it. • This can be done by using the formula given and determining the charge of the anion first. • Remember that the total charges of the anion and cation must cancel each other out. Formula CuCl CuCl2 Fe2O Fe2O3 PbO2 PbCO3 Ions Cu+ Cu2+ Fe2+ Fe3+ Pb4+ Pb2+ ClClO2O2O2CO32- Name copper(I) chloride copper(II) chloride iron(II) oxide iron(III) oxide lead(IV) oxide lead(II) carbonate Formula Making: Compounds with Polyatomic Ions • Formula making with polyatomic ions is very similar to what you have learned so far. • Just DON’T forget to use ( ) around polyatomic ions when there is more then one of them! Names Ions Formula magnesium sulfate Mg2+ SO42MgSO4 ammonium fluoride NH4+ FNH4Cl lithium carbonate Li+ CO32Li2CO3 calcium nitrate Ca2+ NO3Ca(NO3)2 beryllium hydroxide Be2+ OHBe(OH)2 Naming Binary Molecular Compounds • When two nonmetals combine, they form a molecular compound whose formula shows the actual number of each kind of atom found in a molecule of the compound. • To name these compounds, we use a similar method to naming ionic cmps (see endings) except we can use prefixes to denote number of Prefixes for Naming Covalent Compounds each atoms. Prefix monoditritetrapentahexaheptaoctanonadeca- Number of atoms 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Example NO SiO2 SO3 SCl4 SCl5 CBr6 IF7 N3O8 I4O9 S2F10 Name nitrogen monoxide silicon dioxide sulfur trioxide sulfur tetrachloride sulfur pentachloride carbon hexabromide iodine heptafluoride trinitrogen octoxide tetriodine nonoxide disulfur decafluoride • Note: when there is only atom of the first element in the compound mono- is not used before the atom’s name. • Note: when using prefixes with atoms that start with a vowel, the last vowel of the prefix is dropped. Naming Practice: Binary Molecular Cmpds Formula Name NH3 nitrogen trihydride PCl5 phosphorous pentachloride SeF6 selenium hexafluoride NO nitrogen monoxide P2O7 diphophorous heptoxide C3H8 tricarbon octahydrogen Naming Acids • For now, the acids that we will learn how to name contain hydrogen ions, H+. (formulas start with H) Naming Rules: 1. When the anion name ends in -ide, the stem of the anion name begins with the prefix hydro- and ends with -ic. The name is then followed by the word acid. 2. When the anion name ends in -ite, the anion ends with -ous, followed by the word acid. 3. When the anion name ends in -ate, the anion name ends with -ic, followed by the word acid. Naming Acids Formula HBr HCl HI H2S H2SO4 H2SO3 H3PO3 H3PO4 HClO HClO4 Anion Ending -ide -ide -ide -ide -ate -ite -ite -ate -ite -ate Acid Name hydrobromic acid hydrochloric acid hydriodic acid hydrosulfuric acid sulfuric acid sulfurous acid phosphorous acid phosphoric acid hypochlorous acid perchloric acid