Identifying and Implementing Effective Transition Services
advertisement

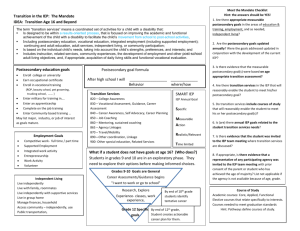
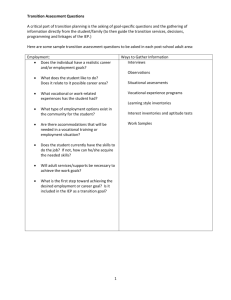
Catherine Fowler, NSTTAC Dawn Rowe, NPSO 2nd Annual Rhode Island Secondary Transition State institute Bristol, RI March 14, 2014 To ensure that all children with disabilities have available to them a free appropriate public education that emphasizes special education and related services designed to meet their unique needs AND prepares them for further education, employment, and independent living 2 IDEA Regulations §300.1(a) Beginning not later than the first IEP to be in effect when the child turns 16, or younger if determined appropriate by the IEP Team, and updated annually, thereafter, the IEP must include— (1) Appropriate measurable postsecondary goals based upon age appropriate transition assessments related to training, education, employment, and, where appropriate, independent living skills; and (2) The transition services (including courses of study) needed to assist the child in reaching those goals 3 Seattle University - Center for Change in Transition Services, 2010 Seattle University - Center for Change in Transition Services, 2010 Transition services a coordinated set of activities for a child with a disability that … (a) is designed to be within a results oriented process, that is focused on improving the academic and functional achievement of the child with a disability to facilitate the child’s movement from school to post-school activities, including: postsecondary education vocational education integrated employment (including supported employment) continuing and adult education adult services independent living, or community participation; and 6 (b) is based on the individual child’s needs, taking into account the child’s strengths, preferences, and interests; and includes: instruction related services community experiences development of employment and other postschool adult living objectives, and, if appropriate, acquisition of daily living skills and provision of a functional vocational evaluation (IDEA, 2004; 20 U.S.C. 1401(34)) 7 COORDINATED: These activities have a purpose and a goal. They are selected with a plan in mind to accomplish a specific goal. RESULTS ORIENTED PROCESS: We are focused on the “outcomes” of the students instead of the “process”. The central question is What has the student learned? ACADEMIC AND FUNCTIONAL ACHIEVEMENT: Link to standard course of study that is functionally meaningful as students set and attain goals 8 SCHOOL TO POST-SCHOOL: From secondary school (i.e., high school) to adult life experiences. INDIVIDUAL’S NEEDS STRENGTHS PREFERENCES AND INTERESTS: Student’s input is critical to the transition process. The goals in the plan should reflect the goals of the student. For students with significant disabilities, using PIC SYMS to FACILITATE planning and decision making during the transition process. 9 Finally, for many of the students you teach, instruction will be needed to acquire daily living skills. A FUNCTIONAL VOCATIONAL EVALUATION may be needed to assess what the student can do in terms of EMPLOYMENT and INDEPENDENCE & INTERDEPENDENCE in the COMMUNITY 10 What activities did you do in high school? Are there transition services in the IEP that focus on improving the academic and functional achievement of a student to facilitate his or her movement from school to post school? Is a type of: instruction, related service, community experience, development of employment and other post school adult living objectives, and if appropriate, acquisition of daily living skills, and provision of a functional evaluation listed in association with meeting the post-secondary goal? More Transition Service Questions 1. 2. 3. What experiences must the student participate in this academic year that are necessary for achieving the identified postsecondary goals? What services and specific instruction are essential this year for the student to develop skills and knowledge to attain their postsecondary goals? Do we know enough about this student’s vocational skills to identify an appropriate postsecondary employment goal or design activities to support the identified goal? Instruction on using picture symbol recipes Instruction related to laundry skills Instruction on personal hygiene Instruction related to the water cycle Community-based instruction on purchasing lunch supplies Visit to a McDonald’s food prep area Part time employment in a position related to working with children Complete application process at community college Apply for possible college financial aid Apply for college and disability support service, no later than December 2006 Interview for a full-time position at a local day care Instructional support of guided notes for lessons Touring child care facilities Modified ACT testing Audio-taped texts for English 12 Paid work •Earn certifications for computer networking positions while attending MMTC •Open a bank account to manage her money •Job shadow in the field of computer technical support at the local hospital/ summer employment in automotive industry •Make plans to live independently in the future •Learn to obtain, complete, and submit an application for employment/ college application •Learn how to manage household responsibilities •Take a driver’s education course •Will be referred to VR for further evaluation/ services 17 •Will investigate case management and in home services through adult service agencies and learn how to access those services •Will learn self-advocacy skills, social behavior, and home maintenance skills •Will continue to gain experiences in the community through Life Skills class work experiences and other activities • Access tutorial services through disability services in college •Will develop skills regarding task completion, budgeting, cooking, and other home-care skills •Complete additional assessments for transition planning 18 All transition services provided to a student must support attainment of postsecondary goals. For transition services that are likely to be provided or paid for by other agencies with parent (or child once the age of majority is reached) consent, there must be evidence that representatives of the agency (ies) were invited to the IEP meeting? SERVICES SHOULD BE INDIVIDUALIZED A predictor is defined as an in-school experience, typically a program (e.g., a workbased learning experience) correlated with improved postschool outcomes. Career Awareness Occupational Courses Paid Employment/Work Experience Vocational Education Work Study Community Experiences Exit Exams/High School Diploma Status Inclusion in General Education Program of Study Independent Living Skills Self-Determination Skills Social Skills Interagency Collaboration Parental Involvement Parent Expectations Student Support Transition Program 21 Paid employment/work experience has been operationally defined as: any activity that places the student in an authentic workplace, and could include: work sampling, job shadowing, internships, apprenticeships, and paid employment. Paid employment can include existing standard jobs in a company or organization or customized work assignments negotiated with the employer, but these activities always feature competitive pay (e.g., minimum wage) paid directly to the student by the employer. Rowe, D. A., Alverson, C. Y., Unruh, D., Fowler, C., Kellems, R., & Test, D. W. (2014). Operationalizing evidence-based predictors in secondary transition: A delphi study. Career Development and Transition for Exceptional Individuals. Provide opportunities to participate in job shadowing, work-study, apprenticeships, or internships. **Consider work study, apprenticeships, and internship environments that are culturally sensitive to students from different cultural backgrounds. Provide instruction in employment skills (e.g., problem solving, communicating with authority figures, responding to feedback, promptness) and occupational specific skills (e.g., clerical, machine operation). Provide transportation training, including the use of public transportation and job-site and community safety. Conduct job performance evaluations by student, school staff, and employer. Anthony is a 19 year old student identified with emotional and behavioral disabilities. Anthony’s has good interpersonal skills and a strong work ethic. He exhibits strengths in mechanical occupations. Career assessments indicate that he is likely to be a serious, dedicated employee. Post-school Goal • Upon graduation from community college, Anthony will obtain a small business license and contract his services as a welder in his uncle’s car shop. Where is Anthony going? What does he need to get there? MOVEMENT FROM SCHOOL TO POST-SCHOOL ACTIVITIES Postsecondary education Vocational education Integrated employment (including supported employment) Continuing and adult education Adult services Independent living, or community participation PREFERENCES, INTERESTS, NEEDS, AND STRENGTHS Instruction Community-Based Experiences Related Services Employment and other postschool adult living objectives Daily living skills and provision of a functional vocational evaluation For the past few years, Anthony and his friends have fixed up a car they bought from the junk yard for a few hundred dollars. They enter local races on the weekends to win cash prizes. Anthony does not race the cars; he does the body work on them. He does not always wear the necessary protective gear when welding, which is dangerous. His uncle sometimes helps him with the more detailed welding work in his welding shop. Anthony loves to work on the cars and attend the races on the weekends. This hobby has prepared him with valuable vocational skills related to welding and automotives, but these races are illegal. The local police have begun to pay more attention to these events. Anthony does not express any concern that he will be caught participating in the races. Post-School Goal • After graduation, Anthony will follow the laws of his community, demonstrating an understanding of the need for laws to ensure his and others’ safety. Instruction: in Social Skills, in Self-advocacy/ Self-determination Thinking about predictors, what transition Related Services: refer to VR for hearing aid maintenance (student services would support Anthony’s post-school support) goal? Community-Based Experiences: visit to legal racing venue Instruction – teaching academics, work-related skills, community skills Related Services – transportation, OT, PT, job coach Community Experiences – work-based, daily living Employment & other Post-school Adult Living Objectives – financial planning, health care, self-advocacy, selfdetermination Daily Living Skills – learning to drive, banking, health care Functional Vocational Evaluation – formalized employment assessment 29 Emmett is a 16-year-old Has a specific learning disability in reading fluency, reading comprehension, written expression, and oral language processing Strengths related to managing money Struggles with use of calendar or other planners Reading and writing performance require accommodations for testing and participation in the general curriculum extended time, read-aloud computer software resources to support listening comprehension and writing 40 Post-school Goal: Upon completion of high school, Emmett will attend courses at Ocean County Community College working toward a degree in computer science that will transfer to a four year college to obtain a bachelors degree. Transition Services (predictors): instruction – learning self determination skills; enrolled in vocational education courses/CTE via Program of Study related services – meeting with Disability Services on campus via VR community experiences – visiting campus multiple times servicesand would support Emmett’s post-school employment other post-school adult living objectives – interview IT specialist for the high school regarding education requirements and critical goal? components of the job (career awareness) daily living skills/functional vocational evaluation Thinking about predictors, what transition 23 Reflect upon your current IEPs How many transition services reflect the predictors we’ve discussed today? How many transition services are written specifically for THAT student’s postsecondary goals? (each of the goals?) 1. A measurable postsecondary goal in education: Upon completion of high school, Emmett will complete his associates degree in computer science at Ocean County Community College. 2. Identify 3 appropriate transition service/s to support attainment of this PS goal. Use predictors to target resources and increase the likelihood of youth being positively engaged after high school. 45 Dawn Rowe, drowe3@uoregon.edu www.psocenter.org Catherine Fowler, chfowler@uncc.edu www.nsttac.org