Tang and Song rdg guide
advertisement

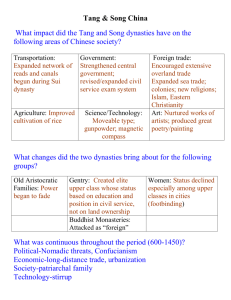
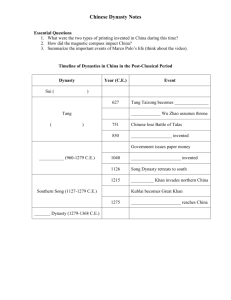
Postclassical China 589 – 1279 C.E. Ch. 13 pg. 264-286 1. Label the Tang and Song Dynasties on the map. Also include the Grand Canal, Yellow River (Huang He), Yangzi River, Chang’an and Hangzhou. 2. Timeline: Must include dates for start and end of Sui, Tang and Song Dynasties. 3. Explain one continuity during the rule of Tang Taizong from Classical China (Han Dynasty). 4. What three policies helped the Tang dynasty become successful? 5. Analyze/Explain why Transportation and Communications helped ensure the success of the Tang dynasty. 6. Describe the Equal Field System. 8. What territories did the Tang dynasty conquer? 9. Explain kowtow. 10. The fall of the Tang dynasty took from 755 – 907 C.E. Fill in the categories from the Empire Model. Poor Leadership Rebellion Military defeat 11. How was China ruled after the fall of the Tang dynasty? What key term describes this type of government (Hint: not mentioned in the reading)? 12. What did the Song dynasty focus on instead of the military? 13. What were the Song dynasties two greatest weaknesses? 14. Explain fast-ripening rice. What effect did the rice and new agricultural techniques have on China’s population? (Be specific) 15. Describe the capital city of Hangzhou during the Song dynasty. 16. Describe foot binding? How did it reinforce the patriarchal social structure of China? 17. Describe at least two technological developments of Postclassical China (Tang and Song) 18. Fill in the chart below in order to organize trade during Postclassical China. (Hint: Not all categories will be filled in because trade is not always a two way street) Trade Partners Abbasid Empire Byzantine Empire Arab, Persian, Indian, Malay mariners Southeast Asia Route(s) Used Products received from China Products given to China