Preparing Students with Special Needs for College and Career
advertisement

Preparing Students with Special
Needs for College and Career
March 26
Educator’s Institute 2012
Lovegren-O’Brien
Bass
3/26/12
Learning Objectives:
1. Review & discuss IDEA 2004 & ADA
and the differences between them
(see handout)
2. Introduce the “Transition Process”
3. Clarify appropriate measurable
postsecondary goals
4. Define responsibilities/roles of key
players
A. Definition of Transition Services
The term “transition services” means a coordinated set of
activities for a child with a disability that is designed to be
within a results-oriented process, that is focused on
improving the academic and functional achievement of the
child with a disability to facilitate the child’s movement from
school to post-school activities, including postsecondary
education, vocational education, integrated employment
(including supported employment); continuing and adult
education, adult services, independent living, or community
participation;
Definition of Transition, Continued
is based on the individual’s child’s needs, taking into
account the child’s strengths, preferences, and interests;
and
includes instruction, related services, community
experiences, the development of employment and
other post-school adult living objectives, and, if
appropriate, acquisition of daily living skills and
functional vocational evaluation.
[34 CFR 300.43 (a)] [20 U.S.C. 1401 (34)]
Differences Between HS & COLLEGE –
Legal Protections
• The law is the Individuals with
Disabilities Education Act (IDEA).
• IDEA is about success.
• Education is a RIGHT and must be
accessible to you.
• Core modifications of classes and
materials are required.
• School district develops Individual
Education Programs (IEPs) and
must follow this legal document
in the provision of educational
services.
• Laws are Americans with
Disabilities Act (ADA) and Section
504 of the Rehabilitation Act.
• ADA is about access.
• Education is NOT a right. Students
must apply to attend.
• NO modifications are requiredonly accommodations.
• Student must identify needs and
ask for services. NO IEP exists and
is not considered legal
documentation.
Differences Between HS & COLLEGE –
Advocacy and Access
• Student is helped by parents and
teachers, even without asking
directly.
• School is responsible for
arranging for accommodations
and modifications
• Parent has access to student
records.
• Parent advocates for student.
• Teachers meet regularly with
parents to discuss their child’s
educational progress.
• Students need parent's
permission to participate in most
activities.
• Student must request
accommodations from Disability
Services Office.
• Student must self-advocate and
arrange for accommodations.
• Parent has no access to student
records without student’s written
consent.
• Student advocates for self.
• College faculty members seldom,
if ever, interact with parents and
expect the students to address
issues with them directly.
• Student is adult and gives own
permission.
http://www.thinkcollege.net/for-professionals/high-school-v-college
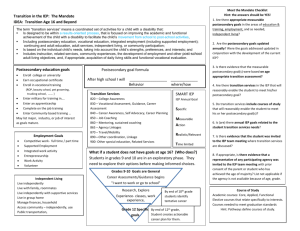
Transition Process
Results of Age
Appropriate
Transition
Assessments
Desired
Post-School
Outcomes
Appropriate
Measurable
Postsecondary
Goals
Transition
Services
(including
Courses of Study,
Activities and
Linkages)
Present Levels of
Academic
Achievement and
Functional
Performance (PLoP)
Annual Goals
and
Accommodations
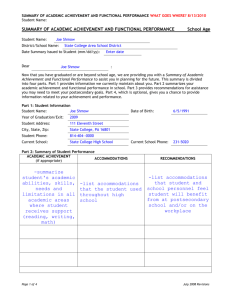
…the IEP shall include:
Age-appropriate measurable postsecondary
goals based upon age appropriate transition
assessments related to:
training,
education,
employment, and, where appropriate,
independent living skills; and
8VAC20-81 Special Education Regulations
(34 CFR 300.43 and 34 CFR 300.320(b)
VDOE T/TAC
TRAINING
1. What does this mean to you?
Postsecondary Education
1. What does this mean to you?
Types of Accommodations
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Extended time for tests
Reader service
Campus mobility training
Tape Textbooks
Note taker
Enlarged print
Scribe for written exams
Tape-record lectures
Exams read aloud
• Sign language interpreter
• Distraction-free testing
environment
• Calculator
• Use of a word processor
for essay exams
• Specialized assistive
technology
• Course substitutions of
non-essential program
requirements
Employment
1. What does this mean to you?
Challenges that Impede IDEA Youth Transition to
Postsecondary Education and Employment
• Lack of self-advocacy training
• Insufficient information about the Transition Process
• Insufficient vocational education {CTE} and work-related
experiences
• Lack of transportation after high school to work or postsecondary school
• Absence of linkages between school systems and adult service
providers
Federal Actions Can Assist States in Improving Postsecondary Outcomes for Youth
GAO Report to the Ranking Minority Member, Committee on Health, Education, Labor and Pensions, U.S. Senate
August 1, 2003
OUR CHALLENGE
GUIDANCE/
EDUCATORS
STUDENT
CAREER &
TECH (CTE)
EMPLOYER
Contact Information
Joan Lovegren-O’Brien
Virginia Department of Education
Training and Technical Assistance Center
Virginia Commonwealth University
jlovegrenobr@vcu.edu
Wanda Bass, Program Specialist
Virginia Department of Education
Training and Technical Assistance Center
Virginia Commonwealth University
wbass3@vcu.edu