Brain and Behavior
advertisement

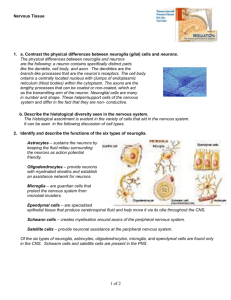
Psychology 101 By: Marina Sangkavichai Brain and Behavior What is the difference between the mind and brain? Question of the Day How can one cure depression naturally? Define the neuron, synapse, and neurotransmitter and their effects on human behavior. Brain and Behavior Mind: is perceiving, feeling, thinking Brain: the physical organ Everything psychological is simultaneously biological. Your every idea, every mood, every urge is a biological happening. Brain and Behavior The brain’s ultimate challenge is to understand itself How does the brain process information from the world around us? Brain Research Areas of Einstein’s brain were 15% larger and had more connections than the average person London cab drivers show larger hippocampus due to work Jugglers learning new routines used the right side of their frontal lobes Brain and Behavior All behavior can be traced to the activity of neurons. In the early 1800’s, Franz Gall invented phrenology. He believed bumps on our skulls could reveal our mental abilities and our character traits. Nevertheless, the assumption that different parts of the brain do control different aspects of behavior hold true. Brain Facts The brain consists of 100 billion neurons! ( illustration) Vast neurons form networks and they communicate with one another Neurotransmitters are released and alter activity in the neurons next to them More than 100 transmitter chemicals are found in the brain Neurons in the Brain Example of Transmitter Chemicals Acetycholine: the neurotransmitter released by neurons to activate muscles. Also involved in learning and memory An undersupply of acetycholine marks Alzheimers Disease. The Drug called Curare causes paralysis. South American Indians put on the tips of their hunting darts. This would cause paralysis by blocking ACH receptors. Animals would become paralyzed when struck with these darts. Sarin Gas-Weapon of Mass Destruction Example of Transmitter Chemicals Botulin- a poison that can form in improperly canned food, causes paralysis by blocking ACH release from the sending neuron. Injections of Botulin aka BOTOX smooths wrinkles by paralyzing the underlying facial muscles. Example of Transmitters Dopamine: influences movement, learning, attention, and emotion. Excess dopamine is linked to schizophrenia. Less dopamine the brain produces the tremors and decreased mobility of Parkinsons Disease. More Neurotransmitters Serotonin: affects mood, hunger, sleep, and arousal. A decrease of serotonin levels is linked to DEPRESSION. Prozac and other antidepressant drugs raise the serotonin levels. Many drugs imitate, duplicate, or block these transmitters. Normal vs Depression Normal Vs Depressed Loss of neurotransmitter Activity in the depressed individuals functioning. Primary areas affected are those related to mood, emotions, motor activity, cognitive functioning, sex drive, appetite, and sleep. More on these “Messengers” These neurotransmitters tell the next neuron what to do! Synapse: the microscopic space between two neurons is over which messages are passed. Neurotransmitters Being Passed Through the Synapse The Nervous System The central nervous system includes the BRAIN and THE SPINAL CORD. ILLUSTRATION on BOARD ( The Peripheral Nervous System ) Picture of a Neuron The Amazing Neuron Neuron: the basic cell that makes up the nervous system and that receives and sends messages within that system Dendrites: branch like structures that receive messages from other neurons Soma: the cell body of the neuron responsible for maintaining the life of the cell Axon: tube like structure that carries the neural message to other cells The Neuron Forest Real work of the brain goes on in individual cells. An adult brain contains about 100 billion nerve cells or neurons with branches that connect more than 100 trillion points. Signals traveling through the neuron forest form the basis of memories, thoughts, and feelings. Neurons are the chief type of cell destroyed by Azheimers disease. Brain Cells CNS and Peripheral Nervous System The Peripheral Nervous System Is divided into two parts: Somatic System and Autonomic System Somatic System ( controls voluntary movement ) ( like Running ) Autonomic System: serves internal organs and glands of the body”self governing”. Controls body parts you don’t even have to think of like heart rate, breathing, digestion, perspiration ) It is on “automatic pilot”. Somatic System and Autonomic System Messages from the somatic system can make the hand move but not make the eyes dilate. Only messages from the autonomic system can do that Autonomic Nervous System System on automatic pilot ( autonomic system ) can be divided into two parts: Sympathetic system: gets you ready for action ( like when a dog lunges at you ) Gets you ready for fight or flight! Speeds up heart rate, eyes dilate, produces adrenaline to give you that surge of energy Parasympathetic system: Calms you down after a stressful event, for example, slows down heart rate. The Nervous System and Its Different Branches The Brain’s Lobes and Their Specialities p. Frontal lobes: decision making, problem solving, controlling emotions, planning Occipital lobes: rear of the head, processes visual information Parietal lobes: sensations, such as touch, temperature, pressure Temporal lobes: auditory information. ie. Music, language. Stimulating this area would cause a series of sound sensations The Different Lobes Split Brain Patient When a visual image (an orange) is flashed on the right side of the screen, it is transmitted to the left hemisphere. When asked what he sees, the split-brain patient replies, “I see an orange.” When an image (an apple) is flashed on the left side of the screen, it is transmitted only to the right hemisphere. Because the split-brain patient’s left hemisphere did not receive the image he replies, “I see nothing.” But he can pick out the apple by touch if he uses his left hand, proving his right hemisphere “saw” the apple. Left Side: talkative, analytical, Right side: emotional, music, visual spatial. Proof of lateralization Broca’s Aphasia Broca’s area in the left frontal lobe. Damage to this area causes a person to be unable to get words out in a smooth connected, fashion. Mispronounce words, for example, cot instead of clock, sair instead of chair. Wernickes Area Lies in left temporal lobe Area involved in understanding the meaning of words Could speak fluently but use the wrong words to express themselves. Instead of get me something out of the refrigerator, person will say get me something out of the air conditioner! Facial Agnosia Brain injury resulting in a person not being able to perceive familiar faces. One could patient could not recognize her husband when he came to visit her in the hospital until he spoke. The underside of the occipital lobe specializes in recognizes faces. Research Methods How do we study the brain? Ablation: means surgical removal of parts of the brain. This helps us gain insight into purpose of the missing parts. Or when this part of the brain is damaged, can give us insight into what its purpose is. Research Methods A steel rod went through the frontal lobes of Phineas Gage and proceeded through his frontal lobes.Survived. However, never the same. His personality changed! Became a liar and foul mouthed. This offers evidence that specific parts of the brain are responsible for certain functions. Frontal lobes play a part in emotions, reading other peoples emotions and planning and executing actions and responses. Phineas Gage Research Methods We can actually open up a persons skull and stimulate parts of the brain with an electrode. When this is done during brain surgery, patients can describe how the stimulation affected them. The BRAIN has no PAIN receptors! So it’s not painful at all. Research Methods MRI Scan: Magnetic Resonance Imaging ( MRI ) Produces an image of the brains interior. Magnetic Resonance Imaging © Huntington Magnetic Resonance Center, Pasadena, California PET SCAN PET Scan stands for Positron Emission Tomography ( PET ) It is a computer generated image of brain activity based on glucose consumption ( sugar ) of the brain. This is the closest thing we have to seeing thought. PET SCAN shows which areas are showing high energy. PET SCAN Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis Methamphetamine And The Brain Effects of “Meth” Brain of a normal person vs brain on Meth Rot “ Ice “ Pornography and the Brain Pornography has evolved The themes are more aggressive and filmmakers believe in pushing the envelope For those who consume these images, they’ve built a tolerance to them It influences young people with little sexual experience and esp. plastic minds, forming their sexual tastes and desires. Brain on Pornography Watching porn as addictive as cocaine, meth, and alcohol. It was discovered the frontal lobe of the brain shrinks in people who are addicted to porn. Hijacks the brains pleasure system and person is prone to irritability and impulsiveness. Pornography Many men who were hooked on adult movies were finding it harder to get excited over their partners. Downloading new scripts Tolerance Neurons that fire together, wire together! Seven Habits of Highly Effective Brains Continue Learning!( your brain is developing new neurons and synapses as you learn) Good nutrition Physical exercise Challenge your brain with new activities Don’t outsource your brain ( think for yourself!) Stimulating friendships Laugh often at complex humor