PRE BOARD EXAMINATION, 2012 XII CHEMISTRY TIME: 3
advertisement

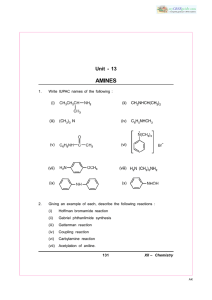
PRE BOARD EXAMINATION, 2012 XII CHEMISTRY TIME: 3 HOURS M.M.70 General Instructions: (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Question number 1 to 8 carrying 1 mark each Question number 9 to 18 carrying 2 marks each Question number 19 to 27 carrying 3 marks each Question number 28 to 30 carrying 5 marks each Why LiCl acquires pink colour on heating in Li vapours? Name the products formed at anode and cathode during the electrolysis of Con.H 2SO4? For the reaction N2(g) + 3H2(g) → 2NH3(g) , ∆[NH3]/∆t = 4x10-8. What is the value of ∆[H2]/∆t? Why ferric chloride is is preferred over potassium chloride in the case of a cut leading to the bleeding? What is hydro metallurgy? Which xenon compound is isostructural with IBr4- ? What happens to the colour of copper sulphate crystals when it is heated strongly? Give reason. Name the alkyl halide and sodium alkoxide used for the preparation of 2- Ethoxy 2 methyl pentane by Williamson’s synthesis. Give reason (i) Conductivity of a solution decreases with dilution (ii) Rusting is a setting up of an electrochemical cell Show that the time taken for the completion of three-fourth of a first order reaction is twice the time required for the completion of half reaction. OR The rate constants for a reaction at 600 and 800K are 0.02s -1 and 0.08s-1 respectively. Calculate the value of activation energy for the reaction. [R=8.314JK-1mol-1]. 11 What is meant by (i) Molecularity and order of a reaction (ii) Collision theory of chemical reactions 12 (i) (ii) Give disproportionation reaction of H3PO3. Why are halogens coloured? 13 (i) (ii) Suggest a method to estimate the amount of gas which protects us from u-v rays. Write the reactions of F2 and Cl2 with water 14 (i) (ii) 15 16 17 18 19 Explain the bonding in [Co(NH3)6]3+ using valance bond theory What is meant by stability of co-ordination compound in solution? What are the factors which govern the stability of complexes? Give reasons (i) Even though amine group is ortho para directing electrophilic substitution of aniline on nitration gives a substantial amount of meta nitro aniline (ii) Aniline does not undergo Freidel Crafts reaction. Explain (i) Carbylamine reaction (ii) Sand Mayer reaction Niobium crystallizes in a body centred crystal lattice. If its density is 8.55g/cm3calculate atomic radius. [atomic mass of Nb =93] What is a semi conductor? Discuss two types of semi conductors (i) How much electricity in terms of coulombs are required to produce 20g of Ca from molten CaCl2 (ii) In button cell used in watches and following reaction take place. Zn(s) → Zn2+(aq) + 2eEθ(Zn2+/Zn) = (-0.76v) Ag2O + H2O + 2e→ 2 Ag + 2OH- Eθ(Ag+/Ag) = 0.34 v Calculate standard electrode potential and standard Gibbs free energy. 20 Give reasons (i) Colloid is not a substance but a state of a substance (ii) Adsorption is always exothermic (iii) Substances like platinum and palladium are used for carry out electrolysis in aqueous solutions 21 (i) What is the role of depressant in the froth floatation process? (ii) How is leaching carried in low grade copper ore? (iii) The value of ∆fGθ for the formation of CrO3 is (-540)Kj/mol and that of Al2O3 is (-827)Kj/mol. Is the reduction of Al2O3 by Cr is possible? OR How will you refine (i) Nickel (ii) Zirconium (iii) Germanium? 22 What happens when (i) NaCl is heated with conc. H2SO4 in presence of MnO2 (ii) Cl2 gas is passed through hot concentrated NaOH solution (iii) Phosphine is passed through mercuric chloride solution 23 Give reasons (i) Sulphuric acid is not used in the reaction of alcohols with KI. (ii) The products formed by the reaction of alkyl halides with aqueous KOH and alcoholic KOH are different (iii) Alkyl halides are insoluble in water 24 (i) Write the structural and functional differences between DNA and RNA (ii) What is meant by peptide bond, glycosidic linkage and denaturation of proteins? (i) Write the name of a bio degradable polymer. Also mention name and structure of its monomers (ii) Medicines should not be taken without consulting doctor.Why? (iii) Explain cationic detergents with example (i) How does the presence of double bonds in rubber influence their structure? (ii) What is meant by the functionality of a polymer? (iii) What is chemotherapy? 25 26 27 Give tests to distinguish between (i) Phenol and ethanol (ii) Isopropyl alcohol and n-propyl alcohol (iii) Methyl ethanoate and ethyl ethanoate 28 (i) State Herry’s law and its two applications (ii) (iii) What are the advantages of osmotic pressure method over other colligative properties? 100 g of a liquid A (Molecular mass 140 g) was dissolved in 1000 g of a liquid B (molecular mass 180 g). The vapour pressure of pure liquid B is 500 torr. Calculate vapour pressure of pure liquid A and its vapour pressure in solution. Total pressure is 475 torr. OR What is meant by azeo tropic mixture? Explain two types of azeotropes with examples. 100 g of a protein is dissolved in water to make 10.0 ml of solution. If this solution has an osmotic pressure of 13.3 mm of Hg at 250 C, what is the molar mass of the protein? (i) (ii) 29 (i) Why is Cu+ not stable in solution? (ii) (iii) (iv) Why is Ce+4 a strong oxidizing agent? How is KMnO4 prepared? Explain oxidizing property of alkaline KMnO4 using its reaction with iodine (I-) and thio sulphate ( 𝑆2 𝑂32− ) ions OR Give reasons: (a) Oxidizing power of oxides of transition elements are in order 𝑉𝑂2+ <Cr2 𝑂7− <MnO4(b) Oxo anions of a transition metal shows higher oxidation state What is lanthanide contraction? What are its consequences? What is misch metal? Give one of its uses (i) (ii) (iii) 30 (i) An organic compound (A) which has characteristic odour, on treatment with NaOH it forms two compounds (B) and (C). Compound (B) has molecular formula C7H8O which on oxidation gives back A. The compound C is sodium salt of an acid. When C is treated with soda lime it yields an aromatic hydrocarbon (D). Deduce the structures of A, B, C, and D. Write the sequence of reactions involved. (ii) Arrange the following in the increasing order of the property indicated: (a) Benzoic acid, 4-Nitro benzoic acid, 3, 5-dinitrobenzoic acid, 4-Methoxybenzoic acid (acid strength) (b) Acetaldehyde, Acetone, Di-tertbutylketone, Methyltert-butyl ketone (Reactivity towards HCN) OR Complete each synthesis by filling the missing starting materials, reagents or products(X, Y and Z) (i) (a) C6H6CHO + CH3CH2CHO (b) CH3CH2CH2CH2OH (c) CH3(CH2)9COOC2H6 (ii) 𝑁𝑎𝑂𝐻 → 𝑌 → X CH3CH2CH2COOH 𝑍 → CH3(CH2)9 CHO How will you bring about the following conversations in not more than two steps? (a) Toulene to Benzaldehyde (b) Ethylcyanide to 1-phenylpropanone