File
advertisement

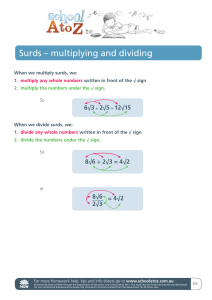
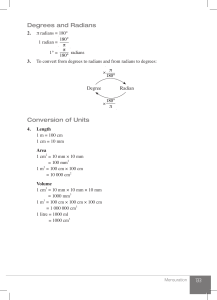
(b0mMM2) Year 10 MM Formula Sheet Name: Surface area of a cone = r 2 r s Straight line graphs Gradient (slope): m Equation: y 2 y1 x2 x1 y mx c or y y1 m( x x1 ) Measurement Pythagoras’ theorem c2 a2 b2 1 ( a b c) 2 Area of a circle: r 2 Heron's formula: A s( s a)(s b)(s c) where s Circumference of a circle: 2 r Volume of a sphere: Volume of a cone: 4 3 r 3 Surface area of a sphere: 4 r 2 1 2 r h 3 Volume of a cylinder: r 2 h Volume of a prism: area of base height Volume of a pyramid: 1 area of base height 3 Trigonometry To change radians to degrees multiply by 180 To change degrees to radians multiply by 180 Exponential Surds 1)a0 =1 2) ab a b 3) b b b Probability The probability of an event occurring is defined by the rule Number of favourable outcomes Pr( A) Total number of possible outcomes 0 Pr( A) 1 p( x) 1 Pr( A) Pr( A) 1 Complementary events Pr(A B) Pr(A) Pr(B) Pr(A B) If two events A and B, are mutually exclusive then Pr( A B) 0 and Pr( A B) Pr( A) Pr( B) If two events A and B, are independent then Pr( A B) Pr( A) Pr( B) Pr( A B) Conditional probability is defined by the rule Pr( A / B) , where Pr( B) 0 Pr( B) Pr(A) 1 Pr(A' ) Probability table (Karnaugh table) B B/ A Pr( A B) Pr( A B) Pr( A) A/ Pr( A B ) Pr( A B) Pr( A) Pr(B) Pr(B) 1 Deductive Geometry