Chapter 2 Rocks PowerPoint
advertisement

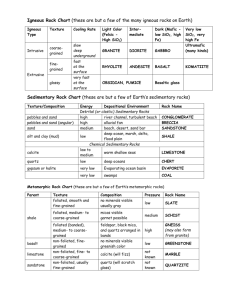
Chapter 2 Rocks Section 1 Lesson Objectives Define rock Describe how rocks change List rock characteristics that help to identify it Define rock Keywords Rock Rock cycle Igneous Sedimentary Metamorphic Describe how rocks change List rock characteristics that help to identify it Define rock Describe how rocks change List rock characteristics that help to identify it Keywords: rock, rock cycle Rock • Naturally occurring solid mixture made of minerals and organic matter Define rock Describe how rocks change List rock characteristics that help to identify it Keywords: igneous, sedimentary, metamorphic Rock type is determined by how it is formed Three types of Rock • Igneous- formed from magma • Sedimentary- formed as a by-product of weathering, erosion, decomposition • Metamorphic- formed from changes in temperature and/or pressure Define rock Describe how rocks change List rock characteristics that help to identify it Keywords: Rock cycle Rock Cycle • The continual process by which new rock forms from old rock • Rock cycle animation http://www.classzone.com/books/earth_science/terc/content/investigations/es0602/es0602page02.cfm Define rock Describe how rocks change List rock characteristics that help to identify it Keywords: igneous Ways to tell which rocks are which: Igneous: • Intrusive igneous rocks– large crystals cemented together. – Crystallize below Earth's surface – Slow cooling that occurs there allows large crystals to form. • Extrusive igneous rocks – – – – – small crystals some are not visible Smooth surface May have air pockets May look like glass erupt onto the surface where they cool quickly Define rock Describe how rocks change List rock characteristics that help to identify it Keywords: sedimentary Ways to tell which rocks are which: Sedimentary: • Clastic sedimentary rocks – Fragments of rocks cemented together – Can be course grained like “conglomerate” or fine grained like shale • Chemical – Liquid evaporates leaving cemented crystals behind • Organic – May contain fossils Define rock Describe how rocks change Keywords: metamorphic Ways to tell which rocks are which: Metamorphic: • Foliated– Banded – crystals seem to go in the same direction • Non-foliated– No bands – Can have a glittery appearance List rock characteristics that help to identify it Type of Rock? Igneous (Intrusive) Notice the air bubbles Type of Rock? Igneous (Extrusive) Notice the absence of visible crystals Type of Rock? Metamorphic Notice the bands Type of Rock? Sedimentary Notice the pebble-like crystals Type of Rock? Sedimentary Notice the sand-like texture Type of Rock? Igneous Notice the air bubbles Type of Rock? Igneous Notice the separate crystals Type of Rock? Metamorphic Notice the Type of Rock? Sedimentary Notice the glass-like appearance Type of Rock? Metamorphic Notice the glittery appearance Section 2 Lesson Objectives Describe three ways that igneous rocks form Explain how cooling speed affects texture Distinguish between intrusive and extrusive Describe three ways that igneous rocks form Keywords Texture Composition Igneous Extrusive Intrusive Explain how cooling speed affects texture Distinguish between intrusive and extrusive Describe three ways that igneous rocks form Explain how cooling speed affects texture Distinguish between intrusive and extrusive Keywords: texture, composition Texture and composition give clues as to how rocks are formed, and are used to classify rocks • Composition – the type of material a rock contains • Texture – the size, shape and arrangement of the minerals/particles that make up a rock. • Cooling rate affects texture: • Rocks that cool faster have very small crystals, air pockets, and can be glassy • Rocks that cool slower have larger crystals Describe three ways that igneous rocks form Explain how cooling speed affects texture Distinguish between intrusive and extrusive Keywords Igneous Rocks2 types depending on how formed Extrusive rocks- formed by cooling lava so cools quickly obsidian Texture: • glassy (obsidian) • porous (pumice) • fine-grained (basalt) pumice Intrusive rocks- formed by cooling magma so cools slowly Texture: • coarse-grained (granite) basalt granite Formation of Extrusive Igneous Rocks Formation of Intrusive Igneous Rock Section 3 Lesson Objectives Describe the 5 agents of erosion Describe, deposition, compaction and cementation Differentiate between types of sedimentary rocks and how they form Describe the 5 agents of erosion Keywords Erosion Deposition Compaction Cementation Wind Gravity Running water Glaciers Waves Sedimentary Clastic Chemical Organic Describe, deposition, compaction and cementation Differentiate between types of sedimentary rocks and how they form Describe the 5 agents of erosion Describe, deposition, compaction and cementation Differentiate between types of sedimentary rocks and how they form Keywords: sedimentary Sedimentary Rocks • Formed from the erosion, deposition, compaction and cementation of minerals and other materials • Occurs at or near the earth’s surface • Three types: • Clastic • Chemical • Organic Describe the 5 agents of erosion Describe, deposition, compaction and cementation Differentiate between types of sedimentary rocks and how they form Keywords: clastic, chemical, organic • Clastic Rocks (rock fragments) • Conglomerates (pebbles) • Sandstones (sand) • Shales (mud & clay) • Chemical Rocks (evaporation) • Ex: rock salt, limestone, geodes, gypsum • Organic Rocks (once living) • Ex: limestone(coral and shells), coal (plants) Clastic Sedimentary Rock… made from fragments of rocks cemented together Conglomerate Shale Sandstone Chemical Sedimentary Rocks… formed from dissolved minerals that have crystallized out of solution Gypsum rock Limestone Geode Organic Sedimentary Rocks… made from previously living organisms Coal (plant mateiral) Limestone (shell & coral) Describe the 5 agents of erosion Describe, deposition, compaction and cementation Differentiate between types of sedimentary rocks and how they form Keywords Five Agents of Erosion • • • • • Gravity (Mass wasting) Wind Running water Glaciers Waves Describe the 5 agents of erosion Describe, deposition, compaction and cementation Differentiate between types of sedimentary rocks and how they form Keywords: gravity Gravity (Mass Wasting) Soil creep Slumping Describe the 5 agents of erosion Describe, deposition, compaction and cementation Keywords: wind Wind Differentiate between types of sedimentary rocks and how they form Describe the 5 agents of erosion Describe, deposition, compaction and cementation Differentiate between types of sedimentary rocks and how they form Keywords: running water Niagara Falls Yellowstone Canyon & River Describe the 5 agents of erosion Keywords: glaciers Glaciers Describe, deposition, compaction and cementation Differentiate between types of sedimentary rocks and how they form Describe the 5 agents of erosion Keywords: waves Waves Describe, deposition, compaction and cementation Differentiate between types of sedimentary rocks and how they form Describe the 5 agents of erosion Describe, deposition, compaction and cementation Differentiate between types of sedimentary rocks and how they form Keywords: deposition Deposition Examples Nile River Delta: landform that forms at the mouth of a river, where the river flows into an ocean, sea, estuary, or lake Lateral moraine: parallel ridges of debris deposited along the sides of a glacier Describe the 5 agents of erosion Describe, deposition, compaction and cementation Differentiate between types of sedimentary rocks and how they form Keywords: compaction, cementation Compaction and Cementation Section 4 Lesson Objectives Describe how metamorphic rocks are formed Differentiate between foliated and non-foliated rocks Determine whether rocks will become either foliated or non-foliated Describe how metamorphic rocks are formed Keywords: Metamorphic Foliated Non-foliated Differentiate between foliated and non-foliated rocks Determine whether rocks will become either foliated or non-foliated Describe how metamorphic rocks are formed Differentiate between foliated and non-foliated rocks Determine whether rocks will become either foliated or non-foliated Keywords: metamorphic Metamorphic Rocks • Formed by tremendous heat & pressure, and chemical reactions inside the crust. • Formed from all three rock types. Describe how metamorphic rocks are formed Differentiate between foliated and non-foliated rocks Keywords: foliated Foliated texture Give examples of some metamorphic rocks Describe how metamorphic rocks are formed Differentiate between foliated and non-foliated rocks Differentiate between types of sedimentary rocks and how they form Keywords: foliated Types of Metamorphic Rock Slate • Foliated (bands or layers) Ex: schist, slate, gneiss Gneiss Describe how metamorphic rocks are formed Differentiate between foliated and non-foliated rocks Determine whether rocks will become either foliated or non-foliated Keywords: non-foliated Types of Metamorphic Rock continued • Non-Foliated (no bands or layers) Ex: marble and quartzite Describe how metamorphic rocks are formed Differentiate between foliated and non-foliated rocks Determine whether rocks will become either foliated or non-foliated Keywords: non-foliated Pressure determines if metamorphic rocks will be foliated or non-foliated • If there is unequal pressure, rocks will be foliated • If there is equal pressure, rocks will be nonfoliated Closure: 1. In igneous rocks how is cooling rate and crystal size related? 2. Which rock type would you have the best chance of finding a fossil? Why?